
Concept explainers
Lysozyme is an enzyme that cleaves bacterial cell walls. A sample of lysozyme extracted from egg white has a molar mass of 13,930 g. A quantity of 0.100 g of this enzyme is dissolved in 150 g of water at 25°C. Calculate the vapor-pressure lowering, the depression in freezing point, the elevation in boiling point, and the osmotic pressure of this solution. (The vapor pressure of water at 25°C is 23.76 mmHg.)
Interpretation:
For given solution vapor pressure lowering, freezing point depression, boiling point elevation and osmotic pressures to be calculated.
Concept introduction
Boiling point elevation
Where,
Freezing point depression
Where,
Osmotic pressure is the pressure that is needed to stop osmosis. Osmotic pressure of the solution is directly proportional to the concentration of the solution. We can calculate osmotic pressure by using this formula is given by,
Where,
Vapor pressure lowering: Vapor pressure lowering is one of the colligative properties. Pure solvent has higher vapour pressure than its solution have non-volatile liquid. Thus vapour pressure lowering guide boiling point elevation.
Where,
Answer to Problem 12.83QP
Vapour pressure lowering of the solution = 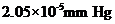
Freezing point elevation = 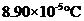
Boiling point elevation = 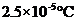
Osmotic pressure = 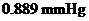
Explanation of Solution
Given data
Molar mass of egg white =
Amount of enzyme which is dissolved in water =
Amount of water =
Vapor pressure of water =
Calculation of number of moles in lysozyme and water
Molecular mass of water =
By plugging in the value of amount of Isozyme and molar mass of egg white, mole of Isozyme has calculated. Similarly, by plugging in the value of amount of water and molar mass of water, mole of water has calculated.
Calculation of vapour pressure lowering of the solution
By plugging in the values of mole fraction of Isozyme and vapour pressure of water, vapour pressure lowering of the solution has calculated.
Calculation freezing point depression of the solution
Molal freezing point depression constant =
By plugging in the values of molal freezing point depression constant and molality of the solution, freezing point depression of the solution has calculated.
Calculation of boiling point elevation of the solution
Boiling point elevation constant =
By plugging in the values of boiling point elevation constant and molality of the solution, boiling point elevation of the solution has calculated.
Calculation of osmotic pressure of the solution
As known above, we assume the density of the solution is
By plugging in the values of molarity of the solution, ideal gas constant and temperature in Kelvin, the osmotic pressure of the solution has calculated.
Vapour pressure lowering of the solution was calculated as
Freezing point elevation has calculated as
Boiling point elevation has calculated as
Osmotic pressure has calculated as
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Chemistry
- For the condensation reaction between Alamine and histamine, please help me write the amididation reaction mechanism. Then write the three letter code for the product of the reaction, then write the one letter code for the product of the reaction. arrow_forwardHow to draw the reaction mechasnism belowarrow_forwardName the following molecules with IUpacarrow_forward
- What is the molecular orbital for cyclopropenyl anion and is it aromatic, antiaromatic or nonaromatic?arrow_forwardUsing the chart describe the change from cystine to tyrosine and its impact on the protein. Using the chart describe the change from histidine to aspartic acid and its impact on the protein.arrow_forwardHow to get the predicted product of this reaction belowarrow_forward
- Please help me fill out the chart then using the chart describe the change from cystine to tyrosine and its impact on the protein. Then using the chart describe the change from histidine to aspartic acid.arrow_forwardWrite the Esterification reaction mechanism for acetic acid, and one propanol to make propanol ethanoate (molecule that gives peas its odor in flavor)arrow_forwardProvide solutionsarrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning





