
Loose Leaf For Introduction To Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781259878084
Author: Smith Termodinamica En Ingenieria Quimica, J.m.; Van Ness, Hendrick C; Abbott, Michael; Swihart, Mark
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 12, Problem 12.25P
Problems 12.22 through 12.28 refer to the Txy diagram for chloroform(1)/tetrahydrofuran(2) at 120 kPa shown in Fig. 12.22.
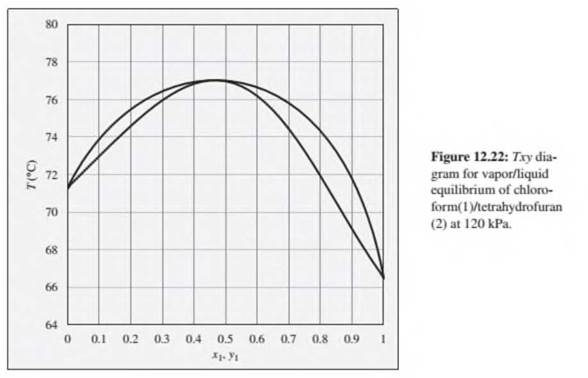
12.25. Consider a chloroform(1)/tetrahydrofuran(2) mixture with x1= 0.20, initially at 70°C and 120 kPa. Describe the evolution of phases and phase compositions as the temperature is gradually increased to 80°C.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
I need a detailed drawing with explanation
so
A
4
しか
شكا
Write a complete C++ program that
includes a function to check whether a
given sequence of parentheses is
balanced using stack or Linked stack
7:30 م
PU + 9625
=-2c125
750 x2.01
58³
Ternary Phase Diagram+ Material balance
Feed mixture weighing 200 kg of unknown composition containing water, acetic acid, isopropyl ether is
contacted in a single stage with 280kg mixture containing 40wt% acetic acid. 10wt% water and 50wt% isopropyl
ether. The resulting raffinate layer weight 320 kg and containing 29.5 wt% acetic acid, 66.5 wt% water and 4wt%
isopropyl ether. Determine the composition of the original feed mixture and the extract layer
Water layer
Isopropyl ether layer
acetic acid
0
water
98.8
Isopropyl ether
1.2
acetic acid
0
water
Isopropyl ether
0.6
99.4
0.69
98.1
1.2
0.18
0.5
99.3
1.41
97.1
1.5
0.37
0.7
98.9
2.89
95.5
1.6
0.79
0.8
98.4
6.42
91.7
1.9
1.93
1
97.1
13.3
84.4
2.3
4.82
1.9
93.3
25.5
71.1
3.4
11.4
3.9
84.7
36.7
58.9
4.4
21.6
6.9
71.5
44.3
5.1
10.6
31.1
10.8
58.5
46.4
37.1
16.5
36.2
15.1
48.7
Graphically+Material balance
2500 kg/hr of (20-80) nicotine water solution is to be extracted with benzene containing 0.5% nicotine in
the 1st and 2nd stages while the 3rd stage is free of nicotine. Cross-current operation is used with different amounts
of solvent for each stages 2000kg/hr in the 1st stage, 2300 kg/hr in the 2nd stage, 2600 kg/hr in the 3rd,
determine:-
a- The final raffinate concentration and % extraction.
b- b-The minimum amount of solvent required for counter-current operation if the minimum concentration
will be reduced to 5% in the outlet raffinate.
Equilibrium data
Wt % Nicotine in water
0
4
16
25
Wt % Nicotine in benzene
0
4
21
30
Chapter 12 Solutions
Loose Leaf For Introduction To Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.1PCh. 12 - Prob. 12.2PCh. 12 - Prob. 12.3PCh. 12 - Problems 12.3 through 12.8 refer to the Pxy...Ch. 12 - Problems 12.3 through 12.8 refer to the Pxy...Ch. 12 - Problems 12.3 through 12.8 refer to the Pxy...Ch. 12 - Problems 12.3 through 12.8 refer to the Pxy...Ch. 12 - Problems 12.3 through 12.8 refer to the Pxy...Ch. 12 - Problems 12.9 through 12.14 refer to the Txy...Ch. 12 - Problems 12.9 through 12.14 refer to the Txy...
Ch. 12 - Problems 12.9 through 12.14 refer to the Txy...Ch. 12 - Problems 12.9 through 12.14 refer to the Txy...Ch. 12 - Problems 12.9 through 12.14 refer to the Txy...Ch. 12 - Problems 12.9 through 12.14 refer to the Txy...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.15PCh. 12 - Problems 12.16 through 12.21 refer to the Pxy...Ch. 12 - Problems 12.16 through 12.21 refer to the Pxy...Ch. 12 - Problems 12.16 through 12.21 refer to the Pxy...Ch. 12 - Problems 12.16 through 12.21 refer to the Pxy...Ch. 12 - Problems 12.16 through 12.21 refer to the Pxy...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.21PCh. 12 - Problems 12.22 through 12.28 refer to the Txy...Ch. 12 - Problems 12.22 through 12.28 refer to the Txy...Ch. 12 - Problems 12.22 through 12.28 refer to the Txy...Ch. 12 - Problems 12.22 through 12.28 refer to the Txy...Ch. 12 - Problems 12.22 through 12.28 refer to the Txy...Ch. 12 - Problems 12.22 through 12.28 refer to the Txy...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.28PCh. 12 - Problems 12.29 through 12.33 refer to the xy...Ch. 12 - Problems 12.29 through 12.33 refer to the xy...Ch. 12 - Problems 12.29 through 12.33 refer to the xy...Ch. 12 - Problems 12.29 through 12.33 refer to the xy...Ch. 12 - Problems 12.29 through 12.33 refer to the xy...Ch. 12 - Consider a binary liquid mixture for which the...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.35PCh. 12 - Prob. 12.36P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- graphically +material balance 1000 Kg/hr on an acetone water mixture containing 10% of acetone is to be extracted with trichloroethane. The recovered solvent to be used is free of acetone. If 95% recovery of acetone is desired, the equilibrium relationship is given by kg acetone/kg trichloroethane 1.65 kg acetone/kg water. Estimate the number of stages required if 1.5 times the minimum solvent is used when: - a- b- Cross-current is to be extracted. b- Counter-current is to be extracted.arrow_forwarduse Graphically 1000 Kg/hr on an acetone water mixture containing 10% of acetone is to be extracted with trichloroethane. The recovered solvent to be used is free of acetone. If 95% recovery of acetone is desired, the equilibrium relationship is given by kg acetone/kg trichloroethane 1.65 kg acetone/kg water. Estimate the number of stages required if 1.5 times the minimum solvent is used when: - Cross-current is to be extracted. a- b- b- Counter-current is to be extracted.arrow_forwardA solution of 5% acetaldehyde in toluene is to be extracted with water in five stage co-current operation. If 25kg/100kg feed is used, what is the mass of acetaldehyde extracted and the final concentration? The Equilibrium relation is given by: kg acetaldehyde /kg water = 2.2 kg acetaldehyde / kg toluene.arrow_forward
- Feed mixture weighing 200 kg of unknown composition containing water, acetic acid, isopropyl ether is contacted in a single stage with 280kg mixture containing 40wt% acetic acid. 10wt% water and 50wt% isopropyl ether. The resulting raffinate layer weight 320 kg and containing 29.5wt% acetic acid, 66.5 wt% water and 4wt% isopropyl ether. Determine the composition of the original feed mixture and the extract layer Water layer Isopropyl ether layer acetic acid water Isopropyl ether acetic acid water Isopropyl ether 0 98.8 1.2 0 0.6 99.4 0.69 98.1 1.2 0.18 0.5 99.3 1.41 97.1 1.5 0.37 0.7 98.9 2.89 95.5 1.6 0.79 0.8 98.4 6.42 91.7 1.9 1.93 1 97.1 13.3 84.4 2.3 4.82 1.9 93.3 25.5 71.1 3.4 11.4 3.9 84.7 36.7 58.9 4.4 21.6 6.9 71.5 44.3 5.1 10.6 31.1 10.8 58.5 46.4 37.1 16.5 36.2 15.1 48.7arrow_forward2000 Kg/hr on an acetone water mixture containing 10% of acetone is to be extracted with trichloroethane. The recovered solvent to be used is free of acetone. If 95% recovery of acetone is desired, the equilibrium relationship is given by kg acetone/kg trichloroethane 1.65 kg acetone/kg water. Estimate the number of stages required if 1.5 times the minimum solvent is used when: - a- Cross-current is to be extracted. b- b- Counter-current is to be extracted.arrow_forward2/1000kg/h of an acetone - water mixture containing 20wt% by weight of acetone is to be counter currently extracted with trichloroethane. The recovered solvent to be used is free from acetone. The water and trichloroethane are insoluble. If 90% recovery of acetone is desired estimate the number of stages required if 1.5 times the minimum solvent is used. The kg acetone/kg extract=1.65 kg water/kg raffinate. a- Repeat the calculation of A if the solvent used has purity of 98.5%. b- If co-current extractor is used instead of counter-current extractor in A and B estimate the number of stages required if equal amount of solvent used in each stage.arrow_forward
- Water is pumped from a large reservoir to a point 75 feet higher than the reservoir. How many feet of head must be added by the pump if 7600 lbm/hr flows through a 6-inch pipe and the frictional head loss is 3 feet? The density of the fluid is 60 lbm/ft³ and the pump efficiency is 70%. Assume the kinetic energy correction factor equals 1.arrow_forwardA firefighter is using a large water tank to supply water for extinguishing a fire. The tank has a small hole at the bottom, and water is leaking out due to gravity. The hole is located 2.5 meters below the water surface inside the tank. a. Determine the speed at which the water exits the hole. Assume there is no air resistance and that the water flow is ideal (neglect viscosity and turbulence). b. If the hole has a diameter of 2 cm, calculate the flow rate (discharge rate) in liters per second.arrow_forwardWhat kind of boundary must a system have to undergo the stated Interaction with its surroundings if possible ( mention the 3 qualities of the boundary in each case A. WORK INTERACTIONS ONLY B. MASS AND HEAT INTERACTIONS ONLY C. HEAT INTERACTIONS ONLY IS THIS POSSIBLE, EXPLAIN. D. WORK AND MASS INTERACTIONS ONLY. E. WORK AND HEAT INTERACTIONS ONLY F. MASS INTERACTIONS ONLY. IS THIS POSSIBLE OR NOT. EXPLAINarrow_forward
- Answer the questionsarrow_forwardFigure below shows a portion of a fire protection system in which apump draws water at 60 F from a reservoir and delivers it to point B at the flow rate of 1500 gal/min a). Calculate the required height of the water level in the tank in order to maintain 5.0 psig pressure at point A. Answer: h = 12,6 ft b). Assuming that the pressure at A is 5.0 psig, calculate the power delivered by the pump to the water in order to maintain the pressure at point B at 85 kPa. Include energy lost due to friction but neglect any other energy losses. P₁ =19,2 hparrow_forwardWater at 60° F is being pumped from a stream to a reservoir whose surface is 210 ft above the pump. The pipe from the pump to the reservoir is an 8-in Schedule 40 steel pipe 2500 ft long. The pressure at the pump inlet is - 2,36 psig. If 4.00 ft³/s is being pumped, a). Compute the pressure at the outlet of the pump. Answer: 0,997 MPa b). Compute the power delivered by the pump to the water. Answer: 151 hp Consider the friction loss in the discharged line, but neglect other lossesarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780133887518
Author:H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781285061238
Author:Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780072848236
Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Equilibrium - Chemical Equilibrium - Chemistry Class 11; Author: Ekeeda;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8V9ozZSKl9E;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY