
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The model structure has to be converted into line drawing along with identification of Functional Group.
Concept Introduction:
Line structure is a simple and quick way to represent organic molecules without showing carbons and hydrogens present. Drawing a molecule in this way is very simple:
It follows the following guide line:
- Each carbon- carbon bond is represented by a line.
- Anywhere a line ends or begins, as well as any vertex where two lines meet represents a carbon atom.
- Any atom other than another’s carbon or hydrogen attached to a carbon must be shown.
- Since a neutral carbon atom form four bonds, all bonds not shown for any carbon are understood to be the number of carbon – hydrogen bonds needed to have.
Functional group: Organic compounds can be classified into various families according to the

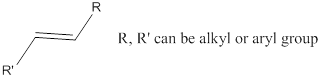
Ether: A class of organic compounds, where oxygen is attached to two alkyl or aryl groups.
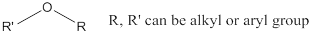
(b)
Interpretation:
The model structure has to be converted into line drawing along with identification of Functional Group.
Concept Introduction:
Line structure is a simple and quick way to represent organic molecules without showing carbons and hydrogens present. Drawing a molecule in this way is very simple:
It follows the following guide line:
- Each carbon- carbon bond is represented by a line.
- Anywhere a line ends or begins, as well as any vertex where two lines meet represents a carbon atom.
- Any atom other than another’s carbon or hydrogen attached to a carbon must be shown.
- Since a neutral carbon atom form four bonds, all bonds not shown for any carbon are understood to be the number of carbon – hydrogen bonds needed to have.
Functional group: Organic compounds can be classified into various families according to the functional groups they contain a functional group is a part of a larger molecule and is composed of a group of atoms that has characteristic structure and chemical reactivity.
Functional group:
An atom or group of atoms which has physical and chemical properties is known as functional group.
Ketone: A compound containing a carbonyl group

Alkene: Unsaturated hydrocarbons containing double bonds.
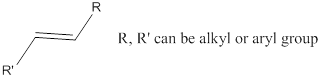
Ether: A class of organic compounds, where oxygen is attached to two alkyl or aryl groups.
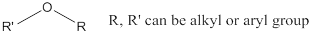
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 12 Solutions
EP FUND.OF GENERAL,ORG...-MOD.MASTERING
- 7. What is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction sequence? Ph A OH 99 Ph OH D Br HOCH2CH2OH H2SO4 1. Mg, Et₂O 2. PhCH2CHO HCI, H₂O Br OH Ph Ph OH B C Br OH Ph Earrow_forwardPls helparrow_forwardH₂N NH peptide_0e60 A dipeptide is made up of two (2) amino acids. The figure above shows one such dipeptide with an unknown sequence. Your task is to find out the two (2) letter sequence of this dipeptide.arrow_forward
- carbons in each of the structures below. For instance, the central carbon of chloromethylbutane (pictured 3. A chiral carbon is a carbon that is single-bonded to four different types of groups. Identify the chiral above) is a chiral carbon. (Can you see how the groups attached to it are all chemically different?) In each of the chiral molecules below, identify all the carbons that are chiral carbons by drawing a circle around each one of them. (a) the carbohydrate glucose H O (b) the carbohydrate fructose CH₂OH 1C H-C-OH 3 HO-C-H 4 H-C-OH 5 H-C-OH 6CH₂OH D-Glucose (linear form) (c) the amino acid leucine O O H3C. HO H H- -OH CH 3 NH2 H- -OH CH₂OH OHarrow_forwardWe always include controls in the Annexin-V-GFP/Propidium Iodide flow cytometric assay to study apoptosis. List four types of controls in this assay. Why do we need these controls? Explain your answers. After the flow assay, if we like to examine the morphology of the viable, early apoptotic and late apoptotic cells by confocal microscopy, what can we do and what are the expected results?arrow_forward3. (2 points) Your lab partner accidentally used a pen instead of a pencil to mark the baseline and label the lanes of their TLC plate. Briefly (1-2 sentences for each point) describe (a) what would happen to the ink when you develop the TLC plate; and (b) how this would affect the experiment. 1arrow_forward
- Do schwann cells produce or act as myelin in the peripheral nervous system? I know that they encase and wrap around axons, but where does the myelin come into play?arrow_forwardThe enzyme lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) catalyzes the conversion of pyruvate to lactatein skeletal muscle cells using NAD/NADH during anaerobic “balanced” fermentation.Answer the following questions about this reaction. (a) Write out the two reductive half reactions and indicate the E ̊' for each half reaction. Write out the full balanced reaction for the pyruvate to lactate rxn and indicate the ∆E ̊' for the reaction. (b) What is the free energy change under standard state conditions for thisreaction? Which direction is spontaneous?(c) Assume that in skeletal muscle cells the ratio of [NAD+] to [NADH] is 100, and that the[pyruvate] = 0.40 mM and [lactate] = 4.0 mM. What is the free energy change (∆G')for the conversion of pyruvate to lactate? Indicate the direction in which the reactionis spontaneous under these cellular conditions.arrow_forwardWhy did the authors worry about the temperature-dependent solubility of the carriers in thebilayer? How did the authors determine whether the effect of freezing the lipid bilayer wasto decrease the solubility of the carriers (nonactin and valinomycin) or whether the effectwas to impair their ability to diffuse through the membrane (decrease their mobility)?arrow_forward
 Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning





