
Concept explainers
Exercises 1-26 involve probabilities with independent events.
Use the spinner shown to solve Exercises 1-10. It is equally probable that the pointer will land on any one of the six regions. If the pointer lands on a borderline, spin again. If the pointer is spun twice, find the probability it will land on
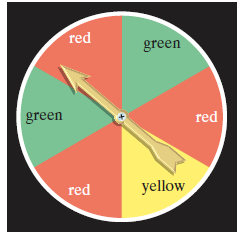
If the pointer is spun three times, find the probability it will land on
red every time.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 11 Solutions
Thinking Mathematically plus NEW MyLab Math with Pearson eText -- Access Card Package (6th Edition)
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Pathways To Math Literacy (looseleaf)
Intermediate Algebra (13th Edition)
Graphical Approach To College Algebra
Probability And Statistical Inference (10th Edition)
Elementary Statistics: A Step By Step Approach
Finite Mathematics for Business, Economics, Life Sciences and Social Sciences
- 4.96 The breaking strengths for 1-foot-square samples of a particular synthetic fabric are approximately normally distributed with a mean of 2,250 pounds per square inch (psi) and a standard deviation of 10.2 psi. Find the probability of selecting a 1-foot-square sample of material at random that on testing would have a breaking strength in excess of 2,265 psi.4.97 Refer to Exercise 4.96. Suppose that a new synthetic fabric has been developed that may have a different mean breaking strength. A random sample of 15 1-foot sections is obtained, and each section is tested for breaking strength. If we assume that the population standard deviation for the new fabric is identical to that for the old fabric, describe the sampling distribution forybased on random samples of 15 1-foot sections of new fabricarrow_forwardEach of the following statements is an attempt to show that a given series is convergent or divergent using the Comparison Test (NOT the Limit Comparison Test.) For each statement, enter C (for "correct") if the argument is valid, or enter | (for "incorrect") if any part of the argument is flawed. (Note: if the conclusion is true but the argument that led to it was wrong, you must enter I.) ☐ 1. For all n > 1, seriesΣ In(n) In(n) converges. 2, 1, arctan(n) the series arctan(n) n³ ☐ 4. For all n > 1, 123 converges. 1 n ln(n) series In(n) diverges. 2n . and the seriesΣconverges, so by the Comparison Test, 2, 3, and the series converges, so by the Comparison Test, the series-3 1 converges. ☐ 6. For all n > 2, In(n) >, and the series Σ converges, so by the Comparison Test, the seriesΣ In(n) converges.arrow_forwardIn 2012, the employees of Radcliff Ltd. agreed to purchase 5% of the share capital of 10 million shares of $2 each. There are 20 employees in the plan, and each purchased an equal number of shares. Johnson works at Radcliff Ltd. What would be his ESOP share deduction? $45,000 $25,000 $75,000 $50,000.arrow_forward
- Instructions. "I have written solutions in text form, but I need experts to rewrite them in handwriting from A to Z, exactly as I have written, without any changes."arrow_forwardBoth in images okk. Instructions. "I have written solutions in text form, but I need experts to rewrite them in handwriting from A to Z, exactly as I have written, without any changes."arrow_forwardQuestion 1: If a barometer were built using oil (p = 0.92 g/cm³) instead of mercury (p = 13.6 g/cm³), would the column of oil be higher than, lower than, or the same as the column of mercury at 1.00 atm? If the level is different, by what factor? Explain. (5 pts) Solution: A barometer works based on the principle that the pressure exerted by the liquid column balances atmospheric pressure. The pressure is given by: P = pgh Since the atmospheric pressure remains constant (P = 1.00 atm), the height of the liquid column is inversely proportional to its density: Step 1: Given Data PHg hol=hgx Poil • Density of mercury: PHg = 13.6 g/cm³ Density of oil: Poil = 0.92 g/cm³ • Standard height of mercury at 1.00 atm: hμg Step 2: Compute Height of Oil = 760 mm = 0.760 m 13.6 hoil = 0.760 x 0.92 hoil = 0.760 × 14.78 hoil = 11.23 m Step 3: Compare Heights Since oil is less dense than mercury, the column of oil must be much taller than that of mercury. The factor by which it is taller is: Final…arrow_forward
- Question 3: A sealed flask at room temperature contains a mixture of neon (Ne) and nitrogen (N2) gases. Ne has a mass of 3.25 g and exerts a pressure of 48.2 torr. . N2 contributes a pressure of 142 torr. • What is the mass of the N2 in the flask? • Atomic mass of Ne = 20.1797 g/mol • Atomic mass of N = 14.0067 g/mol Solution: We will use the Ideal Gas Law to determine the number of moles of each gas and calculate the mass of N2. PV = nRT where: • P = total pressure • V volume of the flask (same for both gases) n = number of moles of gas • R 0.0821 L atm/mol K • T = Room temperature (assume 298 K) Since both gases are in the same flask, their partial pressures correspond to their mole fractions. Step 1: Convert Pressures to Atmospheres 48.2 PNe = 0.0634 atm 760 142 PN2 = = 0.1868 atm 760 Step 2: Determine Moles of Ne nNe = mass molar mass 3.25 nNe 20.1797 nne 0.1611 mol Step 3: Use Partial Pressure Ratio to Find narrow_forward"I have written solutions in text form, but I need experts to rewrite them in handwriting from A to Z, exactly as I have written, without any changes."arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvote Already got wrong chatgpt answerarrow_forward
- Construct a table of values for all the nonprincipal Dirichlet characters mod 16.arrow_forwardMI P X /courses/segura10706/products/171960/pages/611?locale=&platformId=1030&lms=Y ☆ Finish Part I: Mathematics for Elementary and Middle School Teachers Continue in the app JJ 576 Chapter 12. Area of Shapes 9. Determine the area of the shaded shapes in Figure 12.48. Explain your reasoning. 1 unit S Figure 12.48 1 unit unit and the yarn for thearrow_forwardSuppose p > 3 is a prime. Show that (p − 3)!= − P+1 (mod p). Hint: Use Wilson's theorem.arrow_forward
 College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL

