
Concept explainers
The basic barometer can be used to measure the height of a building. If the barometric readings at the top and at the bottom of a building are 675 and 695 mmHg, respectively, determine the height of the building. Take the densities of air and mercury to be 1.18 kg/m3 and 13.600 kg/m3, respectively.

The height of the building.
Answer to Problem 56P
The height of the building is
Explanation of Solution
Show the free body diagram of the building.
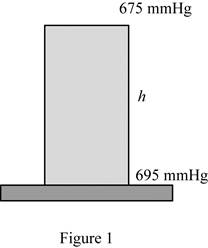
Write the expression of pressure at the top.
Here, the density is
Write the expression of pressure at the top.
Write the expression of an air column between the top and bottom of the mountain and writing a force balance per unit base area.
Conclusion:
Write the unit conversion from mm of Hg to m of Hg.
For
For
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the height of the building is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
SURVEY OF OPERATING SYSTEMS
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, And Service (6th Edition) (halderman Automotive Series)
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
- Solve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forwardSolve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forwarddraw the pneumatic circuit to operate a double-acting cylinder with: 1. Extension: Any of two manual conditions plus cylinder fully retracted, → Extension has both meter-in and meter-out, 2. Retraction: one manual conditions plus cylinder fully extended, → Retraction is very fast using quick exhaust valve.arrow_forward
- Correct answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution with fbd only. I will upvote, thank you. Expert solution plsarrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution with fbd only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution with fbd only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forward
- Correct answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution only with fbd. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution with fbd only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forward
- Correct answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution with fbd only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





