
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of the given compound
Concept Introduction:
Lewis structure:
The representation of valence shell electrons around the atom is known as Lewis structure or Lewis dot structure. Electrons are represented as a dot in Lewis structures, a single dot represents unpaired electron and paired of dots represents paired electrons.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Given compound,
The total number of valence electrons in
The skeletal structure of
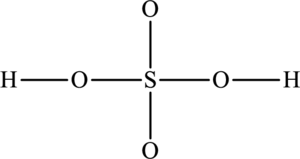
The total number of 12 electrons are used for bonding. Remaining 22 electrons can be distributed over oxygen atoms to get the octet.
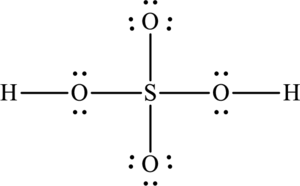
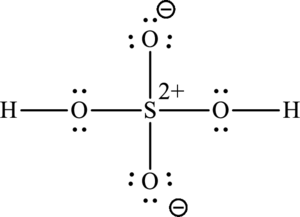
The Lewis structure of compound showing charges can be given as follows:
(b)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of the given compound
Concept Introduction:
Refer part (a)
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Given compound,
The total number of valence electrons in
The skeletal structure of
The total number of 8 electrons are used for bonding. Remaining 16 electrons can be distributed over oxygen atoms to get the octet.
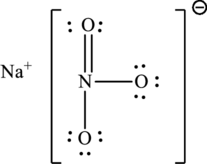
The Lewis structure of compound showing charges can be given as follows:
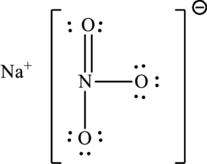
(c)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of the given compound
Concept Introduction:
Refer part (a)
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Given compound,
The total number of valence electrons in
The skeletal structure of
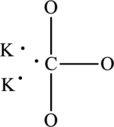
The total number of 6 electrons are used for bonding. Remaining 18 electrons can be distributed over oxygen atoms to get the octet.
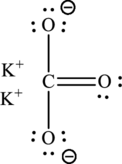
The Lewis structure of compound showing charges can be given as follows:
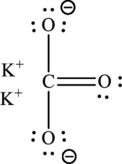
(d)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of the given compound
Concept Introduction:
Refer part (a)
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Given compound,
The total number of valence electrons in
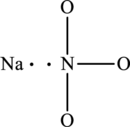
The skeletal structure of
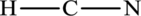
The total number of four electrons are used for bonding. Remaining 6 electrons can be distributed over nitrogen and carbon atoms to get the octet.
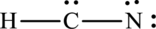
The Lewis structure of compound showing charges can be given as follows:
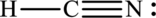
(e)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of the given compound
Concept Introduction:
Refer part (a)
(e)
Explanation of Solution
Given compound,
The total number of valence electrons in
The skeletal structure of
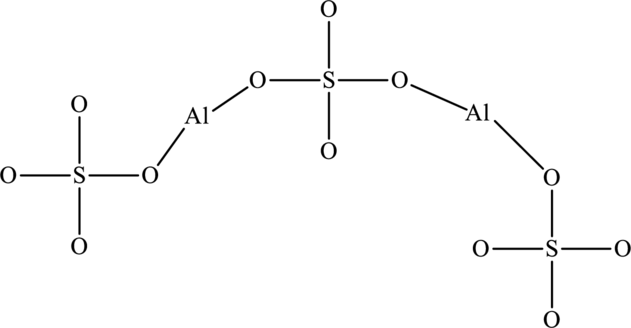
The total number of 32 electrons are used for bonding. Remaining 64 electrons can be distributed over oxygen atoms to get the octet.
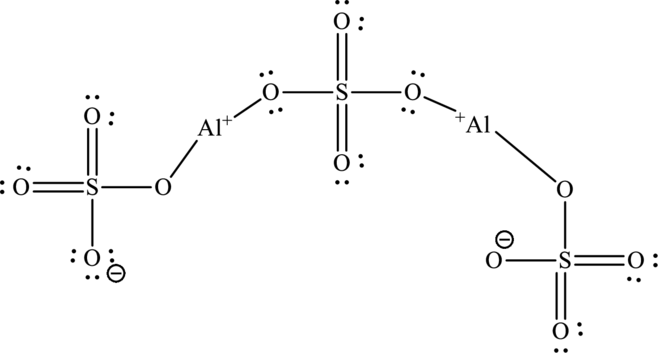
The Lewis structure of compound showing charges can be also be represented as follows:
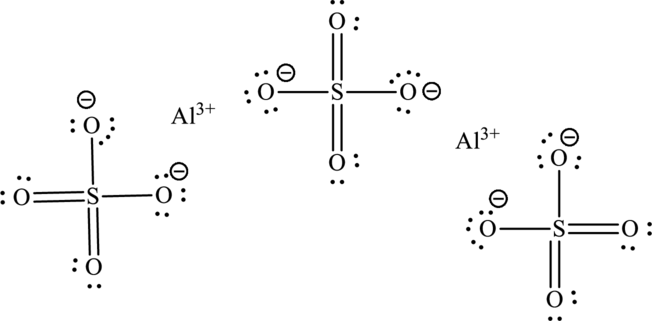
(f)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of the given compound
Concept Introduction:
Refer part (a)
(f)
Explanation of Solution
Given compound,
The total number of valence electrons in
The skeletal structure of
The total number of 14 electrons are used for bonding. Remaining 10 electrons can be distributed over oxygen and carbon atoms to get the octet.
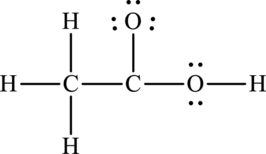
Here octet of carbon attached to oxygen is not completed. Therefore, the Lewis structure of compound can be given as follows:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Foundations of College Chemistry 15e Binder Ready Version + WileyPLUS Registration Card
- Provide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forwardFirst image: Why can't the molecule C be formed in those conditions Second image: Synthesis for lactone C its not an examarrow_forwardFirst image: I have to show the mecanism for the reaction on the left, where the alcohol A is added fast in one portion Second image: I have to show the mecanism of the reaction at the bottom. Also I have to show by mecanism why the reaction wouldn't work if the alcohol was primaryarrow_forward
- First image: I have to explain why the molecule C is never formed in those conditions. Second image: I have to propose a synthesis for the lactone Aarrow_forwardFirst image: I have to explain why the molecule C is never formed in these conditions Second image: I have to propose a synthesis for the lactone Aarrow_forwardHelp fix my arrows pleasearrow_forward
- Provide the drawing of the unknown structure that corresponds with this data.arrow_forward20.44 The Diels-Alder reaction is not limited to making six-membered rings with only car- bon atoms. Predict the products of the following reactions that produce rings with atoms other than carbon in them. OCCH OCCH H (b) CH C(CH₂)s COOCH མ་ནས་བ (c) N=C H -0.X- (e) H C=N COOCHS + CH2=CHCH₂ →→arrow_forwardGiven the attached data, provide the drawing for the corresponding structure.arrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
