
COST ACCOUNTING W/CONNECT
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781264022021
Author: LANEN
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 11, Problem 56P
Solve for Unknowns: Direct Method
Frank’s Foods has a warehouse that supplies products to its store locations. The warehouse has two service departments, Information Services (S1) and Operation Support (S2), and two operating departments, Order Processing (P1) and Delivery (P2). As an internal auditor, you are checking the company’s procedures for cost allocation. You find the following cost allocation results for September:

Total costs for the two service departments are $120,000.
Operation Support’s services are provided as follows:
- percent to Order Processing.
- percent to Delivery.
The direct method of allocating costs is used.
Required
- a. What are the total service department costs (S1 + S2) allocated to P2?
- b. Complete the following:
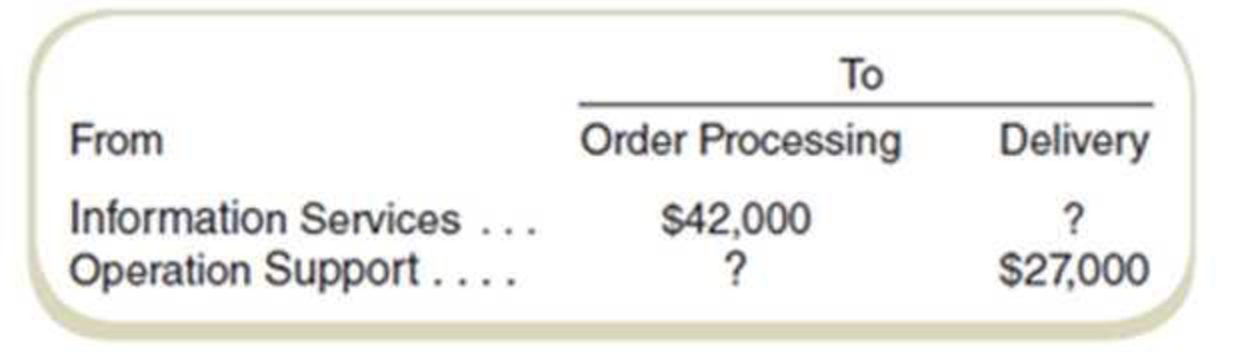
- c. What proportion of S1’s costs were allocated to P1 and P2?
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Tower Company owned a service truck that was purchased at the beginning of Year 1 for $48,000. It had an estimated life of three
years and an estimated salvage value of $3,000. Tower company uses straight-line depreciation. Its financial condition as of January 1,
Year 3, is shown on the first line of the horizontal statements model.
In Year 3, Tower Company spent the following amounts on the truck:
January 4 Overhauled the engine for $7,600. The estimated life was extended one additional year, and the salvage value was
revised to $2,000.
July 6 Obtained oil change and transmission service, $410.
August 7 Replaced the fan belt and battery, $510.
December 31 Purchased gasoline for the year, $9,100.
December 31 Recognized Year 3 depreciation expense.
Required
Record the Year 3 transactions in a statements model.
Note: In the Statement of Cash Flows column, use the initials OA for operating activities, FA for financing activities, or IA for
investing activity. Enter any decreases to…
Cara's Cookie Company provided the following accounts from its year-end trial balance.
(Click the icon to view the year-end trial balance accounts.)
The company is subject to a 35% income tax rate.
Requirement
Prepare a multiple-step income statement for the current year.
Trial balance
Cara's Cookie Company
Adjusted Trial Balance (Selected Accounts)
For the Current Year Ended
Account
Debit
Credit
Prepare Cara's multiple-step income statement for the current year, one section at a time. (List the subheadings in the order they
Cara's Cookie Company
Statement of Net Income
Common Stock (no par): Beginning Balance
Retained Earnings: Beginning Balance
$ 462,000
1,200,000
Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income: Beginning Balance
Dividends
$
63,000
69,000
Sales
3,200,000
For the Current Year Ended
Sales
Less: Cost of Goods Sold
3,200,000
610,000
Interest Income
3,800
Dividend Income
3,600
Gross Profit
Operating Expenses:
Selling Expenses:
Gain on Disposal of Plant Assets
92,000
2,590,000…
History
口
AA
1
୪
Fri Feb 14 2:45 PM
Mc
Gw Mini Cases
Qmcgrow hill goodweek tires pr × |
Ask a Question | bartleby
× +
Bookmarks
Profiles Tab Window Help
Graw McGraw Hill
MC
☑
Hill
prod.reader-ui.prod.mheducation.com/epub/sn_d82a5/data-uuid-0e12dd568f3f4e438c00faed4ea436f1
Chrome File Edit View
Λ
LTI Launch
88
Netflix
YouTube
A BlackBoard
Mail - Stiffler, Zac...
SBI Jobs
E
Aa
Finish update:
☐
All Bookmarks
Goodweek Tires, Inc.
After extensive research and development, Goodweek Tires, Inc., has recently developed a new tire, the SuperTread, and must decide whether to make the investment necessary
to produce and market it. The tire would be ideal for drivers doing a large amount of wet weather and off-road driving in addition to normal freeway usage. The research and
development costs so far have totaled about $10 million. The SuperTread would be put on the market beginning this year, and Goodweek expects it to stay on the market for a
total of four years. Test marketing costing $5…
Chapter 11 Solutions
COST ACCOUNTING W/CONNECT
Ch. 11 - Why do companies allocate costs? What are some of...Ch. 11 - What are the three methods of allocating service...Ch. 11 - What are the similarities and differences among...Ch. 11 - What criterion should be used to determine the...Ch. 11 - What is a limitation of the direct method of...Ch. 11 - What is a limitation of the step method of...Ch. 11 - Prob. 7RQCh. 11 - Why would a number of accountants express a...Ch. 11 - Prob. 9RQCh. 11 - What is the basic difference between the...
Ch. 11 - Prob. 11RQCh. 11 - If cost allocations arc arbitrary and potentially...Ch. 11 - Prob. 13CADQCh. 11 - Prob. 14CADQCh. 11 - Prob. 15CADQCh. 11 - Prob. 16CADQCh. 11 - Prob. 17CADQCh. 11 - Prob. 18CADQCh. 11 - What are some of the factors that a company needs...Ch. 11 - Prob. 20CADQCh. 11 - Prob. 21CADQCh. 11 - Prob. 22CADQCh. 11 - How is joint cost allocation like service...Ch. 11 - Prob. 24CADQCh. 11 - In what ways is joint cost allocation similar to...Ch. 11 - Why Are Costs Allocated?Ethical Issues You are the...Ch. 11 - Cost Allocation: Direct Method Caro Manufacturing...Ch. 11 - Allocating Service Department Costs First to...Ch. 11 - Cost Allwat ion: Direct Method University Printers...Ch. 11 - Prob. 30ECh. 11 - Cost Allocation: Step Method
Refer to the data for...Ch. 11 - Cost Allocation: Reciprocal Method
Refer to the...Ch. 11 - Cost Allocation: Reciprocal Method, Two Service...Ch. 11 - Cost Allocation: Reciprocal Method
Refer to the...Ch. 11 - Prob. 35ECh. 11 - Prob. 36ECh. 11 - Prob. 37ECh. 11 - Prob. 38ECh. 11 - Prob. 39ECh. 11 - Prob. 40ECh. 11 - Net Realizable Value Method: Multiple Choice
Oak...Ch. 11 - Sell or Process Further: Multiple Choice
Refer to...Ch. 11 - Net Realizable Value Method Euclid Corporation...Ch. 11 - Estimated Net Realizable Value Method Blasto,...Ch. 11 - Net Realizable Value Method to Solve for Unknowns...Ch. 11 - Net Realizable Value Method Bixel Components...Ch. 11 - Net Realizable Value Method with By-Products...Ch. 11 - Net Realizable Value Method Deming Sons...Ch. 11 - Physical Quantities Method
Refer to the facts in...Ch. 11 - Sell or Process Further
Refer to the facts in...Ch. 11 - Physical Quantities Method The following questions...Ch. 11 - Physical Quantities Method; Sell or Process...Ch. 11 - Physical Quantities Method with By-Product...Ch. 11 - Step Method with Three Service Departments Model,...Ch. 11 - Comparison of Allocation Methods BluStar Company...Ch. 11 - Solve for Unknowns: Direct Method Franks Foods has...Ch. 11 - Solve for Unknowns: Step Method RT Renovations is...Ch. 11 - Cost Allocation: Step Method with Analysis and...Ch. 11 - Prob. 59PCh. 11 - Prob. 60PCh. 11 - Direct, Step, and Reciprocal Methods:...Ch. 11 - Cost Allocation: Step and Reciprocal Methods...Ch. 11 - Allocate Service Department Costs: Direct and Step...Ch. 11 - Prob. 64PCh. 11 - Prob. 65PCh. 11 - Prob. 66PCh. 11 - Prob. 67PCh. 11 - Prob. 68PCh. 11 - Fletcher Fabrication, Inc., produces three...Ch. 11 - Findina Missing Data: Net Realizable Value Spartan...Ch. 11 - Finding Missing Data: Net Realizable Value Blaine,...Ch. 11 - Joint Costing in a Process Costing Context:...Ch. 11 - Find Maximum Input Price: Estimated Net Realizable...Ch. 11 - Effect of By-Product versus Joint Cost Accounting...Ch. 11 - Prob. 75PCh. 11 - Prob. 76P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Damerly Company (a Utah employer) wants to give a holiday bonus check of $375 to each employee. As it wants the check amount to be $375, it will need to gross-up the amount of the bonus. Calculate the withholding taxes and the gross amount of the bonus to be made to John Rolen if his cumulative earnings for the year are $46,910. Besides being subject to social security taxes and federal income tax (supplemental rate), a 4.95% Utah income tax must be withheld on supplemental payments.arrow_forwardPlease given correct answer general Accountingarrow_forwardHii ticher please given correct answer general Accountingarrow_forward
- On a particular date, FedEx has a stock price of $89.27 and an EPS of $7.11. Its competitor, UPS, had an EPS of $0.38. What would be the expected price of UPS stock on this date, if estimated using the method of comparables? A) $4.77 B) $7.16 C) $9.54 D) $10.50arrow_forwardHow much will you accumulated after 35 year? General accountingarrow_forwardGiven correct answer general Accountingarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning
Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...
Accounting
ISBN:9781305970663
Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337912020
Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:South-Western College Pub

Excel Applications for Accounting Principles
Accounting
ISBN:9781111581565
Author:Gaylord N. Smith
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Cost Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781305087408
Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Inspection and Quality control in Manufacturing. What is quality inspection?; Author: Educationleaves;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ey4MqC7Kp7g;License: Standard youtube license