
Diethylhydrazine reacts with iodine according to the following equation:
Â
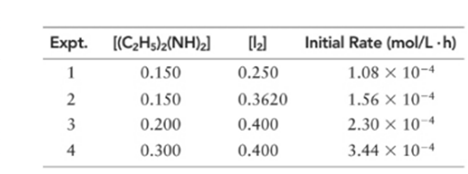
(a) What is the order of the reaction with respect to diethylhydrazine, iodine, and overall?
(b) Write the rate expression of the reaction.
(c) Calculate k for the reaction.
(d) What must [(C2H5)2] be so that the rate of the reaction is
(a)
Interpretation:
To determine the order of reaction with respect to (C2 H5 )2 (NH)2, I2 and overall for the following reaction:
Concept introduction:
Rate of a chemical reaction: It tells us about the speed at which the reactants are converted into products.
Mathematically, rate of reaction is directly proportional to the product of concentration of each reactant raised to the power equal to their respective stoichiometric coefficients.
Let’s say we have a reaction:
Answer to Problem 28QAP
Order of given reaction:
With respect to (C2 H5 )2 (NH)2 =1
With respect to I2 =1
Overall =2.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Here the chemical reaction is:

Let’s assume the reaction to be ‘t’ order with respect to (C2 H5 )2 (NH)2 and ‘y’ order with respect to I2.
Then, rate law for experiment 1, 2, 3 and 4 in above reaction will be;
Dividing (1) by (2) to get value of ‘y’.
Thus, order with respect to I2 is 1
Dividing (3) by (4) to get value of ‘t’.
Thus, order with respect to (C2 H5 )2 (NH)2 is 1.
And the order of reaction will be:
Thus, overall order of reaction is 2.
(b)
Interpretation:
To write the rate expression for the given reaction.
Concept introduction:
Rate of a chemical reaction: It tells us about the speed at which the reactants are converted into products.
Mathematically, rate of reaction is directly proportional to the product of concentration of each reactant raised to the power equal to their respective stoichiometric coefficients.
Let’s say we have a reaction:
Answer to Problem 28QAP
Rate law expression for above reaction will be;
Explanation of Solution
Here the chemical reaction is:
Order of reaction with respect to (C2 H5 )2 (NH)2 = 1
Order of reaction with respect to I2 = 1
Let the rate constant be ‘k’.
Then, rate law expression for above reaction will be;
(c)
Interpretation:
To determine the rate constant and its unit for the given reaction.
Concept introduction:
Rate of a chemical reaction: It tells us about the speed at which the reactants are converted into products.
Mathematically, rate of reaction is directly proportional to the product of concentration of each reactant raised to the power equal to their respective stoichiometric coefficients.
Let’s say we have a reaction:
Answer to Problem 28QAP
Rate constant is
Explanation of Solution
Here the chemical reaction is:
Writing rate law for experiment 1 in above reaction will be;
Hence, the rate constant is
(d)
Interpretation:
To determine the concentration of (C2 H5 )2 (NH)2.
Concept introduction:
Rate of a chemical reaction: It tells us about the speed at which the reactants are converted into products.
Mathematically, rate of reaction is directly proportional to the product of concentration of each reactant raised to the power equal to their respective stoichiometric coefficients.
Let’s say we have a reaction:
Answer to Problem 28QAP
Concentration of (C2 H5 )2 (NH)2 is 0.347 mol/L
Explanation of Solution
Here the chemical reaction is:
Rate law expression for above reaction:
Here we have:
[(C2 H5 )2 (NH)2 ]= let it ‘y’ M
[I2 ] = 0.500 M
Rate constant =
Rate of reaction = 5.00×10-4 mol/L.h
Plugging values in rate law as:
Hence, the concentration of (C2 H5 )2 (NH)2 is 0.347 mol/L
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Bundle: Chemistry: Principles and Reactions, 8th, Loose-Leaf + OWLv2, 1 term (6 months) Printed Access Card
- Pt + H₂ Draw the molecule on the canvas by choosing buttons from the Tools (for bonds), Atoms, and Advanced Templ 9 2 0 © 120arrow_forwardComplete boxes in the flow chart. Draw the structure of the organic compound foundin each layer after adding 3M NaOH and extraction. Make sure to include any charges. Provide explanation on answers.arrow_forward== Vid4Q2 Unanswered ☑ Provide IUPAC name of product in the reaction below A 3,4-dimethylcyclohexene B 1,2-dimethylcyclohexane C 1,2-dimethylcyclohexene D 3,4-dimethylcyclohexane H₂ Pdarrow_forward
- 5. Use the MS data to answer the questions on the next page. 14.0 1.4 15.0 8.1 100- MS-IW-5644 26.0 2.8 27.0 6.7 28.0 1.8 29.0 80 4.4 38.0 1.0 39.0 1.5 41.0 1.2 42.0 11.2 43.0 100.0 44.0 4.3 79.0 1.9 80.0 2.6 Relative Intensity 40 81.0 1.9 82.0 2.5 93.0 8.7 20- 95.0 8.2 121.0 2.0 123.0 2.0 136.0 11.8 0 138.0 11.5 20 40 8. 60 a. Br - 0 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 220 m/z Identify the m/z of the base peak and molecular ion. 2 b. Draw structures for each of the following fragments (include electrons and charges): 43.0, 93.0, 95.0, 136.0, and 138.0 m/z. C. Draw a reasonable a-fragmentation mechanism for the fragmentation of the molecular ion to fragment 43.0 m/z. Be sure to include all electrons and formal charges. 6. Using the values provided in Appendix E of your lab manual, calculate the monoisotopic mass for the pyridinium ion (CsH6N) and show your work.arrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardStereochemistry: Three possible answers- diastereomers, enantiomers OH CH₂OH I -c=0 21108 1101 41745 HOR CH₂OH IL Но CH₂OH TIL a. Compounds I and III have this relationship with each other: enantiomers b. Compounds II and IV have this relationship with each other: c. Compounds I and II have this relationship with each other: d. *Draw one structure that is a stereoisomer of II, but neither a diastereomer nor an enantiomer. (more than one correct answer)arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStaxChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStaxChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





