
Fox and McDonald's Introduction to Fluid Mechanics
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781118912652
Author: Philip J. Pritchard, John W. Mitchell
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 11, Problem 28P
Calculate y2, h, and y3 for this two-dimensional flow picture. State any assumptions clearly.
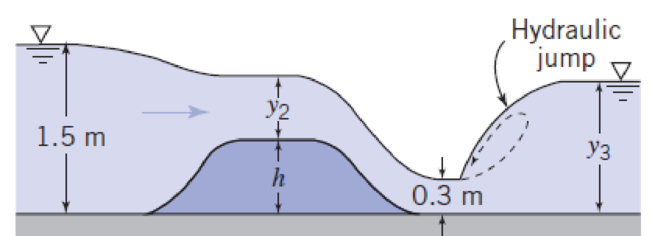
P11.28
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Q1/ A vertical, circular gate with water on one side as shown. Determine
the total resultant force acting on the gate and the location of the center of
pressure, use water specific weight 9.81 kN/m³
1 m
4 m
I need handwritten solution with sketches for each
Given answers to be: i) 14.65 kN; 6.16 kN; 8.46 kN ii) 8.63 kN; 9.88 kN iii) Bearing 6315 for B1 & B2, or Bearing 6215 for B1
Chapter 11 Solutions
Fox and McDonald's Introduction to Fluid Mechanics
Ch. 11 - Verify the equation given in Table 11.1 for the...Ch. 11 - A pebble is dropped into a stream of water that...Ch. 11 - Solution of the complete differential equations...Ch. 11 - A water flow rate of 250 cfs flows at a depth of 5...Ch. 11 - Determine and plot the relation between water...Ch. 11 - Capillary waves (ripples) are small amplitude and...Ch. 11 - The Froude number characterizes flow with a free...Ch. 11 - Consider waves on the surface of a tank of water...Ch. 11 - A submerged body traveling horizontally beneath a...Ch. 11 - Water flows in a rectangular channel at a depth of...
Ch. 11 - A partially open sluice gate in a 5-m-wide...Ch. 11 - Find the critical depth for flow at 3 m3/s in a...Ch. 11 - Flow occurs in a rectangular channel of 6 m width...Ch. 11 - What is the maximum flow rate that may occur in a...Ch. 11 - A rectangular channel carries a discharge of 10...Ch. 11 - Flow in the channel of Problem 11.15 has a...Ch. 11 - Consider the Venturi flume shown. The bed is...Ch. 11 - Eleven cubic meters per second of water are...Ch. 11 - A rectangular channel 10 ft wide carries 100 cfs...Ch. 11 - At what depths can 800 cfs flow in a trapezoidal...Ch. 11 - At a section of a 10-ft-wide rectangular channel,...Ch. 11 - Water, at 3 ft/s and 2 ft depth, approaches a...Ch. 11 - A horizontal rectangular channel 3 ft wide...Ch. 11 - A hydraulic jump occurs in a rectangular channel...Ch. 11 - A hydraulic jump occurs in a wide horizontal...Ch. 11 - A hydraulic jump occurs in a rectangular channel....Ch. 11 - The depths of water upstream and downstream from a...Ch. 11 - Calculate y2, h, and y3 for this two-dimensional...Ch. 11 - The hydraulic jump may be used as a crude flow...Ch. 11 - A hydraulic jump occurs on a horizontal apron...Ch. 11 - A hydraulic jump occurs in a rectangular channel....Ch. 11 - A positive surge wave, or moving hydraulic jump,...Ch. 11 - A 2-m-wide rectangular channel with a bed slope of...Ch. 11 - Determine the uniform flow depth in a rectangular...Ch. 11 - Determine the uniform flow depth in a trapezoidal...Ch. 11 - Water flows uniformly at a depth of 1.2 m in a...Ch. 11 - This large uniform open channel flow is to be...Ch. 11 - A rectangular flume built of timber is 3 ft wide....Ch. 11 - A channel with square cross section is to carry 20...Ch. 11 - A triangular channel with side angles of 45 is to...Ch. 11 - A flume of timber has as its cross section an...Ch. 11 - At what depth will 4.25 m3/s flow uniformly in a...Ch. 11 - A semicircular trough of corrugated steel, with...Ch. 11 - A rectangular flume built of concrete with 1 ft...Ch. 11 - Water flows in a trapezoidal channel at a flow...Ch. 11 - What slope is necessary to carry 11 m3/s uniformly...Ch. 11 - Find the normal depth for the channel of Problem...Ch. 11 - For a trapezoidal shaped channel with n = 0.014...Ch. 11 - Compute the critical depth for the channel in...Ch. 11 - A trapezoidal canal lined with brick has side...Ch. 11 - An optimum rectangular storm sewer channel made of...Ch. 11 - For a sharp-crested suppressed weir of length B =...Ch. 11 - A rectangular sharp-crested weir with end...Ch. 11 - What is the depth of water behind a rectangular...Ch. 11 - A broad-crested weir 0.9 m high has a flat crest...Ch. 11 - The head on a 90 V-notch weir is 1.5 ft. Determine...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Write nested if statements that perform the following tests: If amount1 is greater than 10 and amount2 is less ...
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Data Structures (4th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Write an SQL statement to display the breed, type, and DOB for all pets having the type Dog and the breed Std. ...
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Assume a telephone signal travels through a cable at two-thirds the speed of light. How long does it take the s...
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
ICA 8-52
The heat transfer coefficient of steel is 25 watts per square meter degree Celsius [W/(m2 °C)]. Conver...
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (4th Edition)
When displaying a Java applet, the browser invokes the _____ to interpret the bytecode into the appropriate mac...
Web Development and Design Foundations with HTML5 (8th Edition)
1.1 List 10 uses. for surveying in areas other than land
sunreying-
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- (b) A steel 'hot rolled structural hollow section' column of length 5.75 m, has the cross-section shown in Figure Q.5(b) and supports a load of 750 kN. During service, it is subjected to axial compression loading where one end of the column is effectively restrained in position and direction (fixed) and the other is effectively held in position but not in direction (pinned). i) Given that the steel has a design strength of 275 MN/m², determine the load factor for the structural member based upon the BS5950 design approach using Datasheet Q.5(b). [11] ii) Determine the axial load that can be supported by the column using the Rankine-Gordon formula, given that the yield strength of the material is 280 MN/m² and the constant *a* is 1/30000. [6] 300 600 2-300 mm wide x 5 mm thick plates. Figure Q.5(b) L=5.75m Pinned Fixedarrow_forwardHelp ارجو مساعدتي في حل هذا السؤالarrow_forwardHelp ارجو مساعدتي في حل هذا السؤالarrow_forward
- Q2: For the following figure, find the reactions of the system. The specific weight of the plate is 500 lb/ft³arrow_forwardQ1: For the following force system, find the moments with respect to axes x, y, and zarrow_forwardQ10) Body A weighs 600 lb contact with smooth surfaces at D and E. Determine the tension in the cord and the forces acting on C on member BD, also calculate the reaction at B and F. Cable 6' 3' wwwarrow_forward
- Help ارجو مساعدتي في حل هذا السؤالarrow_forwardQ3: Find the resultant of the force system.arrow_forwardQuestion 1 A three-blade propeller of a diameter of 2 m has an activity factor AF of 200 and its ratio of static thrust coefficient to static torque coefficient is 10. The propeller's integrated lift coefficient is 0.3.arrow_forward
- (L=6847 mm, q = 5331 N/mm, M = 1408549 N.mm, and El = 8.6 x 1014 N. mm²) X A ΕΙ B L Y Marrow_forwardCalculate the maximum shear stress Tmax at the selected element within the wall (Fig. Q3) if T = 26.7 KN.m, P = 23.6 MPa, t = 2.2 mm, R = 2 m. The following choices are provided in units of MPa and rounded to three decimal places. Select one: ○ 1.2681.818 O 2. 25745.455 O 3. 17163.636 O 4. 10727.273 ○ 5.5363.636arrow_forwardIf L-719.01 mm, = 7839.63 N/m³, the normal stress σ caused by self-weight at the location of the maximum normal stress in the bar can be calculated as (Please select the correct value of σ given in Pa and rounded to three decimal places.) Select one: ○ 1. 1409.193 2. 845.516 O 3. 11273.545 ○ 4.8455.159 ○ 5.4509.418 6. 2818.386 7.5636.772arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Physics 33 - Fluid Statics (1 of 10) Pressure in a Fluid; Author: Michel van Biezen;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mzjlAla3H1Q;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY