
Concept explainers
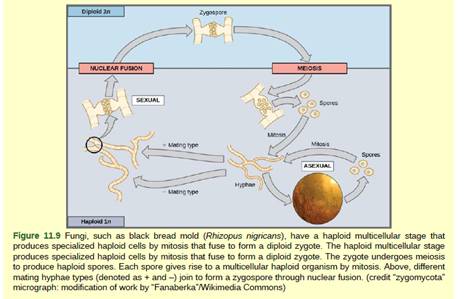
Figure 11.9 If a mutation occurs so that a
it still be able to reproduce?
To analyze:
Whether the fungus is able to reproduce, in case if a mutation takes place and the fungus is not able to produce a minus mating type.
Introduction:
Fungi are the eukaryotic species, which comprise both the multicellular and unicellular species in their genera. In fungi, reproduction is a complicated procedure and certain environmental factors play an essential function in the process of reproduction. Reproduction can take place both sexually and asexually on the basis of the existence and non-existence of the adequate environmental conditions.
Explanation of Solution
Mutation refers to the modification in the sequence of nucleotide that changes the genetic composition of the species. It can result in a harmful effect on the functioning individual and may even result in a fatality. In case, if mutation takes place in the fungus and it influences the generation of minus mating type, then the fungus would no longer possess the tendency to reproduce sexually.
However, the fungus would have the tendency to generate offspring with the help of asexual mode of reproduction. This process would incorporate the fungal hyphae to generate spores that upon meiosis will further produce fungal hyphae. The hyphae can also go through the process of fragmentation from which novel colonies can be developed. Apart from these, it can also reproduce asexually by budding.
The life processes of the fungus to reproduce sexually as well as asexually permits the fungus to reproduce, even in the non-existence of sexual reproduction conditions.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Biology 2e
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
- 1. Match each vocabulary term to its best descriptor A. affinity B. efficacy C. inert D. mimic E. how drugs move through body F. how drugs bind Kd Bmax Agonist Antagonist Pharmacokinetics Pharmacodynamicsarrow_forward50 mg dose of a drug is given orally to a patient. The bioavailability of the drug is 0.2. What is the volume of distribution of the drug if the plasma concentration is 1 mg/L? Be sure to provide units.arrow_forwardDetermine Kd and Bmax from the following Scatchard plot. Make sure to include units.arrow_forward
- Choose a catecholamine neurotransmitter and describe/draw the components of the synapse important for its signaling including synthesis, packaging into vesicles, receptors, transporters/degradative enzymes. Describe 2 drugs that can act on this system.arrow_forwardThe following figure is from Caterina et al. The capsaicin receptor: a heat activated ion channel in the pain pathway. Nature, 1997. Black boxes indicate capsaicin, white circles indicate resinferatoxin. a) Which has a higher potency? b) Which is has a higher efficacy? c) What is the approximate Kd of capsaicin in uM? (you can round to the nearest power of 10)arrow_forwardWhat is the rate-limiting-step for serotonin synthesis?arrow_forward
 Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning





