
(a)
Interpretation:
Line angle formula to be identified for 2,2,4-trimethylhexane.
Concept Introduction:
Example of
In line angle formula each line indicates 2 carbon are linked to each other through a single bond.
Answer to Problem 19P
The line angle formula for 2,2,4-trimethylhexane.
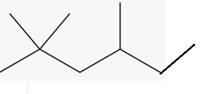
Explanation of Solution
The line angle formula for 2,2,4-trimethylhexane.
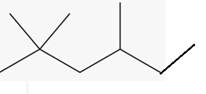
(b)
Interpretation:
Line angle formula to be identified for 2,2-dimethylpropane.
Concept Introduction:
Example of alkane are propane having formula C3 H8, butane having formula C4 H10 etc. Their molecular formula indicate the number of hydrogen is 2 more than twice the number of carbon in the structure and thus the derived formula for alkane is Cn H2n +2.
In line angle formula each line indicates 2 carbon are linked to each other through a single bond.
Answer to Problem 19P
The line angle formula for 2,2-dimethylpropane.

Explanation of Solution
The line angle formula for 2,2-dimethylpropane.

(c)
Interpretation:
Line angle formula to be identified for 3-ethyl-2,4,5-trimethyloctane.
Concept Introduction:
Example of alkane are propane having formula C3 H8, butane having formula C4 H10 etc. Their molecular formula indicate the number of hydrogen is 2 more than twice the number of carbon in the structure and thus the derived formula for alkane is Cn H2n +2.
In line angle formula each line indicates 2 carbon are linked to each other through a single bond.
Answer to Problem 19P
The line angle formula for 3-ethyl-2,4,5-trimethyloctane.
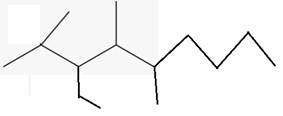
Explanation of Solution
The line angle formula for 3-ethyl-2,4,5-trimethyloctane.
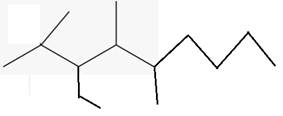
(d)
Interpretation:
Line angle formula to be identified for 5-butyl-2,2-dimethylnonane.
Concept Introduction:
Example of alkane are propane having formula C3 H8, butane having formula C4 H10 etc. Their molecular formula indicate the number of hydrogen is 2 more than twice the number of carbon in the structure and thus the derived formula for alkane is Cn H2n +2.
In line angle formula each line indicates 2 carbon are linked to each other through a single bond.
Answer to Problem 19P
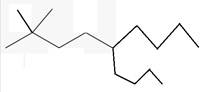
The line angle formula for 5-butyl-2,2-dimethylnonane.
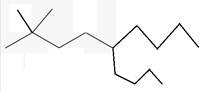
Explanation of Solution
The line angle formula for 5-butyl-2,2-dimethylnonane.
(e)
Interpretation:
Line angle formula to be identified for 4-isopropyloctane.
Concept Introduction:
Example of alkane are propane having formula C3 H8, butane having formula C4 H10 etc. Their molecular formula indicate the number of hydrogen is 2 more than twice the number of carbon in the structure and thus the derived formula for alkane is Cn H2n +2.
In line angle formula each line indicates 2 carbon are linked to each other through a single bond.
Answer to Problem 19P
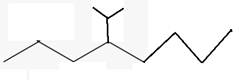
The line angle formula for 4-isopropyloctane.
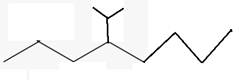
Explanation of Solution
The line angle formula for 4-isopropyloctane.
(f)
Interpretation:
Line angle formula to be identified for 3,3-dimethylpentane.
Concept Introduction:
Example of alkane are propane having formula C3 H8, butane having formula C4 H10 etc. Their molecular formula indicate the number of hydrogen is 2 more than twice the number of carbon in the structure and thus the derived formula for alkane is Cn H2n +2.
In line angle formula each line indicates 2 carbon are linked to each other through a single bond.
Answer to Problem 19P
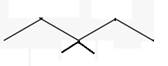
The line angle formula for 3,3-dimethylpentane.
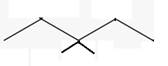
Explanation of Solution
The line angle formula for 3,3-dimethylpentane.
(g)
Interpretation:
Line angle formula to be identified for trans-1,3-dimethylcyclopentane.
Concept Introduction:
Example of alkane are propane having formula C3 H8, butane having formula C4 H10 etc. Their molecular formula indicate the number of hydrogen is 2 more than twice the number of carbon in the structure and thus the derived formula for alkane is Cn H2n +2.
In line angle formula each line indicates 2 carbon are linked to each other through a single bond.
Answer to Problem 19P
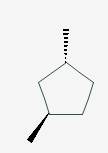
The line angle formula for trans-1,3-dimethylcyclopentane.
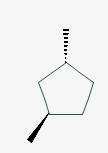
Explanation of Solution
The line angle formula for trans-1,3-dimethylcyclopentane.
(h)
Interpretation:
Line angle formula to be identified for Cis-1,2-diethylcyclobutane.
Concept Introduction:
Example of alkane are propane having formula C3 H8, butane having formula C4 H10 etc. Their molecular formula indicate the number of hydrogen is 2 more than twice the number of carbon in the structure and thus the derived formula for alkane is Cn H2n +2.
In line angle formula each line indicates 2 carbon are linked to each other through a single bond.
Answer to Problem 19P
The line angle formula for Cis-1,2-diethylcyclobutane.
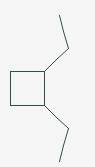
Explanation of Solution
The line angle formula for Cis-1,2-diethylcyclobutane.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Introduction To General, Organic, And Biochemistry
- Propose a synthesis of 1-butanamine from the following: (a) a chloroalkane of three carbons (b) a chloroalkane of four carbonsarrow_forwardSelect the stronger base from each pair of compounds. (a) H₂CNH₂ or EtzN (b) CI or NH2 NH2 (c) .Q or EtzN (d) or (e) N or (f) H or Harrow_forward4. Provide a clear arrow-pushing mechanism for each of the following reactions. Do not skip proton transfers, do not combine steps, and make sure your arrows are clear enough to be interpreted without ambiguity. a. 2. 1. LDA 3. H3O+ HOarrow_forward
- b. H3C CH3 H3O+ ✓ H OHarrow_forward2. Provide reagents/conditions to accomplish the following syntheses. More than one step is required in some cases. a. CH3arrow_forwardIdentify and provide an explanation that distinguishes a qualitative and quantitative chemical analysis. Provide examples.arrow_forward
- Identify and provide an explanation of the operational principles behind a Atomic Absorption Spectrometer (AAS). List the steps involved.arrow_forwardInstructions: Complete the questions in the space provided. Show all your work 1. You are trying to determine the rate law expression for a reaction that you are completing at 25°C. You measure the initial reaction rate and the starting concentrations of the reactions for 4 trials. BrO³¯ (aq) + 5Br¯ (aq) + 6H* (aq) → 3Br₂ (l) + 3H2O (l) Initial rate Trial [BrO3] [H*] [Br] (mol/L) (mol/L) | (mol/L) (mol/L.s) 1 0.10 0.10 0.10 8.0 2 0.20 0.10 0.10 16 3 0.10 0.20 0.10 16 4 0.10 0.10 0.20 32 a. Based on the above data what is the rate law expression? b. Solve for the value of k (make sure to include proper units) 2. The proposed reaction mechanism is as follows: i. ii. BrО¸¯ (aq) + H+ (aq) → HBrO3 (aq) HBrO³ (aq) + H* (aq) → H₂BrO3* (aq) iii. H₂BrO³* (aq) + Br¯ (aq) → Br₂O₂ (aq) + H2O (l) [Fast] [Medium] [Slow] iv. Br₂O₂ (aq) + 4H*(aq) + 4Br(aq) → 3Br₂ (l) + H2O (l) [Fast] Evaluate the validity of this proposed reaction. Justify your answer.arrow_forwardе. Д CH3 D*, D20arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co





