
Physics for Scientists and Engineers
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781337553278
Author: Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 11, Problem 11P
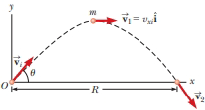
Review. A projectile of mass m is launched with an initial velocity
Figure P11.11
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Identify which of the following vectors are parallel to A.
Vector
Vector A
70°
60°
20°
AAZA!
30°
20°
20°
70°
20°
20°
70°
20°
Need help
3b
Chapter 11 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Ch. 11.1 - Which of the following statements about the...Ch. 11.2 - Recall the skater described at the beginning of...Ch. 11.3 - A solid sphere and a hollow sphere have the same...Ch. 11.4 - A competitive diver leaves the diving board and...Ch. 11 - Prob. 1PCh. 11 - The displacement vectors 42.0 cm at 15.0 and 23.0...Ch. 11 - If AB=AB, what is the angle between A and B?Ch. 11 - Use the definition of the vector product and the...Ch. 11 - Two forces F1 and F2 act along the two sides of an...Ch. 11 - Prob. 6P
Ch. 11 - A particle is located at a point described by the...Ch. 11 - A 1.50-kg particle moves in the xy plane with a...Ch. 11 - A particle of mass m moves in the xy plane with a...Ch. 11 - Heading straight toward the summit of Pikes Peak,...Ch. 11 - Review. A projectile of mass m is launched with an...Ch. 11 - Review. A conical pendulum consists of a bob of...Ch. 11 - A particle of mass m moves in a circle of radius R...Ch. 11 - A 5.00-kg particle starts from the origin at time...Ch. 11 - A ball having mass m is fastened at the end of a...Ch. 11 - A uniform solid sphere of radius r = 0.500 m and...Ch. 11 - A uniform solid disk of mass m = 3.00 kg and...Ch. 11 - Show that the kinetic energy of an object rotating...Ch. 11 - Big Ben (Fig. P10.27, page 281), the Parliament...Ch. 11 - Model the Earth as a uniform sphere. (a) Calculate...Ch. 11 - The distance between the centers of the wheels of...Ch. 11 - You are working in an observatory, taking data on...Ch. 11 - A 60.0-kg woman stands at the western rim of a...Ch. 11 - Prob. 24PCh. 11 - A uniform cylindrical turntable of radius 1.90 m...Ch. 11 - Prob. 26PCh. 11 - A wooden block of mass M resting on a...Ch. 11 - Why is the following situation impossible? A space...Ch. 11 - A wad of sticky clay with mass m and velocity vi...Ch. 11 - A 0.005 00-kg bullet traveling horizontally with a...Ch. 11 - The angular momentum vector of a precessing...Ch. 11 - A light rope passes over a light, frictionless...Ch. 11 - Review. A thin, uniform, rectangular signboard...Ch. 11 - Prob. 34APCh. 11 - We have all complained that there arent enough...Ch. 11 - Prob. 36APCh. 11 - A rigid, massless rod has three particles with...Ch. 11 - Review. Two boys are sliding toward each other on...Ch. 11 - Two astronauts (Fig. P11.39), each having a mass...Ch. 11 - Two astronauts (Fig. P11.39), each having a mass...Ch. 11 - Native people throughout North and South America...Ch. 11 - Two children are playing on stools at a restaurant...Ch. 11 - You are attending a county fair with your friend...Ch. 11 - A uniform rod of mass 300 g and length 50.0 cm...Ch. 11 - Global warming is a cause for concern because even...Ch. 11 - The puck in Figure P11.46 has a mass of 0.120 kg....Ch. 11 - You operate a restaurant that has many large,...Ch. 11 - A solid cube of wood of side 2a and mass M is...Ch. 11 - In Example 11.8, we investigated an elastic...Ch. 11 - Prob. 50CP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 4a Which of the following values COULD NOT be a magnitude? Choose all that apply. 626 0 -0.806 8.63 -48.5 72 131 156 4b Px = -1248 & Py = 261. Determine P.P = Qx = -1540 & Qy = 375. Determine Q.Q = 4c. T = 1105 & Ty = 425. Determine the two possible values for Tx. 4d. Uy = -38. Which of the following COULD NOT be the value of U? Choose all that apply. 10 70 72 31 47 0 75 38 4e. R has a magnitude of 165. Which of the following COULD be Rx? Choose all that apply. 165 -171 155 0 -156 -165 172 -130arrow_forward9.arrow_forward10.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University
Moment of Inertia; Author: Physics with Professor Matt Anderson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZrGhUTeIlWs;License: Standard Youtube License