
(a)
Interpretation:
The point group of CH3Cl has to be stated.
Concept introduction:
A symmetry operation is defined as an action on an object to reproduce an arrangement that is identical to its original spatial arrangement. The group of symmetry operations of which at least one point is kept fixed is called point group. The symmetry operations can be identity, rotation, reflection, inversion and improper rotation.
(a)
Answer to Problem 11E.1P
The point group of CH3Cl is C3v.
Explanation of Solution
The symmetry elements in CH3Cl are shown below.
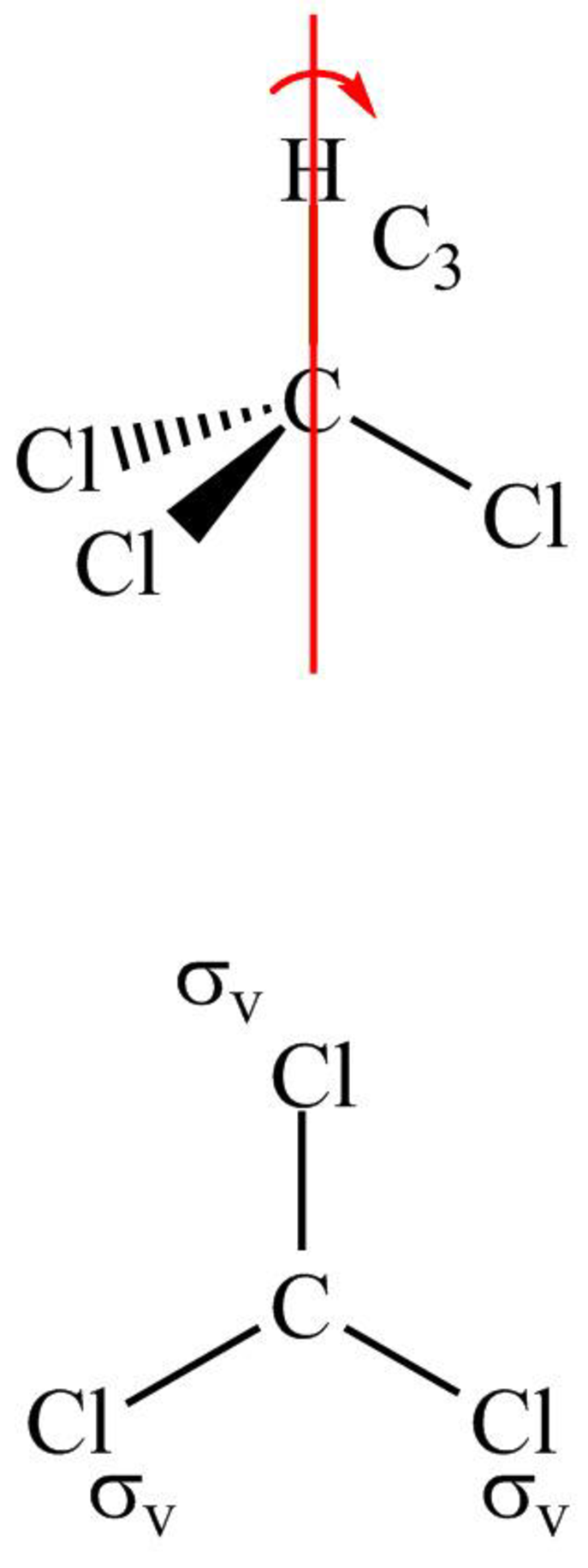
Figure 1
The structure of CH3Cl is tetrahedral with three same and one different group attached to the central atom. It has a threefold axis. The molecule has three vertical planes.
Therefore, the point group of CH3Cl is C3v.
(b)
Interpretation:
The number of normal modes of vibrations in CH3Cl has to be calculated.
Concept introduction:
The complex vibrations exhibit by the polyatomic molecule is known as normal modes of vibrations. The vibrational modes of a molecule are IR or Raman active. If a molecule has centre of symmetry, then the modes which are IR-active will be Raman inactive and the modes that are IR-inactive will be Raman active. The total number of vibrational degrees of freedom for nonlinear molecule is represented by 3N−6.
(b)
Answer to Problem 11E.1P
The number of normal modes of vibration in CH3Cl is 9.
Explanation of Solution
The total number of atoms in the molecule (CH3Cl) is 5.
The total number of vibrational modes of a nonlinear molecule is given by the formula below.
Number of vibrational modes=3N−6 (1)
Where,
- N is the total number of atoms in the molecule.
Substitute the value of N in equation (1).
Number of vibrational modes=3(5)−6=15−6=9
Therefore, the number of normal modes of vibration in CH3Cl is 9.
(c)
Interpretation:
The symmetry species of the normal modes of vibration of CH3Cl has to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The characters of the irreducible representations of the given point group can be multiplied by each other. The only condition is the characters of the same symmetry operations are multiplied together. The multiplication of the characters is commutative.
The great orthogonality theorem for the reducible representation can be expressed as shown below.
aΓ=1h∑all classesof point groupN⋅χΓ⋅χlinear combo
(c)
Answer to Problem 11E.1P
The symmetry species of normal modes of vibrational for CH3Cl is 3A1+4E.
Explanation of Solution
The character table of C3v is shown below.
| C3v | E | 2C3 | 3σv | |
| A1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | z, z2, x2+y2 |
| A2 | 1 | 1 | −1 | Rz |
| E | 2 | −1 | 0 | (x,y), (xy,x2−y2)(yz,zx), (Rx,Ry) |
The irreducible representation of C3v for CH3Cl is shown below.
| C3v | E | 2C3 | 3σv |
| Γred | 15 | 0 | 3 |
The great orthogonality theorem for the reducible representation can be expressed as shown below.
aΓ=1h∑all classesof point groupN⋅χΓ⋅χlinear combo (2)
Where,
- aΓ is the number of times the irreducible representation appears in a linear combination.
- h is the order of the group.
- χΓ is the character of the class of the irreducible representation.
- χlinear combo is the character of the class linear combination.
- N is the number of symmetry operations.
The order of the group is 6.
The great orthogonality theorem orthogonality of the irreducible representation of A1, A2, and E is shown below.
Substitute the value of the order of the group, character of the class of the irreducible representation from character table of C3v point group, the character of the class linear combination and number of symmetry operations for A1 in the equation (2).
aA1=16[(1⋅1⋅15)+(2⋅1⋅0)+(3⋅1⋅3)]=4
The number of times the irreducible representation for A1 appears in a linear combination is 4.
Similarly, for A2, substitute the value of order of the group, character of the class of the irreducible representation from character table of C3v point group, character of the class linear combination and number of symmetry operations in the equation (2).
aA2=16[(1⋅1⋅15)+(2⋅1⋅0)+(3⋅−1⋅3)]=1
The number of times the irreducible representation for A2 appears in a linear combination is 1.
Similarly, for E, substitute the value of the order of the group, character of the class of the irreducible representation from character table of C3v point group, the character of the class linear combination and number of symmetry operations in the equation (2).
aE=16[(1⋅2⋅15)+(2⋅−1⋅0)+(3⋅0⋅3)]=5
The number of times the irreducible representation for E appears in a linear combination is 5.
The displacement of the atoms of CH3Cl span 4A1+A2+5E.
From the C3v character table, A1 and E are the symmetry species for translational motion while A2 and E are the symmetry species for rotational motion.
The symmetry species for the normal mode of vibration is calculated by the formula shown below.
Vibrational=Displacement of atom−(rotational+translational)
Substitute the symmetry species rotational, translational and displacement of the atoms in the above expression.
Vibrational=4A1+A2+5E−(A1+E+A2+E)=4A1+A2+5E−A1−E−A2−E=3A1+4E
Therefore, the symmetry species of normal modes of vibrational for CH3Cl is 3A1+4E.
(d)
Interpretation:
The vibrational modes of CH3Cl which are infrared active have to be stated.
Concept introduction:
As mentioned in the concept introduction in part (b).
(d)
Answer to Problem 11E.1P
The vibrational modes of CH3Cl which are infrared active are E and A1.
Explanation of Solution
The character table of C3v is shown below.
| C3v | E | 2C3 | 3σv | |
| A1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | z, z2, x2+y2 |
| A2 | 1 | 1 | −1 | |
| E | 2 | −1 | 0 | (x,y), (xy,x2−y2)(yz,zx) |
The symmetry species of the normal modes of vibration of CH3Cl is 3A1+4E.
The symmetry species that contains x, y, z are infrared active.
The irreducible representation E and A1 has x, y, and z. Therefore, these are infrared active.
(e)
Interpretation:
The vibrational modes of CH3Cl which is Raman active have to be stated.
Concept introduction:
As mentioned in the concept introduction in part (b).
(e)
Answer to Problem 11E.1P
The vibrational modes of CH3Cl which are Raman active are E and A1.
Explanation of Solution
The character table of C3v is shown below.
| C3v | E | 2C3 | 3σv | |
| A1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | z, z2, x2+y2 |
| A2 | 1 | 1 | −1 | |
| E | 2 | −1 | 0 | (x,y), (xy,x2−y2)(yz,zx) |
The symmetry species of the normal modes of vibration of CH3Cl is 3A1+4E.
The symmetry species that contains quadratic form is Raman active.
The irreducible representation E and A1 has a quadratic form. Therefore, these are Raman active modes.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Student Solutions Manual to accompany Atkins' Physical Chemistry 11th edition
- Steps and explanations pleasearrow_forwardUse diagram to answer the following: 1.Is the overall rxn endo- or exothermic. Explain briefly your answer____________________2. How many steps in this mechanism?_____________3. Which is the rate determining step? Explain briefly your answer____________________4. Identify (circle and label) the reactants,the products and intermediate (Is a Cation, Anion, or a Radical?) Please explain and provide full understanding.arrow_forwardDraw the entire mechanism and add Curved Arrows to show clearly how electrons areredistributed in the process. Please explain and provide steps clearly.arrow_forward
- Match the denticity to the ligand. Water monodentate ✓ C₂O2 bidentate H₂NCH₂NHCH2NH2 bidentate x EDTA hexadentate Question 12 Partially correct Mark 2 out of 2 Flag question Provide the required information for the coordination compound shown below: Na NC-Ag-CN] Number of ligands: 20 Coordination number: 2✔ Geometry: linear Oxidation state of transition metal ion: +3 x in 12 correct out of 2 question Provide the required information for the coordination compound shown below. Na NC-Ag-CN] Number of ligands: 20 Coordination number: 2 Geometry: linear 0 Oxidation state of transition metal ion: +3Xarrow_forwardCan you explain step by step behind what the synthetic strategy would be?arrow_forwardPlease explain step by step in detail the reasoning behind this problem/approach/and answer. thank you!arrow_forward
- 2. Predict the product(s) that forms and explain why it forms. Assume that any necessary catalytic acid is present. .OH HO H₂N OHarrow_forwardconsider the rate of the reaction below to be r. Whats the rate after each reaction? Br + NaCN CN + NaBr a. Double the concentration of alkyl bromide b. Halve the concentration of the electrophile & triple concentration of cyanide c. Halve the concentration of alkyl chloridearrow_forwardPredict the organic reactant that is involved in the reaction below, and draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic reactant. Please include all steps & drawings & explanations.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





