
Package: Loose Leaf for Organic Chemistry with Biological Topics with Connect Access Card
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781260170405
Author: SMITH
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 11, Problem 11.47P
Draw a stepwise mechanism for each reaction.
a. 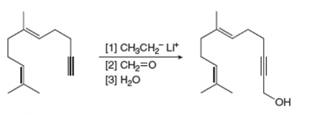
b. 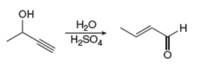
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Amorphous polymers are usually transparent and semi-crystalline polymers are usually opaque. Correct?(a) No. They are all made up of polymer chains. True if they were monomers.(b) Yes. The arrangement of the chains determines the passage of light.(c) No. It is the other way around.(d) Crystallinity or amorphousness does not affect the transparency or opacity of the material.
The name ferrites refers to a family of(a) ceramic materials that exhibit ferrimagnetic behavior due to their ionic composition.(b) polymeric materials that exhibit ferrimagnetic behavior due to their ionic composition.(c) concrete-based materials that exhibit ferrimagnetic behavior due to their ionic composition.(d) superconducting materials that exhibit ferrimagnetic behavior due to their ionic composition.
State the two main factors affecting ion packing in the solid state.(a) Number of covalent bonds and their unsaturation.(b) Mechanical properties and degradation temperature.(c) Number of crystalline phases present and grain size.(d) Electroneutrality and ion size.
Chapter 11 Solutions
Package: Loose Leaf for Organic Chemistry with Biological Topics with Connect Access Card
Ch. 11 - Problem 11.1 Neopheliosyne B is a novel acetylenic...Ch. 11 - Give the IUPAC name for each compound.Ch. 11 - Give the structures corresponding to each of the...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.4PCh. 11 - Prob. 11.5PCh. 11 - Which bases can deprotonate acetylene? The pKa...Ch. 11 - Draw the organic products formed when each alkyne...Ch. 11 - Draw additional resonance structures for each...Ch. 11 - Problem 11.9 Draw the products formed when is...Ch. 11 - Explain the following result. Although alkenes...
Ch. 11 - Problem 11.11 Draw the keto tautomer of each...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.12PCh. 11 - a Draw two different enol tautomers of...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.14PCh. 11 - Problem 11.15 Draw the organic products formed in...Ch. 11 - Problem 11.16 What acetylide anion and alkyl...Ch. 11 - Problem. 11.17 Show how , and can be used to...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.18PCh. 11 - Draw the products of each reaction. a. b.Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.20PCh. 11 - Problem 11.21 Use retrosynthetic analysis to show...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.22PCh. 11 - Give the IUPAC name for each compound. a. b.Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.24PCh. 11 - 11.25 Answer the following questions about...Ch. 11 - 11.26 Give the IUPAC name for each alkyne.
a. ...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.27PCh. 11 - Which of the following pairs of compounds...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.29PCh. 11 - 11.30 How is each compound related to A? Choose...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.31PCh. 11 - Prob. 11.32PCh. 11 - 11.33 Draw the products formed when is treated...Ch. 11 - What reagents are needed to convert (CH3CH2)3CCCH...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.35PCh. 11 - 11.36 What alkynes give each of the following...Ch. 11 - 11.37 What alkyne gives each compound as the only...Ch. 11 - 11.38 Draw the organic products formed in each...Ch. 11 - 11.39 Draw the structure of compounds A-E in the...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.40PCh. 11 - Prob. 11.41PCh. 11 - 11.42 What reactions are needed to convert alcohol...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.43PCh. 11 - Prob. 11.44PCh. 11 - 11.45 Explain the following statement. Although ...Ch. 11 - 11.46 Tautomerization in base resembles...Ch. 11 - 11.47 Draw a stepwise mechanism for each...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.48PCh. 11 - Prob. 11.49PCh. 11 - 11.50 What acetylide anion and alkyl halide are...Ch. 11 - 11.51 Synthesize each compound from acetylene. You...Ch. 11 - 11.52 Devise a synthesis of each compound using ...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.53PCh. 11 - Prob. 11.54PCh. 11 - 11.55 Devise a synthesis of the ketone, , from ...Ch. 11 - 11.56 Devise a synthesis of each compound using ...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.57PCh. 11 - Prob. 11.58PCh. 11 - 11.59 N-Chlorosuccinimide (NCS) serves as a source...Ch. 11 - 11.60 Draw a stepwise mechanism for the following...Ch. 11 - 11.61 Draw a stepwise mechanism for the following...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.62PCh. 11 - 11.63 Write a stepwise mechanism for each of the...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.64PCh. 11 - 11.65 Explain why an optically active solution of ...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Label each statement about the polynucleotide ATGGCG as true or false. The polynucleotide has six nucleotides. ...
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
Gregor Mendel never saw a gene, yet he concluded that some inherited factors were responsible for the patterns ...
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
Choose the best answer to each of the following. Explain your reasoning. If Earth were twice as far as it actua...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
11. In the early 1800s, French naturalist Jean Baptiste Lamarck suggested that the best explanation for the rel...
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
An obese 55-year-old woman consults her physician about minor chest pains during exercise. Explain the physicia...
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The ceramic materials alumina (Al2O3) and chromium oxide (Cr2O3) form an isomorphic phase diagram. The solubility will be(a) unlimited of one ceramic in the other.(b) very limited depending on the weight % of Al2O3(c) very limited depending on the weight % of Cr2O3(d) partial of one ceramic in the other.arrow_forwardAmong the main characteristics of optical fibers, indicate which of the following is not included:(a) Opacity and Rigidity(b) Flexibility(c) Transparency(d) Low thicknessarrow_forwardMost ceramic materials have low thermal conductivities because(a) Electron mobility is strongly restricted due to their strong ionic-covalent bonding.(b) False, in general they are excellent thermal conductors (they are used in ovens).(c) Electron mobility is dependent on T and therefore they are poor conductors at high temperatures.(d) Electron mobility is highly restricted by secondary bonds.arrow_forward
- Si increases its conductivity when doped with Ga and P.(a) True, because the conduction mechanism is due to electrons and holes generated by Ga and P as the case may be.(b) True, because a completely different compound is generated.(c) False, because when impurities are introduced, the opposite occurs.(d) False, because the conductivity of Si is only determined by the increase in temperature, which must be controlled.arrow_forwardIndicate whether a configuration and a microstate are the same:a) Yesb) No, a microstate encompasses several configurationsc) No, a configuration is the same as a macrostated) No, a configuration encompasses several microstatesarrow_forwardThe representation of a one-dimensional velocity distribution function for a gas, with increasing temperature the maximum occurs for vi = 0 m/s. Correct?arrow_forward
- The representation of a one-dimensional velocity distribution function for a gas, as the temperature increases:a) it becomes more flattenedb) the maximum occurs for vi = 0 m/sExplain it.arrow_forwardThe velocity distribution function of gas moleculesa) is used to measure their velocity, since the small size of gas molecules means that it cannot be measured in any other wayb) is only used to describe the velocity of particles if their density is very high.c) describes the probability that a gas particle has a velocity in a given interval of velocitiesarrow_forwardExplain why in the representation of a one-dimensional velocity distribution function for a particular gas, the maximum occurs for vi = 0 m/s.arrow_forward
- Explain why the representation of a one-dimensional velocity distribution function for a particular gas becomes flatter as the temperature increases.arrow_forwardDraw a Lewis structure for each of the following molecules and assign charges where appropriate. The order in which the atoms are connected is given in parentheses. a. CIFCIF b. BrCNBrCN 0 c. SOCI2 × (CISCIO) SOC₁₂ (CISCI) You can draw both an octet and a valence shell expanded structure. Considering the following structural information, which is the better one: The measured S-OS-O bond length in SOC12SOCl2 is 1.43 Å. For comparison, that in SO2SO2 is 1.43 Å [Exercise 1-9, part (b)], that in CHзSOHCH3 SOH d. CH3NH2CH3NH2 (methanesulfenic acid) is 1.66 A. e. CH3OCH3 CH3 OCH3 NH2 f. N2H2× (HNNH) N2 H2 (HNNH) g. CH2COCH₂ CO h. HN3× (HNNN) HN3 (HNNN) i. N20 × (NNO) N2O (NNO)arrow_forwardbre The reaction sequence shown in Scheme 5 demonstrates the synthesis of a substituted benzene derivative Q. wolsd works 2 NH2 NaNO2, HCI (apexe) 13× (1 HNO3, H2SO4 C6H5CIN2 0°C HOTE CHINO₂ N O *O₂H ( PO Q Я Scheme 5 2 bag abouoqmics to sounde odi WEIC (i) Draw the structure of intermediate O. [2 marks] to noitsmot od: tot meinedogm, noit so oft listsb ni zaupaib bas wa (ii) Draw the mechanism for the transformation of aniline N to intermediate O. Spoilage (b) [6 marks] (iii) Identify the reagent X used to convert compound O to the iodinated compound [tom E P. vueimado oilovonsa ni moitos nolisbnolov ayd toes ai tedw nisiqx (iv) Identify the possible structures of compound Q. [2 marks] [2 marks] [shom 2] (v) bus noires goiribbeolovo xnivollot adj to subora sidab Draw the mechanism for the transformation of intermediate P to compound Q. [5 marks] vi (vi) Account for the regiochemical outcome observed in the reaction forming compound Q. [3 marks]arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY
Nomenclature: Crash Course Chemistry #44; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=U7wavimfNFE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY