
11.35 For the reaction 2 NO(g) + 2 H?(g) — N,(g) + 2 H,O(g) at 1100°C, the following data have been obtained:
| [NOJ | [HJ | Rate = A(N2]/At |
| (mol L~1) | (mol L_1) | (mol L-1 s_1) |
| 5.0 X 10’1 | 0.32 | 0.012 |
| 1.0 X 10~’ | 0.32 | 0.048 |
| 1.0 X 10"2 | 0.64 | 0.096 |
Derive a rate law for the reaction and determine the value of the rate constant.
Interpretation: Given the experimental data obtained for a reaction at
Concept Introduction: Orders of reaction are constantly determined by doing experiments. Consequently without experimental information, we can't conclude anything about the order of a reaction just by having a look at the equation for the reaction. By doing experiments involving a reaction between A and B, the rate of the reaction is identified to be related to the concentrations of A and B as follows:
This is the Rate Equation.
Where,
Rate is in the units of mol dm-3s-1
k is the rate constant
A, B- concentrations in mol dm-3
a - Order of reaction with respect to A
b- Order of reaction with respect to B
If temperature is given, the rate is usually considered to be a function of the initial concentrations of the reactants A and B.
Answer to Problem 11.35PAE
Solution: The rate law of the reaction is
Explanation of Solution
Given information: Reaction:
Experimental Data
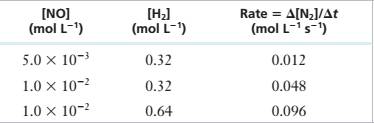
Step 1: For the reaction:
The rate law can be determined using the rate equation as follows:
Where,
a= Order of the reaction with respect to NO
b= Order of the reaction with respect to
Step 2: From the first, second and third rows of the given experimental data,
Step 3: Divide (2) by (3), we get
Step 4: Divide (1) by (2), we get
Step 5: Rate Equation = >
Step 6: Substitute a=2,b=1 values in (1)
It does not make a difference what the number of reactants there are. The concentration of every reactant will be present in the rate equation, raised to some power. These powers resemble the individual orders with respect to each reactant. The sum of these powers results in the overall order of the reaction. The rate constant will be a constant value for a given reaction only if the concentration of the reactants is changed without changing any other factors.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Chemistry for Engineering Students
- What is the final product when D-galactose reacts with hydroxylamine?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forwardIn the two chair conformations of glucose, the most stable is the one with all the OH groups in the equatorial position. Is this correct?arrow_forward
- please help me with my homeworkarrow_forwardhelparrow_forwardThe temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forward
- QUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forwarder your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning





