
a)
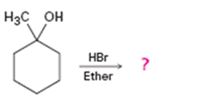
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction shown is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Alcohols gets converted into the corresponding bromides on treatment with HBr in ether solution.
To predict:
The product of the reaction shown.
Answer to Problem 26AP
The product of the reaction shown is
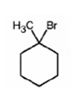
Explanation of Solution
When 1-methylcyclohexanol is treated with HBr, the OH group in it is replaced by the bromine to yield 1-chloro-1-methylcyclohexane and water as products.
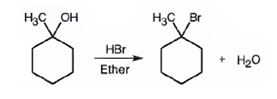
The product of the reaction shown is
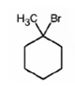
b)
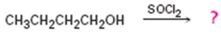
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction shown is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Alcohols when treated with SOCl2 yield the corresponding alkyl chlorides along with SO2 and HCl.
To predict:
The product of the reaction in which 1-butanol reacts with SOCl2 .
Answer to Problem 26AP
The product of the reaction in which 1-butanol reacts with SOCl2 is 1-chlorobutane.
Explanation of Solution
When 1-butanol reacts with SOCl2, the OH group in is replaced by chlorine to yield 1-chlorobutane. SO2 and HCl are obtained as other products.
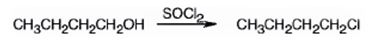
The product of the reaction in which 1-butanol reacts with SOCl2 is 1-chlorobutane.
c)
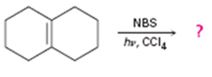
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction shown is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Cycloalkenes on treatment with NBS in CCl4 in the presence of light undergo bromination at the allyl position.
To predict:
The product of the reaction shown.
Answer to Problem 26AP
The products of the reaction shown are
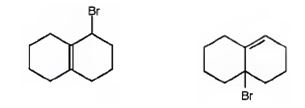
Explanation of Solution
NBS is normally used for allylic bromination. The reaction occurs through a radical mechanism. The radical produced by the homolytic cleavage of the C-H bond in the allyl position gets delocalized with the π electrons of the double bond to yield another radical with an odd electron at the junction of the rings. The attack of bromine radical hence leads to two different products as shown.
The products of the reaction shown are

d)
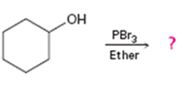
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction shown is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Alcohols give the corresponding bromides as products on treatment with PBr3 in ether solution.
To predict:
The product of the reaction in which cyclohexanol reacts with PBr3.
Answer to Problem 26AP
The product of the reaction in which cyclohexanol reacts with PBr3is
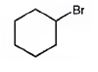
Explanation of Solution
When cyclohexanol is treated with PBr3, the OH group in it is replaced by the bromine to yield bromocyclohexane.
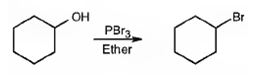
The product of the reaction in which cyclohexanol reacts with PBr3 is

e)
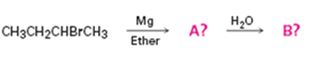
Interpretation:
The products of the reactions shown are to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Alkyl bromides react with Mg in ether to give Grignard reagents. Grignard reagents when treated with water yield the corresponding
To predict:
The products of the reaction shown.
Answer to Problem 26AP
The products of the reaction shown are sec-butyl magnesium bromide (A) and n-butane (B).
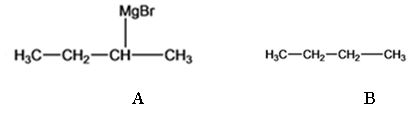
Explanation of Solution
sec-butyl bromide when reacted with Mg in ether yields sec-butyl magnesium bromide, a Grignard reagent. The sec-butyl magnesium bromide reacts with water to yield n-butane.
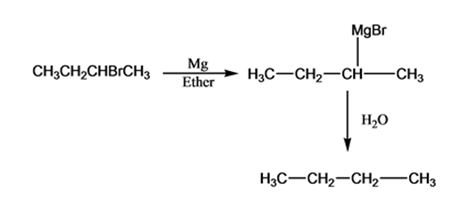
The products of the reaction shown are sec-butyl magnesium bromide (A) and n-butane (B).
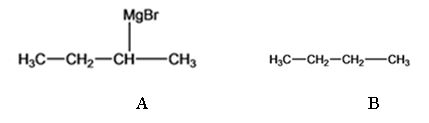
f)
Interpretation:
The products of the reaction shown are to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
To predict:
The product of the reaction shown.
Answer to Problem 26AP
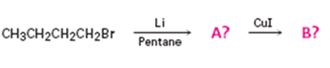
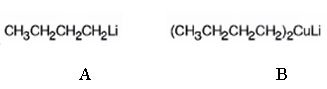
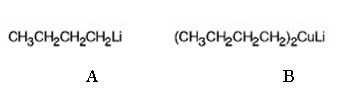
The products of the reaction shown are N-butyllithium (A) and Lithium n-dibutyl copper (B).
Explanation of Solution
n-Butyl bromide reacts with Li to yield n-butyl lithium and lithium bromide. The n-butyl lithium produced when reacted with CuI yields Lithium n-dibutyl copper as the product.
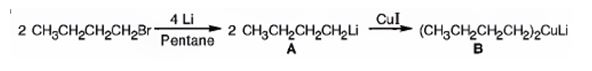
The products of the reaction shown are N-butyllithium (A) and Lithium n-dibutyl
g)
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction shown is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
When alkyl halides are treated with lithium dimethyl copper, the halogens are displaced by an alkyl group and a higher alkane is produced as the product.
To predict:
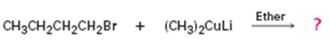
The product of the reaction in which n-butyl bromide reacts with lithium dimethylcopper.
Answer to Problem 26AP
The product of the reaction in which n-butyl bromide reacts with lithium dimethylcopper is n-pentane.
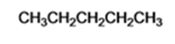
Explanation of Solution
When n-butyl bromide is treated with lithium dimethylcopper, the bromine is replaced by a methyl group to yield n-pentane as the product.
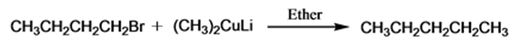
The product of the reaction in which n-butyl bromide reacts with lithium dimethylcopper is n-pentane.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
OWLv2 with Student Solutions Manual eBook, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card for McMurry's Organic Chemistry, 9th
- Please sirrr soollveee these parts pleaseeee and thank youuuuuarrow_forward4. Read paragraph 4.15 from your textbook, use your calculated lattice energy values for CuO, CuCO3 and Cu(OH)2 an explain thermal decomposition reaction of malachite: Cu2CO3(OH)2 →2CuO + H2O + CO2 (3 points)arrow_forwardPlease sirrr soollveee these parts pleaseeee and thank youuuuuarrow_forward
- III O Organic Chemistry Using wedges and dashes in skeletal structures Draw a skeletal ("line") structure for each of the molecules below. Be sure your structures show the important difference between the molecules. key O O O O O CHON Cl jiii iiiiiiii You can drag the slider to rotate the molecules. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Q Search X G ©2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use F 3 W C 3/5arrow_forward3. Use Kapustinskii's equation and data from Table 4.10 in your textbook to calculate lattice energies of Cu(OH)2 and CuCO3 (4 points)arrow_forward2. Copper (II) oxide crystalizes in monoclinic unit cell (included below; blue spheres 2+ represent Cu²+, red - O²-). Use Kapustinski's equation (4.5) to calculate lattice energy for CuO. You will need some data from Resource section of your textbook (p.901). (4 points) CuOarrow_forward
- What is the IUPAC name of the following compound? OH (2S, 4R)-4-chloropentan-2-ol O (2R, 4R)-4-chloropentan-2-ol O (2R, 4S)-4-chloropentan-2-ol O(2S, 4S)-4-chloropentan-2-olarrow_forwardIn the answer box, type the number of maximum stereoisomers possible for the following compound. A H H COH OH = H C Br H.C OH CHarrow_forwardSelect the major product of the following reaction. Br Br₂, light D Br Br Br Brarrow_forward
- Select all molecules which are chiral. Brarrow_forwardUse the reaction coordinate diagram to answer the below questions. Type your answers into the answer box for each question. (Watch your spelling) Energy A B C D Reaction coordinate E A) Is the reaction step going from D to F endothermic or exothermic? A F G B) Does point D represent a reactant, product, intermediate or transition state? A/ C) Which step (step 1 or step 2) is the rate determining step? Aarrow_forward1. Using radii from Resource section 1 (p.901) and Born-Lande equation, calculate the lattice energy for PbS, which crystallizes in the NaCl structure. Then, use the Born-Haber cycle to obtain the value of lattice energy for PbS. You will need the following data following data: AH Pb(g) = 196 kJ/mol; AHƒ PbS = −98 kJ/mol; electron affinities for S(g)→S¯(g) is -201 kJ/mol; S¯(g) (g) is 640kJ/mol. Ionization energies for Pb are listed in Resource section 2, p.903. Remember that enthalpies of formation are calculated beginning with the elements in their standard states (S8 for sulfur). The formation of S2, AHF: S2 (g) = 535 kJ/mol. Compare the two values, and explain the difference. (8 points)arrow_forward
