
a)
The ratio of mass flow rate of air to mass flow rate of steam in the combined power cycle
a)
Answer to Problem 80P
The ratio of mass flow rate of air to mass flow rate of steam in the combined power cycle is
Explanation of Solution
Draw the T-s diagram for the combined gas-steam power cycle as shown in Figure (1).
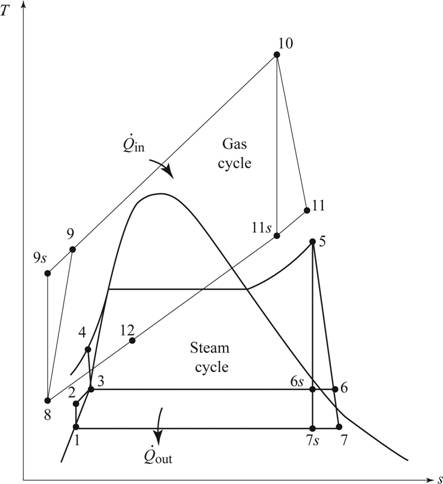
Write the expression for the relation relative pressure and ideal pressure.
Here, the relative pressure at state 9 is
Write the expression for the efficiency of compressor.
Refer to properties table of air, and interpret the value of
Write the expression for the relation relative pressure and ideal pressure.
Here, the relative pressure at state 11 is
Write the expression for the efficiency of turbine.
Write the expression for the specific work input of pump I to the system/
Write the expression for the enthalpy of steam at state 2.
Write the expression for the specific work input of pump II to the system/
Write the expression for the enthalpy of steam at state 4.
Write the expression for the quality of steam at state 6s.
Here, specific entropy of wet steam at 0.6 MPa is
Write the expression for the specific enthalpy of steam at state 6s.
Here, specific enthalpy of wet steam at
Write the expression for the efficiency of turbine.
Write the expression for the quality of steam at state 7s.
Here, specific entropy of wet steam at 20 kPa is
Write the expression for the specific enthalpy of steam at state 7s.
Here, specific enthalpy of wet steam at
Write the expression for the efficiency of turbine.
Write the expression for the energy balance equation for the heat exchanger.
Rewrite Equation (1) and rearrange the terms with mass and enthalpy terms.
Here, mass flow rate of steam is
Conclusion:
From the Table A-17, “Ideal-gas properties of air ”, select the relative pressure
Substitute 1.386 kPa for
From the Table A-17, “Ideal-gas properties of air ”, interpret the value of the the enthalpy
Substitute 0.82 for
From the Table A-17, “Ideal-gas properties of air ”, select the relative pressure
Substitute 450.5 kPa for
From the Table A-17 “Ideal-gas properties of air , interpret the value of
Substitute 0.86 for
From the Table A-5, “saturated water-Pressure table”, select the enthalpy
Substitute
Substitute
From the Table A-5, “saturated water-Pressure table”, select the enthalpy
Substitute
Substitute
From the Table A-5, “Superheated water”, select the enthalpy
Since, the entropy at state 5 is equal to state 6s, so the entropy value of
Interpret the value of
Substitute
Refer to steam tables, and interpret the value of
Substitute
Substitute 0.86 for
Since, the entropy at state 5 is equal to the entropy at state 7, the entropy value of
Refer to steam tables A-5 “saturated water-Pressure table”, obtain the value of
Substitute
Refer to steam tables A-5 “saturated water-Pressure table”, obtain the value of
Substitute
Substitute 0.86 for
Refer to steam tables A-17 “Ideal gas properties of air”, obtain the value of
Substitute
Thus, the ratio of mass flow rate of air to mass flow rate of steam in the combined power cycle is
b)
The rate of heat input in the combustion chamber.
b)
Answer to Problem 80P
The rate of heat input in the combustion chamber is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the energy balance equation for the open feed water heater.
Rewrite Equation (3) and rearrange the terms with mass and enthalpy terms.
Here, fraction of steam extracted is y.
Write the expression for the specific power output of the turbine.
Write the expression for the specific net work output from the steam.
Write the expression for the specific net work output from the gas stream.
Write the expression for the net work output per unit mass of gas.
Write the expression for the mass flow rate of air.
Write the expression for the rate of heat input to the cycle.
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute 0.86 for
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the rate of heat input in the combustion chamber is
c)
The thermal efficiency of the combined power cycle
c)
Answer to Problem 80P
The thermal efficiency of the combined power cycle is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the thermal efficiency of the combined power cycle.
Conclusion:
Substitute
Thus, the thermal efficiency of the combined power cycle is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
EBK THERMODYNAMICS: AN ENGINEERING APPR
- My ID# 016948724 last 2 ID# 24 Last 3 ID# 724 Please help to find the correct answer for this problem using my ID# first write le line of action and then help me to find the forces {fx= , fy= mz=arrow_forwardmy ID is 016948724 Last 2 ID# 24 Last 3 ID# 724 please help me to solve this problem step by step show me how to solve first wirte the line actions and then find the forces {fx=, fy=, mz= and for the last step find the support reactions and find forcesarrow_forwardUppgift 1 (9p) 3 m 3 m 3 m 3 m H G F 3 m ↑ Dy D B AAY 30° 8 kN Ay Fackverket i figuren ovan är belastat med en punktlast. Bestäm normalkraften i stängerna BC, BG och FG.arrow_forward
- The cardiovascular countercurrent heat exchnager mechanism is to warm venous blood from 28 degrees C to 35 degrees C at a mass flow rate of 2 g/s. The artery inflow temp is 37 degrees C at a mass flow rate of 5 g/s. The average diameter of the vein is 5 cm and the overall heat transfer coefficient is 125 W/m^2*K. Determine the overall blood vessel length needed too warm the venous blood to 35 degrees C if the specific heat of both arterial and venous blood is constant and equal to 3475 J/kg*K.arrow_forwardThe forces Qy=12 kNQy=12kN and Qz=16 kNQz=16kN act on the profile at the shear center C. Calculate: a) Shear flow at point B (2 points)b) Shear stress at point D (3 points)arrow_forwardConsider the feedback controlled blending system shown below, which is designed to keep theoutlet concentration constant despite potential variations in the stream 1 composition. The density of all streamsis 920 kg/m3. At the nominal steady state, the flow rates of streams 1 and 2 are 950 and 425 kg/min,respectively, the liquid level in the tank is 1.3 m, the incoming mass fractions are x1 = 0.27, x2 = 0.54. Noticethe overflow line, indicating that the liquid level remains constant (i.e. any change in total inlet flow ratetranslates immediately to the same change in the outlet flow rate). You may assume the stream 1 flowrate andthe stream 2 composition are both constant. Use minutes as the time unit throughout this problem. d) Derive the first order process and disturbance transfer functions;Gp= Kp/(tou*s+1) and Gd=Kd/(tou*s+1) and calculate and list the values and units of the parameters. e) Using the given information, write the general forms of Gm, GIP, and Gv below(in terms of…arrow_forward
- a) Briefly explain what ratio control is. Give an example of a common chemical engineering situation in whichratio control would be useful and for that example state exactly how ratio control works (what would bemeasured, what is set, and how the controller logic works).b) Briefly explain what cascade control is. Give an example of a common chemical engineering situation inwhich cascade control would be useful and for that example state exactly how cascade control works (whatwould be measured, what is set, and how the controller logic works).arrow_forwardDetermine the reaction force acting on the beam AB, given F = 680 N. 5 4 4 m 3 3 A B 30° 3 m F (N)arrow_forwardThe frame in the figure is made of an HEA 300 profile (E = 210 GPa, material S355).a) Determine the support reactions at point A. (1p)b) Sketch the bending moment diagram caused by the loading. (1p)c) Using the principle of virtual work (unit load method), calculate the vertical displacement at point B using moment diagrams. Also take into account the compression of the column. (3p)arrow_forward
- 9 kN/m 6 kN/m 3 m 6 m Bestäm, med hjälp av friläggning och jämviktsberäkningar, tvärkrafts- och momentdiagram för balken i figuren. Extrempunkter ska anges med både läge och värde.arrow_forwardB C 3.0 E F G 40 kN [m] 3.0 3.0 3.0 Fackverket belastas med en punktlast i G enligt figuren. Bestäm normalkraften i stängerna BC, BF och EF.arrow_forwardL q=8 kN/m P= 12 kN En stång belastas av en punklast P vid sin ena ände samt av en jämnt utbredd last q längs hela sin längd. Stången har en tvärsnittsarea A = 150 mm² och är tillverkad av stål med elasticitetsmodul E-210 GPa. Stångens längd, i sitt obelastade tillstånd, är Z-3 m. a) Hur stor är den största normalspänning som uppstår i stången? b) Hur stor blir förlängningen av stången, orsakad av lasterna P och q?arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





