
To perform each hypothesis test and to complete the following steps:
(a). To state the null and alternative hypotheses.
(b). To determine which distribution to use for the test statistic and to state the level of significance.
(c). To calculate the test statistic.
(d). To draw a conclusion and by comparing the
Answer to Problem 7E
Solution:
(a). The null and alternative hypotheses.
(b). The distribution to use for the test statistic and the level of significance.
Level of significance
(c). The test statistic.
(d). Conclusion and by comparing the
We fail to reject the null hypothesis.
This means that at the
Explanation of Solution
Approach:
The null hypotheses is
Conditions to meet for using normal distribution to perform a hypothesis test for the population proportion:
All possible samples of a given size have an equal probability of being chosen; that is, a simple random sample is used.
The conditions for a binomial distribution are met.
The
Level of significance
Sample proportion.
The test statistic is given by the
Decision.
| Fail to reject the null hypothesis. | |
| Reject the null hypothesis. |
Calculation:
Given,
Type of sample: simple random sample
Number of drivers surveyed
Number of drivers suffer from sleep apnea
Percentage of Americans suffer from sleep apnea is 5.8%.
Safety commission’s claim: Percentage of Americans suffer from sleep apnea is not 5.8%
Level of significance
| Claim | Population proportion |
| Number of trails (sample size) | |
| Probability of success that the claim referencing | |
| Level of significance |
Step (a):
Null and alterative hypothesis:
The safety commission’s claim is that the percentage of Americans suffer from sleep apnea is not 5.8%
Mathematically we can write
The logical opposite of this claim is
Thus the null and alterative hypothesis are stated as follows.
Step (b):
Distribution to use for the test statistic and level of significance:
We are testing a population proportion, se we must check the necessary conditions to use the normal distribution and the
Test for normal distribution:
Let us check that whether the sample size is large enough to ensure that
Calculate:
Thus,
Calculate:
Also
Since, all the conditions are satisfied, we can use the normal distribution and the
Level of significance
Step (c):
Test static
First let us compute the value of sample proportion.
In the sample data
Thus,
Now; substitute the values
Step (d):
Draw a conclusion and to interpret the decision by comparing the p-value to the level of significance:
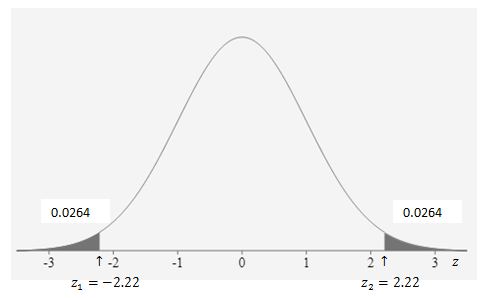
The alternative hypothesis tells us that we are conducting a two tailed test.
Thus, the p- value for this test statistic is the probability of obtaining a test statistic is either less than or equal to
To find the p-value, we need to find the area under the standard normal curve to the left of

Hence, the area under the normal distribution curve the normal distribution curve to the left of
Thus the total area is the twice the area of the left tail.
p-value
Compare the p-value to the level significance.
(i.e.)
Thus, we fail to reject the null hypothesis.
This means that at the
Final statement:
Therefore,
(a). The null and alternative hypotheses.
(b). The distribution to use for the test statistic and the level of significance.
Normal distribution and the
Level of significance
(c). The test statistic.
(d). Conclusion and by comparing the

We fail to reject the null hypothesis.
This means that at the
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Beginning Statistics, 2nd Edition
- A marketing agency wants to determine whether different advertising platforms generate significantly different levels of customer engagement. The agency measures the average number of daily clicks on ads for three platforms: Social Media, Search Engines, and Email Campaigns. The agency collects data on daily clicks for each platform over a 10-day period and wants to test whether there is a statistically significant difference in the mean number of daily clicks among these platforms. Conduct ANOVA test. You can provide your answer by inserting a text box and the answer must include: also please provide a step by on getting the answers in excel Null hypothesis, Alternative hypothesis, Show answer (output table/summary table), and Conclusion based on the P value.arrow_forwardA company found that the daily sales revenue of its flagship product follows a normal distribution with a mean of $4500 and a standard deviation of $450. The company defines a "high-sales day" that is, any day with sales exceeding $4800. please provide a step by step on how to get the answers Q: What percentage of days can the company expect to have "high-sales days" or sales greater than $4800? Q: What is the sales revenue threshold for the bottom 10% of days? (please note that 10% refers to the probability/area under bell curve towards the lower tail of bell curve) Provide answers in the yellow cellsarrow_forwardBusiness Discussarrow_forward
- The following data represent total ventilation measured in liters of air per minute per square meter of body area for two independent (and randomly chosen) samples. Analyze these data using the appropriate non-parametric hypothesis testarrow_forwardeach column represents before & after measurements on the same individual. Analyze with the appropriate non-parametric hypothesis test for a paired design.arrow_forwardShould you be confident in applying your regression equation to estimate the heart rate of a python at 35°C? Why or why not?arrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





