
a)
To plot: The point with the given rectangular coordinates and find the two sets of corresponding polar coordinates.
a)
Answer to Problem 3E
The rectangular coordinates are shown in Figure (1) and the two sets of corresponding polar coordinates are
Explanation of Solution
Given information: A rectangular coordinate is given as
Formula used:
Let the point P have polar coordinates
The other polar coordinates of P can be calculated as
Calculation:
Plot
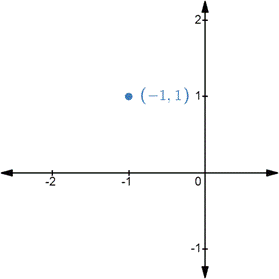
Figure (1)
Find the value of
Find the value of
Thus, the corresponding polar coordinate is
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the two sets of corresponding polar coordinates are
b)
To plot: The point with the given rectangular coordinates and find the two sets of corresponding polar coordinates.
b)
Answer to Problem 3E
The rectangular coordinates are shown in Figure (2) and the two sets of corresponding polar coordinates are
Explanation of Solution
Given information: A rectangular coordinate is given as
Formula used:
Let the point P have polar coordinates
The other polar coordinates of P can be calculated as
Calculation:
Plot
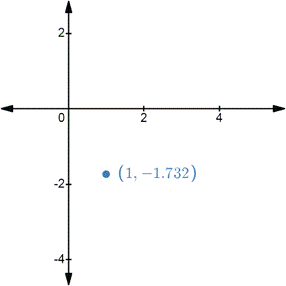
Figure (2)
Find the value of
Find the value of
Thus, the corresponding polar coordinate is
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the two sets of corresponding polar coordinates are
c)
To plot: The point with the given rectangular coordinates and find the two sets of corresponding polar coordinates.
c)
Answer to Problem 3E
The rectangular coordinates are shown in Figure (3) and the two sets of corresponding polar coordinates are
Explanation of Solution
Given information: A rectangular coordinate is given as
Formula used:
Let the point P have polar coordinates
The other polar coordinates of P can be calculated as
Calculation:
Plot
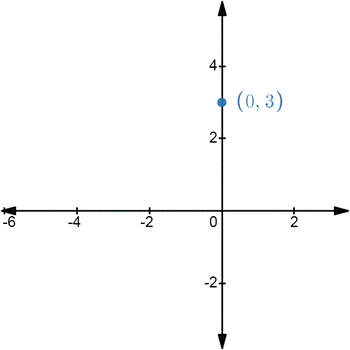
Figure (3)
Find the value of
Find the value of
Thus, the corresponding polar coordinate is
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the two sets of corresponding polar coordinates are
d)
To plot: The point with the given rectangular coordinates and find the two sets of corresponding polar coordinates.
d)
Answer to Problem 3E
The rectangular coordinates are shown in Figure (4) and the two sets of corresponding polar coordinates are
Explanation of Solution
Given information: A rectangular coordinate is given as
Formula used: Let the point P have polar coordinates
The other polar coordinates of P can be calculated as
Calculation:
Plot
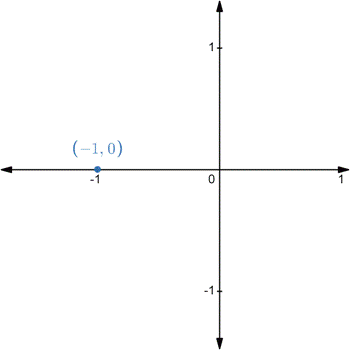
Find the value of
Find the value of
Thus, the corresponding polar coordinate is
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the two sets of corresponding polar coordinates are
Chapter 10 Solutions
Advanced Placement Calculus Graphical Numerical Algebraic Sixth Edition High School Binding Copyright 2020
- A tank initially contains 50 gal of pure water. Brine containing 3 lb of salt per gallon enters the tank at 2 gal/min, and the (perfectly mixed) solution leaves the tank at 3 gal/min. Thus, the tank is empty after exactly 50 min. (a) Find the amount of salt in the tank after t minutes. (b) What is the maximum amount of salt ever in the tank?arrow_forwardpleasd dont use chat gptarrow_forwardBy using the numbers -5;-3,-0,1;6 and 8 once, find 30arrow_forward
- Show that the Laplace equation in Cartesian coordinates: J²u J²u + = 0 მx2 Jy2 can be reduced to the following form in cylindrical polar coordinates: 湯( ди 1 8²u + Or 7,2 მ)2 = 0.arrow_forwardFind integrating factorarrow_forwardDraw the vertical and horizontal asymptotes. Then plot the intercepts (if any), and plot at least one point on each side of each vertical asymptote.arrow_forward
- Draw the asymptotes (if there are any). Then plot two points on each piece of the graph.arrow_forwardCancel Done RESET Suppose that R(x) is a polynomial of degree 7 whose coefficients are real numbers. Also, suppose that R(x) has the following zeros. -1-4i, -3i, 5+i Answer the following. (a) Find another zero of R(x). ☐ | | | | |│ | | | -1 བ ¢ Live Adjust Filters Croparrow_forwardSuppose that R (x) is a polynomial of degree 7 whose coefficients are real numbers. Also, suppose that R (x) has the following zeros. -1-4i, -3i, 5+i Answer the following. (c) What is the maximum number of nonreal zeros that R (x) can have? ☐arrow_forward
- Suppose that R (x) is a polynomial of degree 7 whose coefficients are real numbers. Also, suppose that R (x) has the following zeros. -1-4i, -3i, 5+i Answer the following. (b) What is the maximum number of real zeros that R (x) can have? ☐arrow_forwardi need help please dont use chat gptarrow_forward3.1 Limits 1. If lim f(x)=-6 and lim f(x)=5, then lim f(x). Explain your choice. x+3° x+3* x+3 (a) Is 5 (c) Does not exist (b) is 6 (d) is infinitearrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





