
Concept explainers
(a)
Describe the location of points farther from both R and S than from T.
(a)
Answer to Problem 17WE
Interior of
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Point P is equidistant from R , S , and T.
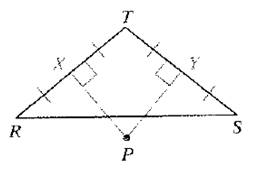
Calculation:
P is equidistant from R, S , and T .
So , any point inside the angle XPY will be closer to T than from R and S , as clearly they are closer to T and at P , all are equidistant from all three points R, S , and T.
(b)
Describe the location of points closer to both R and S than to T.
(b)
Answer to Problem 17WE
Vertically Opposite angle of angle XPY.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
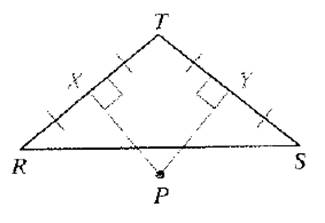
Point P is equidistant from R , S , and T.
Calculation:
P is equidistant from R, S , and T .
So , any point inside the angle XPY will be closer to T than from R and S , as clearly they are closer to T and at P , all are equidistant from all three points R, S , and T.
Hence , any point that will be in the angle opposite to XPY will be farther to T than from R and S , as P is equidistant from all the three points R, S , and T.
Chapter 10 Solutions
McDougal Littell Jurgensen Geometry: Student Edition Geometry
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
Pre-Algebra Student Edition
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
Elementary Statistics
 Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage, Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning
Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning

