
Before you solve Problems 5–14, first classify the problem as one of the following:
Chi-square test of independence or homogeneity
Chi-square goodness of fit
Chi-square for testing or estimating σ2 or σ
F test for two variances
One-way ANOVA
Two-way ANOVA
Then, in each of the problems when a test is to be performed, do the following:
- (i) Give the value of the level of significance. State the null and alternate hypotheses.
- (ii) Find the sample test statistic.
- (iii) Find or estimate the P-value of the sample test statistic.
- (iv) Conclude the test.
- (v) Interpret the conclusion in the context of the application.
- (vi) In the case of one-way ANOVA, make a summary table.
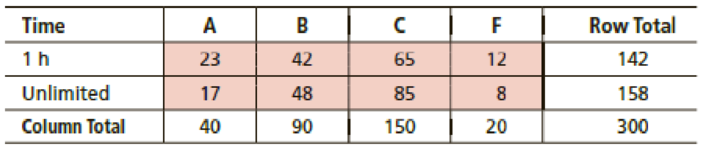
Education: Exams Professor Fair believes that extra time does not improve grades on exams. He randomly divided a group of 300 students into two groups and gave them all the same test. One group had exactly 1 hour in which to finish the test, and the other group could stay as long as desired. The results are shown in the following table. Test at the 0.01 level of significance that time to complete a test and test results are independent.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 10 Solutions
Bundle: Understandable Statistics, Loose-leaf Version, 12th + WebAssign Printed Access Card for Brase/Brase's Understandable Statistics: Concepts and Methods, 12th Edition, Single-Term
- A manager believes that the variance of output on the second shift is greater than the variance on the day shift. The following data are collected: 50 samples on the day shift; variance = 500 40 samples on the second shift; variance = 900 Set up hypotheses Perform a test and state your conclusions.arrow_forwardThe range and the variance are both measures of distance.arrow_forwardThe next seven questions refer to the following scenario: A random sample of 16 Porsche drivers yielded an average age of 50 years with a variance of 9 years and a random sample of also 16 Ferrari drivers yielded an average of 47 years with a variance of 25 years. Porsche Driver Ferrari Driver n 16 16 mean 50 47 Variance 25 Conduct the following hypothesis test at a=0.05. HO: Mean Age Porsche Drivers Mean Age Ferrari Drivers Assume unequal variance.arrow_forward
- Please help me with this question.arrow_forwardSuppose the variance of X is 14. What is the variance of .47X?arrow_forwardThe next test is a t-test for unequal variance. Here is the problem: The human resources department at Sue, Grabitt, and Runne also tracks the cost of one-bedroom apartments in two popular neighborhoods, NoBo and SoBo. The general perception of long-time residents is that rents are probably lower in SoBo. They hope to determine whether the average rent for a one-bedroom apartment is lower in SoBo than in NoBo. The results of their survey are shown in Tables 18 and 19: Step 2. Select the Level of Significance, α A 5 percent significance has been selected. Step 3. State the Null Hypothesis (H0) and Alternate Hypothesis (H1) H0: H1: Step 4. Compose the Decision Rule Step 5. Calculate the Value of the Test Statistic, p-value, and estimate statistical power Use G*Power to calculate statistical powerarrow_forward
- The variance of a population is 6. the size of the sample collected from a population is 228 What is the standard error of the meanarrow_forwardThe Tukey-Kramer procedure is used for which of the following purposes?A. Test for differences in pairwise means.B. Test for normality of residuals.C. Test for independence of errors.D. Test for homogeneity of variances.arrow_forward
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
