
Concept explainers
Prepare comparative income statement and comparative schedule of cost of goods sold for each month under (1) absorption costing method and (2) variable costing method.
Explanation of Solution
Absorption costing: It refers to the method of product costing in which the price of the product is calculated considering all fixed as well as the variable or direct costs. The
Variable costing: It refers to the method of product costing in which the price of the product is calculated considering only the variable or direct costs or the cost that happened to occurred due to the product only. It also called as marginal costing as it takes marginal costs while calculating the product cost.
Prepare comparative income statement and comparative schedule of cost of goods sold for each month under (1) absorption costing method and (2) variable costing method as follows:
Comparative schedule of cost of goods sold for each month:
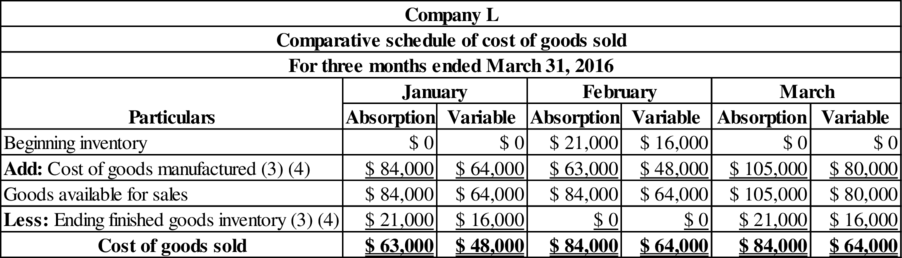
Table (1)
Comparative income statement for each month:
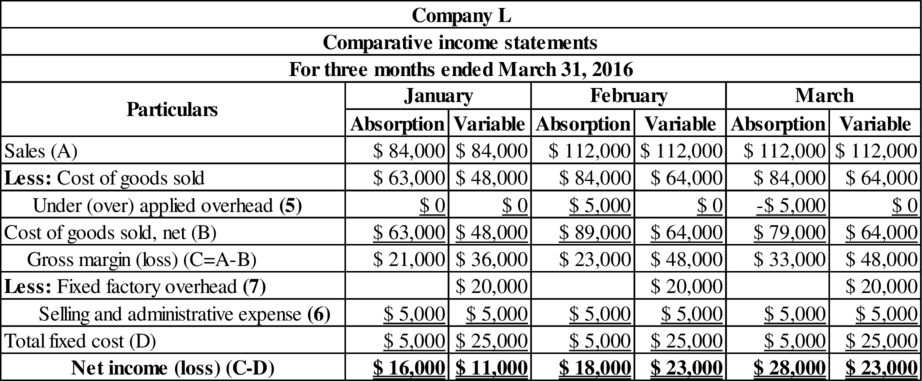
Table (2)
Working note (1):
Calculate the absorption costing per unit.
Working note (2):
Calculate the ending inventory units for each month.
| Particulars | January | February | March |
| Beginning inventory | 0 | 1,000 | 0 |
| Add: Number of units produced | 4,000 | 3,000 | 5,000 |
| Less: Number of units sold | 3,000 | 4,000 | 4,000 |
| Ending inventory | 1,000 | 0 | 1,000 |
Table (3)
Working note (3):
Calculate the cost of goods sold and ending inventory under absorption costing for each month.
| Particulars | January | February | March |
| Number of units produced (A) | 4,000 | 3,000 | 5,000 |
| Absorption cost per unit (B) (1) | $ 21 | $ 21 | $ 21 |
| Cost of goods manufactured | $ 84,000 | $ 63,000 | $ 105,000 |
| Ending inventories units (C) (2) | 1,000 | 0 | 1,000 |
| Absorption cost per unit (D) | $ 21 | $ 21 | $ 21 |
| Ending inventory | $ 21,000 | $ 0 | $ 21,000 |
| Beginning inventory units (E) (2) | 0 | 1,000 | 0 |
| Absorption cost per unit (F) | $ 21 | $ 21 | $ 21 |
| Beginning inventory | $ 0 | $ 21,000 | $ 0 |
Table (4)
Working note (4):
Calculate the cost of goods sold and ending inventory under variable costing for each month.
| Particulars | January | February | March |
| Number of units produced (A) | 4,000 | 3,000 | 5,000 |
| Variable cost per unit (B) | $ 16 | $ 16 | $ 16 |
| Cost of goods manufactured | $ 64,000 | $ 48,000 | $ 80,000 |
| Ending inventories units (C) (2) | 1,000 | 0 | 1,000 |
| Variable cost per unit (D) | $ 16 | $ 16 | $ 16 |
| Ending inventory | $ 16,000 | $ 0 | $ 16,000 |
| Beginning inventory units (E) (2) | 0 | 1,000 | 0 |
| Variable cost per unit (F) | $ 16 | $ 16 | $ 16 |
| Beginning inventory | $ 0 | $ 16,000 | $ 0 |
Table (5)
Working note (5):
Calculate the under or over applied fixed overhead.
January:
February:
March:
Working note (6):
Calculate the fixed selling and administrative expense per month.
Working note (7):
Calculate the fixed factory overhead per month.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Principles of Cost Accounting
- Provide solutionarrow_forwardI need help with this financial accounting question using accurate methods and procedures.arrow_forwardStarlight Medical Equipment maintains inventory cards. Item #456 shows: beginning 210 units, received 320 units, issued 390 units. Physical count reveals 125 units. Determine the missing units. Need answerarrow_forward
- Reva Systems budgeted sales at 30,000 units at $80 per unit. The actual sales were 29,000 units at $83 per unit. What was Reva Systems' sales price variance?arrow_forwardViler business purchased a 6-month, 8% note receivable for $50,000 on March 1. What is the amount of interest income that should be recorded on June 30?arrow_forwardStarlight Medical Equipment maintains inventory cards. Item #456 shows: beginning 210 units, received 320 units, issued 390 units. Physical count reveals 125 units. Determine the missing units.arrow_forward
 Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub- Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,





