
a.
The
a.
Answer to Problem 30P
Option 1
Calculation of income statement of Company CM is as follows:
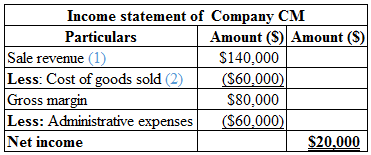
Table (1)
Hence, the net income of Company CM is $20,000.
Calculation of balance sheet of Company CM is as follows:
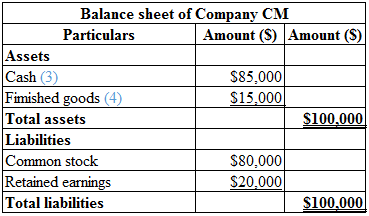
Table (2)
Option 2
Calculation of income statement of Company CM is as follows:
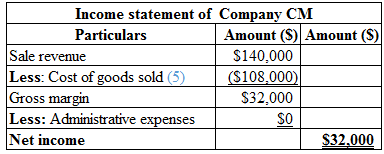
Table (3)
Hence, the net income of Company CM is $32,000.
Calculation of balance sheet of Company CM is as follows:
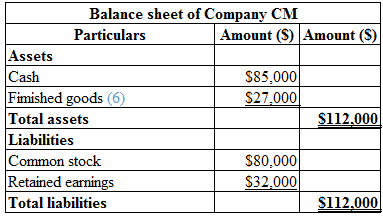
Table (4)
Explanation of Solution
Income statement:
It is the financial statement of a company that shows all the incomes earned and expenditures incurred by the company for a particular period of time.
Balance sheet:
Balance sheet is one of the financial statements that summarizes the assets, the liabilities, and the shareholder’s equity of a company at a given date. It is also known as the statement of financial status of the business.
Working notes:
Calculate the sale revenue:
Hence, the sales revenue is $140,000.
(1)
Calculate the cost per unit:
Hence, the cost per unit is $15.
Calculate the cost of goods sold:
Hence, the cost of goods sold is $60,000.
(2)
Calculate the total cash:
Hence, the total cash is $85,000.
(3)
Calculate the total finished goods:
Hence, the finished goods is $15,000.
(4)
Calculate the cost per unit:
Hence, the cost per unit is $27.
Calculate the cost of goods sold:
Hence, the cost of goods sold is $108,000.
(5)
Calculate the total finished goods:
Hence, the finished goods is $27,000.
(6)
b.
The option in the financial statement that gives a favourable image to the creditors and investors.
b.
Answer to Problem 30P
Option 2 is the financial statement that gives a favorable impression to creditors and investors with a greater net income of $12,000 than option 1’s net income.
Explanation of Solution
Income statement:
Income statement is the financial statement of a company that shows all the incomes gained and expenditures incurred by the company for a time period.
Balance sheet:
Balance sheet is one of the financial statements that summarizes the assets, the liabilities, and the shareholder’s equity of a company at a given date. It is also known as the statement of financial status of the business.
The option that gives the favorable image to the creditors and investors is as follows:
Option 2 provides the financial statement that gives a favorable image to the creditors and investors because the net income in option 2 is greater than the net income in option 1.
c.
The amount of bonus under each option and recognize the option that provides a higher bonus.
c.
Answer to Problem 30P
Option 2 provides the president with a higher bonus of $6,400.
Explanation of Solution
Income statement:
Income statement is the financial statement of a company that shows all the revenues earned and expenses incurred by the company over a period of time.
Balance sheet:
Balance sheet is one of the financial statements that summarizes the assets, the liabilities, and the shareholder’s equity of a company at a given date. It is also known as the statement of financial status of the business.
Calculation of bonus under option 1 is as follows:
Hence, the bonus received by the president under option 1 is $4,000.
Calculation of bonus under option 2 is as follows:
Hence, the bonus received by the president under option 2 is $6,400.
d.
The amount of tax rate under each option and recognize which option pays less tax.
d.
Answer to Problem 30P
Option 1 minimizes the cost of income tax expenses for the company by $6,000.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of income tax under option 1 is as follows:
Hence, the income tax expenses under option 1 is $6,000.
Calculation of income tax under option 2 is as follows:
Hence, the bonus received by the president under option 2 is $9,600
e.
Comment on the conflict among the company’s president as determined in requirement c and the owner-based requirement d, and define an incentive compensation plan that will neglect the conflict.
e.
Explanation of Solution
The conflicts between the owner and the president are as follows:
Option 2 provides the president with a higher bonus of $6,400. Option 1 minimizes the cost of income tax expenses for the company by $6,000. These are the two conflicts between the owner and the president.
The reasons to avoid these conflicts are as follows:
- The bonus plans of the company can be tied up with the company’s stock price, instead of net income.
Market efficiency increases; as a result, the performance of the company increases, which creates a value to the company’s stock price.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Survey Of Accounting
- Can you please answer the financial accounting question?arrow_forwardidentify the key factors that contributed to the collapse of Northern Rock bank. Compile documents and analysis of regulations (magazine articles, newspapers, online sources, working papers from different organizations, activity summaries, results reports, legal regulations, speeches, public statements, press conferences, etc.). Apply, in a practical and theoretical way, what has been learned in class about the financial world, regulation and risk management.arrow_forwardGet accurate answer this general accounting questionarrow_forward
 Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning




