
a.
The total amount of upstream cost.
a.
Explanation of Solution
Upstream cost: This cost is incurred before starting the manufacturing process such as research and development, and product design.
The given information:
- Fashion design cost is $20,000.
- Research and development cost is $30,000.
The calculation of upstream cost is as follows:
Hence, the upstream cost is $50,000.
b.
The total amount of downstream cost.
b.
Explanation of Solution
Downstream: This cost is incurred after starting the manufacturing process such as marketing, distribution, and customer service
The given information:
- Advertisement cost is $25,000.
- Administrative cost is $45,000.
The calculation of downstream cost is as follows:
Hence, the downstream cost is $70,000.
c.
The total amount of midstream cost.
c.
Explanation of Solution
Mid-stream: It is a cost incurred in making a product. It includes direct labor, direct materials, and manufacturing
The given information:
- Direct materials are $15.
- Direct labor is $17
- Manufacturing overheads are $8.
- Total production is 4,000 units.
The calculation of midstream cost is as follows:
Hence, the midstream cost is $160,000.
d.
The total amount of sales price.
d.
Explanation of Solution
The given information:
- Direct materials are $15.
- Direct labor is $17
- Manufacturing overheads are $8.
- Total production is 4,000 units.
- 150% on GAPP defined product.
The calculation of sales price is as follows:
Hence, the sales price is $60.
e.
The income statement based on GAPP.
e.
Answer to Problem 25P
The calculation of income statement of Company D is as follows:
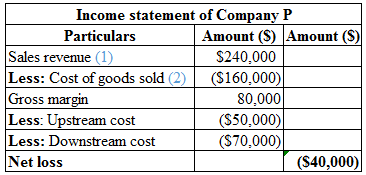
Hence, the company has a net loss of $40,000.
Explanation of Solution
Income statement:
Income statement is the financial statement of a company that shows all the revenues earned and expenses incurred by the company over a period of time.
The given information:
- Direct materials are $15.
- Direct labor is $17
- Manufacturing overheads are $8.
- Total production is 4,000 units.
- Fashion design cost is $20,000.
- Research and development cost is $30,000.
- Advertisement cost is $25,000.
- Administrative cost is $45,000.
The sales revenue is calculated as follows:
Hence, the sales revenue is $240,000.
(1)
The cost of goods sold is calculated as follows:
Hence, the cost of goods sold is $160,000.
(2)
f.
Explain the reason for the net loss.
f.
Explanation of Solution
The management failed to consider the cost of downstream and upstream while pricing the product. Only the cost of GAPP based prices were considered. The selling price of the product is $60 and the total cost price of the product is $70 (3). Therefore, the selling price is less than the cost per unit and this explains why the company is facing loss.
Working notes:
The total cost per unit is calculated as follows:
Hence, the total cost per unit is $70.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
SURVEY OF ACCOUNT.(LL)-W/ACCESS>CUSTOM<
- Regency Distributors wants an ending inventory each month equal to 20% of that month's cost of sales. Cost of sales for April is projected at $150,000. Ending inventory at the end of March was $25,000. Based on this information, purchases for April will be: a. $125,000 b. $130,000 c. $145,000 d. $155,000arrow_forwardHow much must it charge per unit if 4,000 units are sold?arrow_forwardPlease explain the solution to this general accounting problem with accurate explanations.arrow_forward
- The total manufacturing costs incurred for the year are $423,500. The overhead cost was 75% of the direct labor cost, and the direct material cost was $92,500. Direct labor cost was _____.arrow_forwardHow to calculate the gross profit based on the data given below for Salvatore company?arrow_forwardPlease provide the answer to this general accounting question using the right approach.arrow_forward
- Could you explain the steps for solving this financial accounting question accurately?arrow_forwardI need help with this financial accounting question using the proper financial approach.arrow_forwardThe total manufacturing costs incurred for the year are $423,500. The overhead cost was 75% of the direct labor cost, and the direct material cost was $92,500. Direct labor cost was _____. Helparrow_forward
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning



