
Antibiotic Overkill
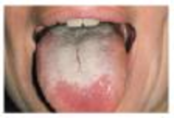
A young woman was taking antibiotic pills for a urinary infection. Several days into her course of medication, she began to experience peculiar symptoms. At first, they were hardly noticeable. Very quickly, however, they worsened and became embarrassing and unbearable.
She noticed a white coating on her tongue, bad breath, and an awful taste in her mouth. Despite persistent brushing and mouthwash applications, she was unable to completely remove the film. Furthermore, she had excessive vaginal discharges consisting of a cheeselike white substance. When she began to have vaginal itching, she finally decided it was time to seek help.
Reluctantly, she revisited her personal physician and described the symptoms. Her doctor explained the symptoms and provided additional prescriptions to alleviate her distress.
- 1. What happened to the young woman in this situation?
- 2. How had her body’s defenses been violated?
- 3. How can she avoid a repeat of this situation?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 10 Solutions
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
- P 200 150- 100 50 w/instrance/ w/insurance 2 100 Demand Assume that the white curve (labeled "Demand") represents an individual's true demand for this particular health care service. The coinsurance associated with insurance option 1 (in blue) is likely _. 0000 100% 25% 50% 0%arrow_forwardUse the figure below. Bob and Nancy have the same income and total utility.. willingness to pay for an insurance premium will be lower than because they are. risk- averse. Total utility Current utility Bob's utility Nancy's utility 0000 Bob; Nancy; less Nancy; Bob; less Nancy; Bob; more Bob; Nancy; more Current Income incomearrow_forwardConsider the figure below. Suppose the true price of a health care service is P1. Suppose further that the individual has obtained insurance that has a fixed copayment for this particular service. The copayment is represented by price P2. represents the quantity of the service the individual would consume without insurance. quantity of the service the individual would consume with the insurance. Health Care Service represents the P. P₂ a Q1;Q2 Q2; Q3 Q1; Q3 Q3; Q1 Q2; Q1 फ f Q ८ g d h Q3\D 7Q 00000arrow_forward
- The table shows the utility Jordan receives at various income levels, but they do not know what their income will be next year. There is a 15% chance their income will be $25,000, a 20% chance their income will be $35,000, and a 65% chance their income will be $45,000. We know that Jordan is Income $25,000 Utility 2,800 30,000 3,200 35,000 3,500 40,000 3,700 45,000 3,800 ☐ none of the above 0 000 risk taker (lover) because their marginal utility of income is increasing risk neutral because their marginal utility of income is constant risk averse because their marginal utility of income is decreasing risk neutral because their marginal utility of income is decreasingarrow_forwardOOOO a d+e d a+b+c Consider the figure below. Suppose the true price of a health care service is P1. Suppose further that the individual has obtained insurance that has a fixed copayment for this particular service. The copayment is represented by price P2. The social loss from moral hazard if the individual has copayment P2 is represented graphically by the area(s): Health Care Service P. a No 4 ८ e g Q2 Q3 Darrow_forwardOOO O The table shows the utility Jordan receives at various income levels, but they do not know what their income will be next year. There is a 15% chance their income will be $25,000, a 20% chance their income will be $35,000, and a 65% chance their income will be $45,000. We know that Jordan's expected income is. Their utility from their expected income is_ Income $25,000 Utility 2,800 30,000 3,200 35,000 3,500 40,000 3,700 45,000 3,800 $45,000; 3,800 $40,000; 3,700 $25,000; 2,800 $35,000; 3,500 $30,000; 3,200arrow_forward
- Question 1 Classify the Bird Mark 7; how is it: Powered Triggered Cycled Classify brid mark 7 Powered: By gas (oxygen) Triggered: Negative Pressure, caused by the patient’s inspiratory effort Cycled: The machine stops delivering gas and allows for exhalationarrow_forwardHypothetical "pedigree" for Sickle Cellarrow_forwardwould this be considered a novel protein and if not how can I fix it so it is and can you draw the corrections pleasearrow_forward
- In as much detail as possible, hand draw a schematic diagram of the hypothalamic-pituitary- gonad (HPG) axis in the human male. Be sure to include all the relevant structures and hormones. You must define all abbreviations the first time you use them. Please include (and explain) the feedback loops.arrow_forwardA negligence action was brought by a mother against a hospital on behalf of her minor daughter. It alleged that when the mother was 13 years of age, the hospital negligently transfused her with Rh-positive blood. The mother's Rh-negative blood was incompatible with and sensitized by the Rh-positive blood. The mother discovered her condition 8 years later during a routine blood screening ordered by her healthcare provider in the course of prenatal care. The resulting sensitization of the mother's blood allegedly caused damage to the fetus, resulting in physical defects and premature birth. Did a patient relationship with the transfusing hospital exist?arrow_forward18. Watch this short youtube video about SARS CoV-2 replication. SARS-CoV-2 Life Cycle (Summer 2020) - YouTube.19. What is the name of the receptor that SARS CoV-2 uses to enter cells? Which human cells express this receptor? 20. Name a few of the proteins that the SARS CoV-2 mRNA codes for. 21. What is the role of the golgi apparatus related to SARS CoV-2arrow_forward
- Essentials of Pharmacology for Health ProfessionsNursingISBN:9781305441620Author:WOODROWPublisher:CengageSurgical Tech For Surgical Tech Pos CareHealth & NutritionISBN:9781337648868Author:AssociationPublisher:Cengage
 Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning





