
Concept explainers
Using nodal analysis, find io(t) in the circuit in Fig. 10.60.
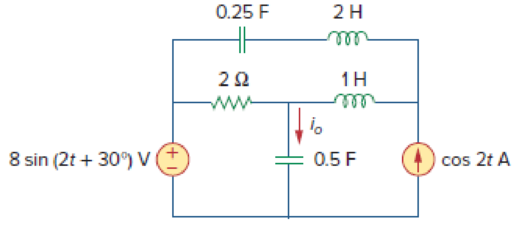
Figure 10.60
For Prob. 10.11.
Find the current
Answer to Problem 11P
The value of current
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Refer Figure 10.60 in the textbook for nodal analysis.
Formula used:
Write the expression to calculate impedance of the inductor.
Here,
Write the expression to calculate impedance of the capacitor.
Here,
Write the general representation of sinusoidal function.
Here,
Write the general expression to phasor transform of sinusoidal function from time domain to frequency domain.
Here,
Write the polar form representation of frequency domain.
Calculation:
Comparing given source voltage
Substitute
Convert
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
The frequency domain representation of given figure with the representation of node voltage is shown in Figure 1.
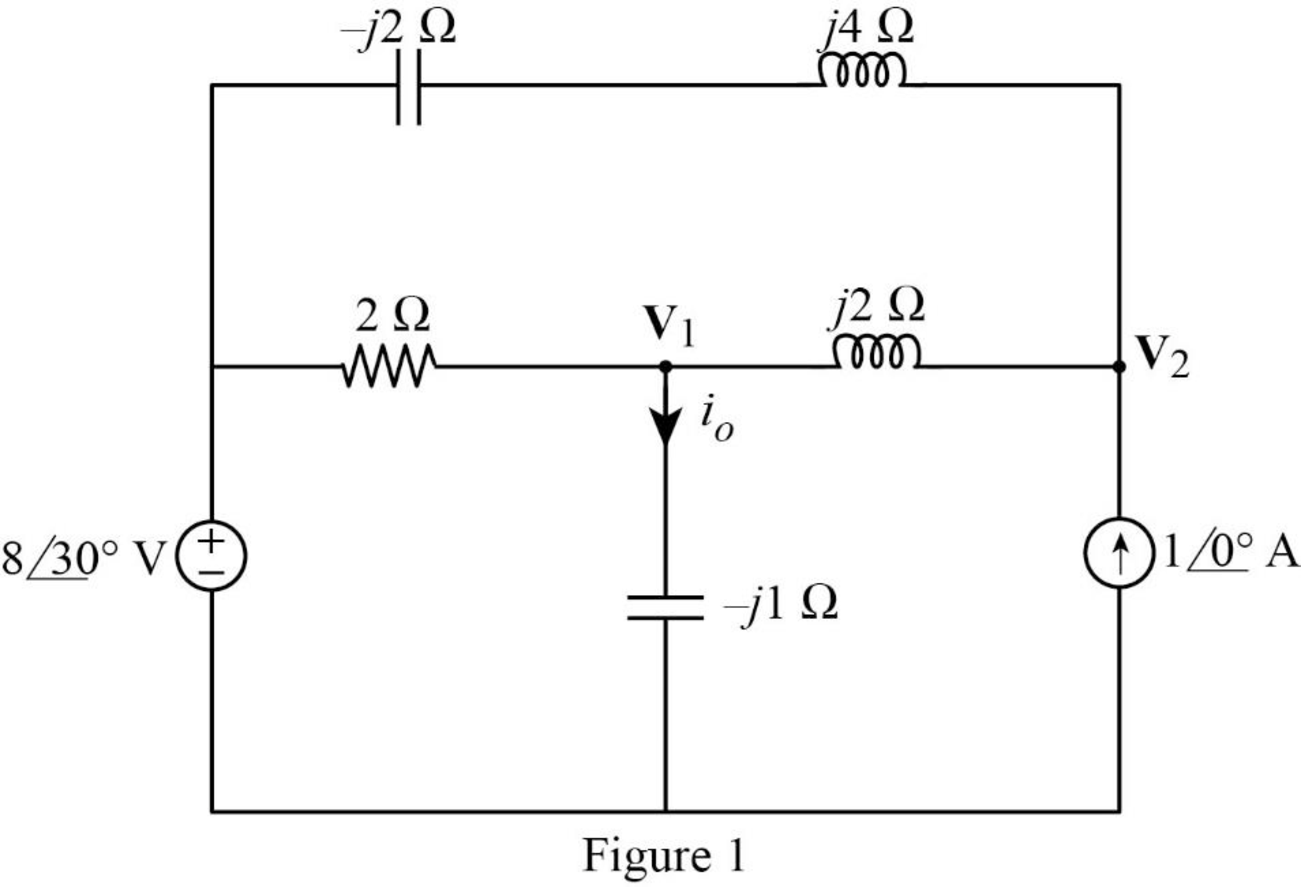
Apply Kirchhoff’s current law at node
Simplify the equation as follows.
Apply Kirchhoff’s current law at node
MATLAB Code:
Solve the two linear equations (5) and (6) using MATLAB to find the node voltages.
syms v1 v2
eq1 = (0.5 + 0.5*1i)*v1 +(0.5*1i)*v2 == 3.464 + 2*1i;
eq2 = (0.5*1i)*v1 +(-1*1i)*v2 == 3 + (-3.464*1i);
sol = solve([eq1, eq2], [v1, v2]);
val1 = sol.v1;
val2 = sol.v2;
v1real=real(val1);
v1imag=imag(val1);
v2real=real(val2);
v2imag=imag(val2);
v1=sprintf('%.3f + (%.3f)i V', v1real, v1imag)
v2=sprintf('%.3f + (%.3f)i V', v2real, v2imag)
The command window output:
v1 = '3.302 + (-4.417)i V'
From Figure 1, write the expression for
Substitute
Represent the current in time domain.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the value of current
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Web Development and Design Foundations with HTML5 (8th Edition)
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Modern Database Management
Management Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm (16th Edition)
- I need help adding a capacitor and a Zener diode to my circuit. I’m looking for a simple sketch or diagram showing how to connect them. i want diagram with final circuit after adding the zener diad and capacitor. don't do calclution or anything. thanksarrow_forwardQuestion 3 AC Motor Drives [15]Calculate the instantaneous currents delivered by the inverter if the direct axiscurrent required at a particular instant is 8.66A and the quadrature current is5A. Derive all equations for the three currents.arrow_forwardA certain signal f(t) has the following PSD (assume 12 load): Sp (w) = new + 8(w) - 1.5) + (w + 1.5)] (a) What is the mean power in the bandwidth w≤2 rad/see? (b) What is the mean power in the bandwidth -1.9 to 0.99 rad/sec? Paress(w) dw 2ㅈ -arrow_forward
- (75 Marks) JA signal (t) is bond 7)(t)(t) and f(t), are band-limited to 1.2 kHz each. These signals are to be limited to 9.6 kHz, and three other signals transmitted by means of time-division multiplexing. Set up scheme for accomplishing this multiplexing requirement, with each signal sampled at its Nyquist rate. What must be the speed of the commutator (the output but ram-k bit/sec)? the minimum band width? (25 Marks)arrow_forwardDraw the digital modulation outputs, ASK Amplitude Shift Keying) FSK (Frequency Shift Keying) and PSK (Phase Shift Keying). For baseband and carriet frequency as shown 101 wwwwwwwwwwww 010 BASESAND basband CARRIER Carralarrow_forwardplease show full working. I've included the solutionarrow_forward
- can you please show working and steps. The answer is 8kohms.arrow_forwardPSD A certain signal f(t) has the following PSD (assume 12 load): | Sƒ(w) = π[e¯\w\ + 8(w − 2) + +8(w + 2)] (a) What is the mean power in the bandwidth w≤ 1 rad/sec? (b) What is the mean power in the bandwidth 0.99 to 1.01 rad/sec? (c) What is the mean power in the bandwidth 1.99 to 2.01 rad/sec? (d) What is the total mean power in (t)? Pav= + 2T SfLw) dw - SALW)arrow_forwardAn AM modulation waveform signal:- p(t)=(8+4 cos 1000πt + 4 cos 2000πt) cos 10000nt (a) Sketch the amplitude spectrum of p(t). (b) Find total power, sideband power and power efficiency. (c) Find the average power containing of each sideband.arrow_forward
- Can you rewrite the solution because it is unclear? AM (+) = 8(1+ 0.5 cos 1000kt +0.5 ros 2000ks) = cos 10000 πt. 8 cos wat + 4 cos wit + 4 cos Wat coswet. -Jet jooort J11000 t = 4 e jqooort jgoort +4e + e +e j 12000rt. 12000 kt + e +e jooxt igoo t te (w) = 8ES(W- 100007) + 8IS (W-10000) USBarrow_forwardCan you rewrite the solution because it is unclear? AM (+) = 8(1+0.5 cos 1000kt +0.5 ros 2000 thts) = cos 10000 πt. 8 cos wat + 4 cos wit + 4 cos Wat coswet. J4000 t j11000rt $14+) = 45 jqooort +4e + e + e j 12000rt. 12000 kt + e +e +e Le jsoort -; goon t te +e Dcw> = 885(W- 100007) + 8 IS (W-10000) - USBarrow_forwardCan you rewrite the solution because it is unclear? Q2 AM ①(+) = 8 (1+0.5 cos 1000πt +0.5 ros 2000kt) $4+) = 45 = *cos 10000 πt. 8 cos wat + 4 cosat + 4 cos Wat coswet. j1000016 +4e -j10000πt j11000Rt j gooort -j 9000 πt + e +e j sooort te +e J11000 t + e te j 12000rt. -J12000 kt + с = 8th S(W- 100007) + 8 IS (W-10000) <&(w) = USB -5-5 -4-5-4 b) Pc 2² = 64 PSB = 42 + 4 2 Pt Pc+ PSB = y = Pe c) Puss = PLSB = = 32 4² = 8 w 32+ 8 = × 100% = 140 (1)³×2×2 31 = 20% x 2 = 3w 302 USB 4.5 5 5.6 6 ms Ac = 4 mi = 0.5 mz Ac = 4 ५ M2 = =0.5arrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





