
Concept explainers
Predict the bond angles for the following molecules: (a) BeCl2, (b) BCl3, (c) CCl4, (d) CH3Cl, (e) Hg2Cl2 (arrangement of atoms: ClHgHgCl), (f) SnCl2, (g) H2O2, (h) SnH4.
(a)
Interpretation: The bond angle of the given molecule should be found.
Concept Introduction:
- Bond angle measured that made between two nearby bonds. The angles between two adjacent bonds are known as bond angle.
- Using VSEPR theory and Lewis structure, the exact geometry of a molecule can be obtained.
- In VSEPR, the geometry of the molecule is explained based on minimizing electrostatic repulsion between the molecules’ valence electrons around a central atom
- Lewis structures is also known as Lewis dot structures which represents the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
Answer to Problem 10.80QP
The bond angle of 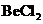 is
is 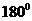 .
.
Explanation of Solution
To find: The bond angle of the given molecule
Given molecule is
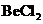 .
.
Lewis structure of the given molecule is drawn below.
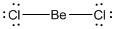
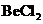 is a triatomic molecule . Here the central atom beryllium atom does not have any lone pair of electrons whereas both terminal chlorine atoms have 3 pairs of electron. It is a
is a triatomic molecule . Here the central atom beryllium atom does not have any lone pair of electrons whereas both terminal chlorine atoms have 3 pairs of electron. It is a 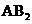 type molecule. Since there are only two bonds, there is only one bond angle. Since there is no lone pair on the central atom, to minimize the repulsion, they form a linear geometry. So the bond angle between two atoms is
type molecule. Since there are only two bonds, there is only one bond angle. Since there is no lone pair on the central atom, to minimize the repulsion, they form a linear geometry. So the bond angle between two atoms is 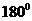 .
.
(b)
Interpretation: The bond angle of the given molecule should be found.
Concept Introduction:
- Bond angle measured that made between two nearby bonds. The angles between two adjacent bonds are known as bond angle.
- Using VSEPR theory and Lewis structure, the exact geometry of a molecule can be obtained.
- In VSEPR, the geometry of the molecule is explained based on minimizing electrostatic repulsion between the molecules’ valence electrons around a central atom
- Lewis structures is also known as Lewis dot structures which represents the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
Answer to Problem 10.80QP
The bond angle of 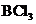 is
is 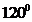 .
.
Explanation of Solution
To find: The bond angle of the given molecule
Given molecule is
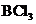 .
.
Lewis structure of the given molecule is drawn below.
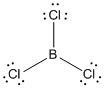
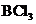 contains four atoms. Here the central atom boron atom does not have any lone pair of electrons whereas the terminal chlorine atoms have 3 pairs of electron. It is a
contains four atoms. Here the central atom boron atom does not have any lone pair of electrons whereas the terminal chlorine atoms have 3 pairs of electron. It is a 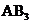 type molecule. Since there are only three bonds, there are two bond angle. Since there is no lone pair on the central atom, to minimize the repulsion, they form a trigonal planar geometry. So the bond angle between two atoms is
type molecule. Since there are only three bonds, there are two bond angle. Since there is no lone pair on the central atom, to minimize the repulsion, they form a trigonal planar geometry. So the bond angle between two atoms is 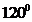 .
.
(c)
Interpretation: The bond angle of the given molecule should be found.
Concept Introduction:
- Bond angle measured that made between two nearby bonds. The angles between two adjacent bonds are known as bond angle.
- Using VSEPR theory and Lewis structure, the exact geometry of a molecule can be obtained.
- In VSEPR, the geometry of the molecule is explained based on minimizing electrostatic repulsion between the molecules’ valence electrons around a central atom
- Lewis structures is also known as Lewis dot structures which represents the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
Answer to Problem 10.80QP
The bond angle of 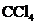 is
is 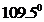 .
.
Explanation of Solution
To find: The bond angle of the given molecule
Given molecule is
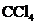 .
.
Lewis structure of the given molecule is drawn below.
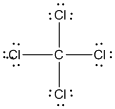
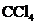 contains five atoms. Here the central atom carbon atom does not have any lone pair of electrons whereas the terminal chlorine atoms have 3 pairs of electron. It is a
contains five atoms. Here the central atom carbon atom does not have any lone pair of electrons whereas the terminal chlorine atoms have 3 pairs of electron. It is a 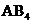 type molecule. Since there is no lone pair on the central atom, to minimize the repulsion, they form a tetrahedral geometry. So the bond angle between two atoms is
type molecule. Since there is no lone pair on the central atom, to minimize the repulsion, they form a tetrahedral geometry. So the bond angle between two atoms is 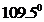 .
.
(d)
Interpretation: The bond angle of the given molecule should be found.
Concept Introduction:
- Bond angle measured that made between two nearby bonds. The angles between two adjacent bonds are known as bond angle.
- Using VSEPR theory and Lewis structure, the exact geometry of a molecule can be obtained.
- In VSEPR, the geometry of the molecule is explained based on minimizing electrostatic repulsion between the molecules’ valence electrons around a central atom
- Lewis structures is also known as Lewis dot structures which represents the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
Answer to Problem 10.80QP
The bond angle of 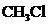 is
is 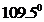 .
.
Explanation of Solution
To find: The bond angle of the given molecule
Given molecule is
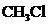 .
.
Lewis structure of the given molecule is drawn below.
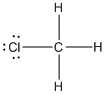
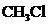 contains five atoms. Here the central atom carbon atom does not have any lone pair of electrons whereas the terminal chlorine atom has 3 pairs of electron. It is a
contains five atoms. Here the central atom carbon atom does not have any lone pair of electrons whereas the terminal chlorine atom has 3 pairs of electron. It is a 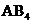 type molecule. Since there is no lone pair on the central atom, to minimize the repulsion, they form a distorted tetrahedral geometry because of the size difference of terminal chlorine and hydrogen atoms. So the bond angle between two atoms is
type molecule. Since there is no lone pair on the central atom, to minimize the repulsion, they form a distorted tetrahedral geometry because of the size difference of terminal chlorine and hydrogen atoms. So the bond angle between two atoms is 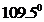 .
.
(e)
Interpretation: The bond angle of the given molecule should be found.
Concept Introduction:
- Bond angle measured that made between two nearby bonds. The angles between two adjacent bonds are known as bond angle.
- Using VSEPR theory and Lewis structure, the exact geometry of a molecule can be obtained.
- In VSEPR, the geometry of the molecule is explained based on minimizing electrostatic repulsion between the molecules’ valence electrons around a central atom
- Lewis structures is also known as Lewis dot structures which represents the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
Answer to Problem 10.80QP
The bond angle of 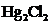 is
is 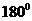 .
.
Explanation of Solution
To find: The bond angle of the given molecule
Given molecule is
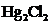 .
.
Lewis structure of the given molecule is drawn below.
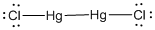
In the case of 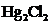 , both mercury atom does not have any lone pair of electrons whereas the terminal chlorine atoms have 3 pairs of electron. Both the mercury atom is of
, both mercury atom does not have any lone pair of electrons whereas the terminal chlorine atoms have 3 pairs of electron. Both the mercury atom is of 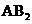 type molecule. . Since there is no lone pair on the central atom, to minimize the repulsion, they form a linear geometry. So the bond angle between two atoms is
type molecule. . Since there is no lone pair on the central atom, to minimize the repulsion, they form a linear geometry. So the bond angle between two atoms is 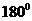 .
.
(f)
Interpretation: The bond angle of the given molecule should be found.
Concept Introduction:
- Bond angle measured that made between two nearby bonds. The angles between two adjacent bonds are known as bond angle.
- Using VSEPR theory and Lewis structure, the exact geometry of a molecule can be obtained.
- In VSEPR, the geometry of the molecule is explained based on minimizing electrostatic repulsion between the molecules’ valence electrons around a central atom
- Lewis structures is also known as Lewis dot structures which represents the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
Answer to Problem 10.80QP
The bond angle of  is
is 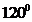 .
.
Explanation of Solution
To find: The bond angle of the given molecule
Given molecule is
 .
.
Lewis structure of the given molecule is drawn below.
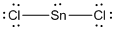
In the case of  , the central atom tin atom have a lone pair of electron whereas the terminal chlorine atoms have 3 pairs of electron and is a
, the central atom tin atom have a lone pair of electron whereas the terminal chlorine atoms have 3 pairs of electron and is a 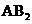 with one lone pair of electron type molecule. There are only two bonds so there is only one bond angle. Since there is one lone pair on the central atom, to minimize the repulsion, they form a bent geometry. So the bond angle between two atoms is
with one lone pair of electron type molecule. There are only two bonds so there is only one bond angle. Since there is one lone pair on the central atom, to minimize the repulsion, they form a bent geometry. So the bond angle between two atoms is 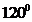 .
.
(g)
Interpretation: The bond angle of the given molecule should be found.
Concept Introduction:
- Bond angle measured that made between two nearby bonds. The angles between two adjacent bonds are known as bond angle.
- Using VSEPR theory and Lewis structure, the exact geometry of a molecule can be obtained.
- In VSEPR, the geometry of the molecule is explained based on minimizing electrostatic repulsion between the molecules’ valence electrons around a central atom
- Lewis structures is also known as Lewis dot structures which represents the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
Answer to Problem 10.80QP
The bond angle of 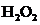 is
is 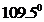 .
.
Explanation of Solution
To find: The bond angle of the given molecule
Given molecule is
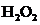 .
.
Lewis structure of the given molecule is drawn below.
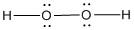
In the case of 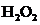 , both oxygen atom have any two lone pair of electrons and is a
, both oxygen atom have any two lone pair of electrons and is a 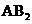 with two lone pair of electron type molecule.. Since there is two lone pair on each oxygen atom, to minimize the repulsion, they form a tetrahedral geometry. So the bond angle between two atoms is
with two lone pair of electron type molecule.. Since there is two lone pair on each oxygen atom, to minimize the repulsion, they form a tetrahedral geometry. So the bond angle between two atoms is 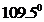 .
.
(h)
Interpretation: The bond angle of the given molecule should be found.
Concept Introduction:
- Bond angle measured that made between two nearby bonds. The angles between two adjacent bonds are known as bond angle.
- Using VSEPR theory and Lewis structure, the exact geometry of a molecule can be obtained.
- In VSEPR, the geometry of the molecule is explained based on minimizing electrostatic repulsion between the molecules’ valence electrons around a central atom
- Lewis structures is also known as Lewis dot structures which represents the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
Answer to Problem 10.80QP
The bond angle of 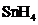 is
is 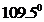 .
.
Explanation of Solution
To find: The bond angle of the given molecule
Given molecule is
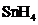 .
.
Lewis structure of the given molecule is drawn below.
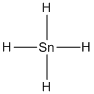
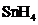 Contains five atoms. Here the central atom tin atom does not have any lone pair of electrons. It is a
Contains five atoms. Here the central atom tin atom does not have any lone pair of electrons. It is a 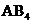 type molecule. Since there is no lone pair on the central atom, to minimize the repulsion, they form a tetrahedral geometry. So the bond angle between two atoms is
type molecule. Since there is no lone pair on the central atom, to minimize the repulsion, they form a tetrahedral geometry. So the bond angle between two atoms is 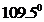 .
.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
EBK CHEMISTRY
- How can i draw the mechanisms for this molecule?arrow_forwarda. Discuss and explain he difference IN Stability between the Chai and Boat Гольцу от судомехане b. For the Following Molecule draw both possible Clain conformations and explain which one is more stable and for what Reason. H. CH₂ CH₂ H "Harrow_forwarddraw out these molecules pleasearrow_forward
- Question 5: Name the following compound in two ways using side chain and using prefix amine (Common name and IUPAC name both) CH3NH2 CH3CH2NHCH3 CH₂CH₂N(CH3)2 Draw the structure of diethyl methyl amine Question 6. Write the balanced combustion reaction for: a. Hexane b. Propyne c. 2-pentene Question 7: Write the following electrophilic substitution reactions of benzene: Hint: Use notes if you get confused a. Halogenation reaction: b. Nitration reaction : c. Sulphonation reaction: d. Alkylation reaction: e. Aceylation reaction:arrow_forwardQuestion 4. Name the following structures ○ CH3-C-N-H H CH3CH2-C-N-H H CH3CH2-C-N-CH3 Harrow_forwardA. Add Water to below compound which 2-methyl 2-butene (addition Reaction) H₂C CH₂ CH, + H₂O-> ? Major product? Minor product? B. Add Bromine to the compound which 2-methyl 2-butene (addition Reaction) CH₂ CH₂ + Br₂→ ? Major product and Minor product both are same in this? C. Add Hydrogen Bromide to the compound which 2-methyl 2-butene (addition Reaction) H,C CH₂ CH₂ + HBr Major product? Minor product? D. Add Hydrogen to the compound which 2-methyl 2-butene (addition Reaction) CH₂ CH₂ + H₂ Major product and Minor product both are same in this?arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





