
The feasibility of installing such a weir which will be accurate and yet not cause the water to overflow to the side of the channel.
Answer to Problem 10.4CP
The first two of these are plausible although H/Y is large than 2 . The third result is not recommended because Y is too far below 9 cm. We can say that reasonable designs are possible.
Explanation of Solution
Figure:
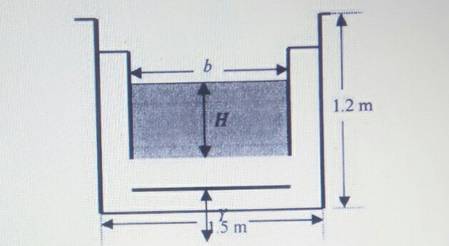
Given:
For asphalt take
Concept Used:
Annuity problem requires the use of the formula as follows:
Here
Area =
Annuity problem requires the use of the formula as follows:
Here,
Hydraulic radius
Annuity problem requires the use of the formula as follows:
Here,
Area=
Annuity problem requires the use of the Weir formula as follows:
Here, width
Calculation:
As per the given problem
Annuity problem requires the use of this formula:
Substitute these values in the formula
Annuity problem requires the use of this formula:
Substitute these values in the formula:
Annuity problem requires the use of this formula
Substitute these values in the formula
The weir discharge must equal this flow rate. Let us being by making b equal to the full available width of 1.5 m and holding Y to the minimum height of 9 cm.
Annuity problem requires the use of the Weir formula as follows
Substitute these values in the formula
To find out the ratio H/Y
The total upstream water depth
If we back down to
The upstream depth
So, a wide weir design is possible with
Similarly,
To let shorter values of b
Annuity problem requires the use of this formula:
Substitute these values in the formula:
Annuity problem requires the use of this formula:
Substitute these values in the formula:
Annuity problem requires the use of this formula:
Substitute these values in the formula:
Annuity problem requires the use of the Weir formula as follows:
Substitute these values in the formula
To find out the ratio H/Y
Annuity problem requires the use of this formula:
Substitute these values in the formula:
Annuity problem requires the use of this formula:
Substitute these values in the formula:
Annuity problem requires the use of this formula:
Substitute these values in the formula:
Annuity problem requires the use of the Weir formula as follows:
Substitute these values in the formula
To find out the ratio H/Y:
Conclusion:
The first two of these are plausible although H/Y is large than 2.0.The third result is not recommended because Y is too far below 9 cm .We conclude that reasonable designs are possible.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Fluid Mechanics
- hand-written solutions only, please.arrow_forwardIn the bending of a U-profile beam, the load path passes through the torsional center C, causing a moment of 25 kNm at the cross-section under consideration. Additionally, the beam is subjected to an axial tensile force of 100 kN at the centroid. Determine the maximum absolute normal stress.(Check hint: approximately 350 MPa, but where?)arrow_forward### Make an introduction to a report of a rocket study project, in the OpenRocket software, where the project consists of the simulation of single-stage and two-stage rockets, estimating the values of the exhaust velocities of the engines used, as well as obtaining the graphs of "altitude", "mass ratio x t", "thrust x t" and "ψ × t".arrow_forward
- A 6305 ball bearing is subjected to a steady 5000-N radial load and a 2000-N thrust load and uses a very clean lubricant throughout its life. If the inner race angular velocity is 500 rpm find The equivalent radial load the L10 life and the L50 lifearrow_forwardWhere on the below beam is the Maxiumum Slope likely to occur? C A; Атят Barrow_forwardWhat is the moment of Inertia of this body? What is Ixx, Iyy, and Izzarrow_forward
- i need the The shaft is supported by a smooth thrust bearing at AA and a smooth journal bearing at BB. Draw the shear diagram for the shaft. Follow the sign convention.arrow_forward4- In the system shown in the figure, the water velocity in the 12 in. diameter pipe is 8 ft/s. Determine the gage reading at position 1. Elevation 170 ft 1 Elevation 200 ft | 8 ft, 6-in.-diameter, 150 ft, 12-in.-diameter, f = 0.020 f = 0.020 A B Hints: the minor losses should consider the contraction loss at A and the expansion loss at B.arrow_forwardWhat is the moment of Inertia of this body? What is Ixx, Iyy, and Izzarrow_forward
- Consider a glass window (Hight = 1.2 m, Width = 2 m). The room thatfaces the window are maintained at 25 o C. The average temperature ofthe inner surface of the window is 5 o C. Calculate the total heat transferrate from through the window a) IdenCfy what type(s) of convecCon is important (circle one). • external forced (Chapter 7)• internal forced (Chapter 8)• natural convecCon (Chapter 9)• boiling and condensaCon (Chapter 10)b) IdenCfy the necessary equaCon(s) needed to solve the problem. c) IdenCfy important fluid properCes you need to solve the problem. d) Calculate the total heat transferred.arrow_forwardWater is condensing on a square plate (0.5 m x 0.5 m) placed verCcally. If the desired rate ofcondensaCon is 0.016 kJ/s, determine the necessary surface temperature of the plate at atmosphericpressure. Assume the film temperature of 90 o C for evaluaCon of fluid properCes of water and thesurface temperature of 80 o C for the evaluaCon of modified latent heat of vaporizaConarrow_forwardWater at 20 o C enters the 4 cm-diameter, 14 m-long tube at a rate of 0.8 kg/s. The surfacetemperature of the pipe is maintained at 165 o Cby condensing geothermal stream at the shellside of the heat exchanger. Use water properCesat 85 o C for all calculaCons.(a) Show that the water flow is turbulent and thermally fully developed. (b) EsCmate the heat transfer coefficient for convecCve heat transfer from the pipe to the water. For a fully developed turbulent flow within the smooth pipe, the Nu number can becalculated from the following equaCon:(c) Calculate the exit temperature of the water. (d) Share your opinion on whether the use of water properties at 85°C is appropriate. Yes or No because:arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





