
Concept explainers
Answer the following questions about the
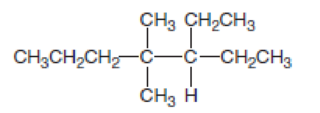
- a. Give the IUPAC name.
- b. Draw one constitutional isomer.
- c. Predict the solubility in water.
- d. Predict the solubility in an organic solvent.
- e. Write a balanced equation for complete combustion.
a.
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of given compound has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC Nomenclature of alkane compounds.
IUPAC nomenclature is a system of writing a name for organic compounds. The full form of IUPAC name is International Union of Pure and Applied chemistry.
There are certain rules followed for writing IUPAC name:
- The longest continuous carbon chain present in compound can be given as parent name. Then add the prefix and suffix name to the parent name. The suffix group represents the functional group present in a molecule. The prefix name explains about the identity, location, and number of substituents present in compound.
- The functional groups or alkyl groups have to be determined. The numbering of carbon starts from left side and ends at right side.
- The suffix group –ane represents alkane molecule. The prefix group represents the number of carbon atom present in the longest carbon chain. Then the substituent group attached to the longest chain can be numbered in alphabetical order. The prefix name can be given, depends on the number of substituent present in molecule.
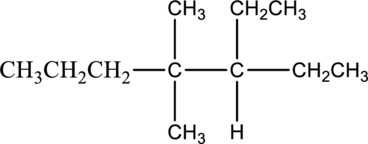
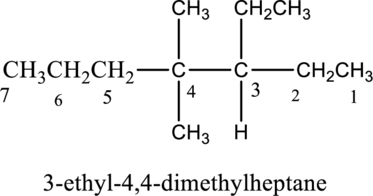
Explanation of Solution
In this compound the longest chain has seven carbon atoms. The parent name of given compound is heptane. Then number the substituents in alphabetical order. The ethyl group
The IUPAC name of compound is given below,
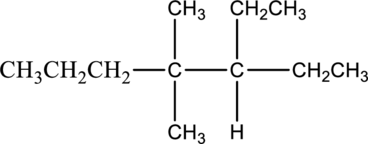
b.
Interpretation
The one constitutional isomer for the given compound has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Isomers:
Isomers contain two or more compounds in which the molecular formula of compounds is same but the atoms are arranged in different order. The arrangement of atoms will be in different manner.
Constitutional isomer:
The compounds have the same molecular formula but atoms are arranged in different connectivity is known as constitutional isomer.
Explanation of Solution
The isomer 3-ethyl-4,5-dimethylheptane has seven carbon atoms present in the longest chain. The two substituents methyl groups
The constitutional isomers of
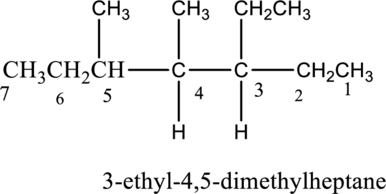
c.
Interpretation:
The solubility of given compound in water has to be predicted.
Concept Introduction:
Solubility:
The solubility is defined as the solid or liquid or gaseous substance which dissolves in suitable solvent. The solubility also depends upon polar or nonpolar molecule. The nonpolar molecule has no separate positive and negative charge. Polar molecules have separate positive and negative charges.
Explanation of Solution
The 3-ethyl-4,4-dimethylheptane is insoluble in water. The water molecule is said to be polar molecules. It has both positive and negative charge. The given compound is a nonpolar alkane. The nonpolar alkanes cannot soluble in water molecule. Hence the given compound 3-ethyl-4,4-dimethylheptane is insoluble in water.
d.
Interpretation:
The solubility of given compound in organic compound has to be predicted.
Concept Introduction:
Refer part: c.
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is soluble in organic solvent. The reason for the solubility of the given compound, it belongs to nonpolar molecule. Nonpolar molecules cannot soluble in polar molecule. The nonpolar molecule has no separate charges. Hence given molecule
3-ethyl-4,4-dimethylheptane is soluble in organic solvent.
e.
Interpretation:
The balanced equation for complete combustion of given compound 3-ethyl-4, 4-dimethylheptane has to be written.
Concept Introduction:
Combustion reaction:
The hydrocarbon compound reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water as product is known as hydrocarbon combustion reaction. It is an exothermic reaction. The hydrocarbon compounds are generally organic compounds contain carbon and hydrogen element. The compounds such as alkanes, alkenes, alkynes and aromatic compounds.
The general equation is given as,
Where,
- x represents the number of carbon atoms present in the hydrocarbon
- y represents the number of carbon atoms present in the hydrocarbon
- N represents the number of oxygen atoms requires in the hydrocarbon combustion reaction
Chemical equation:
In chemical equation, the substance reacts (reactant) to give products. The number of atoms present in reactant side should be equal to the number of atom present in the product side.
Explanation of Solution
The compound 3-ethyl-4, 4-dimethylheptane
The chemical reaction for complete combustion of ethane is given below,
In reactant side the molecules of
The balanced equation for complete combustion reaction of 3-ethyl-4,4-dimethylheptane is given below,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Principles of General, Organic, Biological Chemistry
- ASP please....arrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardConsider the structure of 1-bromo-2-fluoroethane. Part 1 of 2 Draw the Newman projection for the anti conformation of 1-bromo-2-fluoroethane, viewed down the C1-C2 bond. ✡ ぬ Part 2 of 2 H H F Br H H ☑ Draw the Newman projection for the gauche conformation of 1-bromo-2-fluoroethane, viewed down the C1-C2 bond. H F Br H Harrow_forward
- Please help me answer this question. I don't understand how or where the different reagents will attach and it's mostly due to the wedge bond because I haven't seen a problem like this before. Please provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how it can happen and what the final product will look like.arrow_forwardWhich of the following compounds is the most acidic in the gas phase? Group of answer choices H2O SiH4 HBr H2Sarrow_forwardWhich of the following is the most acidic transition metal cation? Group of answer choices Fe3+ Sc3+ Mn4+ Zn2+arrow_forward
- Based on the thermodynamics of acetic acid dissociation discussed in Lecture 2-5, what can you conclude about the standard enthalpy change (ΔHo) of acid dissociation for HCl? Group of answer choices You cannot arrive at any of the other three conclusions It is a positive value It is more negative than −0.4 kJ/mol It equals −0.4 kJ/molarrow_forwardPLEASE HELP URGENT!arrow_forwardDraw the skeletal structure corresponding to the following IUPAC name: 7-isopropyl-3-methyldecanearrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning

