
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-STUD.SOLNS.MAN+SG(LL)
4th Edition
ISBN: 9781119659587
Author: Klein
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 1, Problem 48PP
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation: The total number of
bonds should be counted in the following compound:
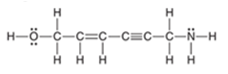
Concept Introduction:
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
8:17 PM Sun Mar 30
Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore
inorganic byproducts.
HSCH2CH2CH2SH, BF3
Probler
Drawing
Ato
Bonds
Cl
presented by Mr L
How the coprion. (Il Done in no wraction, dew the starting redential)
до
8:16 PM Sun Mar 30
K
Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore
inorganic byproducts.
Proble
1. CH3MgBr
2. H3O+
F
Drawing
Chapter 1 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-STUD.SOLNS.MAN+SG(LL)
Ch. 1.2 - Prob. 1LTSCh. 1.2 - Prob. 2ATSCh. 1.2 - Prob. 2LTSCh. 1.3 - Prob. 3LTSCh. 1.3 - Prob. 4PTSCh. 1.3 - Prob. 5PTSCh. 1.4 - Prob. 4LTSCh. 1.4 - Prob. 7PTSCh. 1.4 - Prob. 8PTSCh. 1.4 - Prob. 9ATS
Ch. 1.5 - Prob. 5LTSCh. 1.5 - Prob. 10PTSCh. 1.5 - Prob. 11ATSCh. 1.5 - Prob. 12ATSCh. 1.6 - Prob. 6LTSCh. 1.6 - Prob. 14ATSCh. 1.7 - Prob. 7LTSCh. 1.7 - Prob. 17ATSCh. 1.10 - Prob. 18CCCh. 1.10 - Prob. 20CCCh. 1.10 - Prob. 8LTSCh. 1.10 - Prob. 21PTSCh. 1.10 - Nemotin is a compound that was first isolated from...Ch. 1.10 - Prob. 23CCCh. 1.11 - Prob. 9LTSCh. 1.11 - Prob. 24PTSCh. 1.11 - Prob. 25PTSCh. 1.11 - Prob. 26PTSCh. 1.11 - Prob. 27ATSCh. 1.12 - Prob. 10LTSCh. 1.12 - Prob. 29ATSCh. 1.13 - Prob. 11LTSCh. 1.13 - Prob. 31ATSCh. 1 - Prob. 32PPCh. 1 - Prob. 33PPCh. 1 - Prob. 34PPCh. 1 - Prob. 35PPCh. 1 - Prob. 36PPCh. 1 - Prob. 37PPCh. 1 - Prob. 38PPCh. 1 - Prob. 39PPCh. 1 - Prob. 40PPCh. 1 - Prob. 41PPCh. 1 - Prob. 42PPCh. 1 - Prob. 44PPCh. 1 - Prob. 45PPCh. 1 - Prob. 46PPCh. 1 - Prob. 47PPCh. 1 - Prob. 48PPCh. 1 - Prob. 49PPCh. 1 - Prob. 50PPCh. 1 - Prob. 51PPCh. 1 - Prob. 52PPCh. 1 - Prob. 53PPCh. 1 - Prob. 54PPCh. 1 - Nicotine is an addictive substance found in...Ch. 1 - Prob. 56PPCh. 1 - Prob. 57PPCh. 1 - Prob. 59PPCh. 1 - Prob. 63ASPCh. 1 - Prob. 64ASPCh. 1 - Prob. 66ASPCh. 1 - Prob. 69ASPCh. 1 - Prob. 71ASPCh. 1 - Prob. 72ASPCh. 1 - Prob. 75IP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- о но оarrow_forwardName the major organic product of the following action of 4-chloro-4-methyl-1-pentanol in neutral pollution 10+ Now the product. The product has a molecular formula f b. In a singly hain, the starting, material again converts into a secule with the molecular kormula CIO. but with comply Draw the major organic structure inhalationarrow_forwardMacmillan Learning Alcohols can be oxidized by chromic acid derivatives. One such reagent is pyridinium chlorochromate, (C,H,NH*)(CICTO3), commonly known as PCC. Draw the proposed (neutral) intermediate and the organic product in the oxidation of 1-butanol by PCC when carried out in an anhydrous solvent such as CH₂C₁₂. PCC Intermediate OH CH2Cl2 Draw the intermediate. Select Draw Templates More с H Cr о Product Draw the product. Erase Select Draw Templates More H о Erasearrow_forward
- If I have 1-bromopropene, to obtain compound A, I have to add NaOH and another compound. Indicate which compound that would be. A C6H5 CH3arrow_forwardProvide the reagents for the following reactions.arrow_forwardIf I have 1-bromopropene, to obtain compound Z, I have to add two compounds A1 and A2. Indicate which compounds are needed. P(C6H5)3arrow_forward
- Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Assume that the water side product is continuously removed to drive the reaction toward products. O CH3CH2NH2, TSOH Select to Draw >arrow_forwardPredict the major organic product(s) for the following reaction.arrow_forwardPredict the major organic product(s) for the following reactions.arrow_forward
- Provide the complete mechanism for the reactions below. You must include appropriate arrows,intermediates, and formal charges.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by reacting fluorobenzene with a sulfonitric mixture.arrow_forwardIf I have 1-bromopropene, to obtain compound A, I have to add NaOH and another compound. Indicate which compound that would be. C6H5 CH3arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580343
Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Combination of Atomic Orbitals LCAO; Author: Edmerls;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nq1zwrAIr4c;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Quantum Molecular Orbital Theory (PChem Lecture: LCAO and gerade ungerade orbitals); Author: Prof Melko;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=l59CGEstSGU;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY