
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Given line structure is to be drawn using condensed formula.
Concept introduction:
The condensed formula indicates how the atoms should be connected in a given molecule. Each non-hydrogen atom is written explicitly followed immediately by the number of hydrogen atoms that are bonded to it. Multiple bonds are not shown explicitly in the condensed structure. To arrive at a total charge of zero, each carbon should have a maximum of four bonds while each oxygen should have a maximum of two bonds and two lone pairs. A parenthesis, in the condensed formula, represents that the repetitive unit is attached to the previous carbon atom. The
Answer to Problem 1.64P
For the given line structure, the condensed structure is:
![]()
Explanation of Solution
The given line structure is:
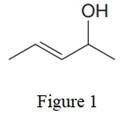
In the given line structure, there is a five carbon chain, with a carbon-carbon double bond and with a hydroxyl group. Each carbon atom is written explicitly followed immediately by the number of hydrogen atoms that are bonded to it. Multiple bonds are not shown explicitly in the condensed formula. Each carbon atom has a maximum of four bonds while each oxygen atom should have a maximum of two bonds. A parenthesis must be used for the carbon atom having three different groups attached. Thus, the hydroxyl group attached to the carbon atom must be shown in the parenthesis.
Thus, the condensed structure for the given line structure is:

The condensed structure for the given line structure is shown in Figure 2 above.
(b)
Interpretation:
Given line structure is to be drawn using condensed formula.
Concept introduction:
The condensed formula indicates how the atoms should be connected in a given molecule. Each carbon atom is written explicitly followed immediately by the number of hydrogen atoms that are bonded to it. To arrive at a total charge of zero, each carbon should have a maximum of four bonds while each oxygen should have a maximum of two bonds and two lone pairs. A parenthesis in the condensed formula represents that the repetitive unit is attached to the previous carbon atom. The
Answer to Problem 1.64P
For the given line structure, the condensed structure is:
![]()
Explanation of Solution
The given line structure is:
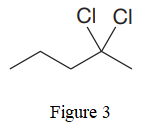
In the given line structure, there is a five carbon chain, with two chlorine atoms attached to one of the carbon atoms of the chain. Each carbon atom should have a maximum of four bonds while each oxygen atom should have a maximum of two bonds. A parenthesis must be used for the carbon atom having three different groups attached. Thus, the
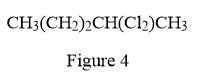
The condensed structure for the given line structure is shown in Figure 4 above.
(c)
Interpretation:
Given line structure is to be drawn using condensed formula.
Concept introduction:
The condensed formula indicates how the atoms should be connected in a given molecule. Each non-hydrogen atom is written explicitly followed immediately by the number of hydrogen atoms that are bonded to it. Multiple bonds are not shown explicitly in the condensed structure. To arrive at a total charge of zero, each carbon should have a maximum of four bonds while each oxygen should have a maximum of two bonds and two lone pairs. A parenthesis in the condensed formula represents that the repetitive unit is attached to the previous carbon atom. The
Answer to Problem 1.64P
For the given line structure, the condensed structure is:
Explanation of Solution
The given line structure is:
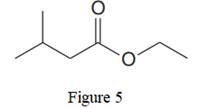
In the given line structure, there is a chain of four carbon atoms on the left side of a singly bonded oxygen. Each carbon atom is written explicitly followed immediately by the number of hydrogen atoms that are bonded to it. Multiple bonds are not shown explicitly in the condensed structure while an ethyl fragment is present at the right side of the singly bonded oxygen atom. The
Thus, the condensed structure for the given line structure is:
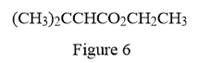
The condensed structure for the given line structure is shown in Figure 6 above.
(d)
Interpretation:
Given line structure is to be drawn using condensed formula.
Concept introduction:
The condensed formula indicates how the atoms should be connected in a given molecule. To arrive at a total charge of zero, each carbon should have a maximum of four bonds while each oxygen should have a maximum of two bonds and two lone pairs. A parenthesis in the condensed formula represents that the repetitive unit is attached to the previous carbon atom. Rings are generally now shown in their condensed formulas, but they are commonly shown in their partially condensed form. Multiple bonds in the ring and outside the ring are shows as they are. Parentheses are also used to clarify when two or three groups are attached to the same carbon atom.
Answer to Problem 1.64P
For the given line structure, the condensed structure is:
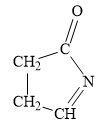
Explanation of Solution
The given line structure is:
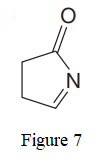
In the given line structure, a five membered ring containing a nitrogen atom is present. While writing a condensed formula, a ring is shown in its partial condensed formula. One of the carbon atoms in the ring forms a double bond with the oxygen atom which is shown as is.
Thus, the condensed structure for the given line structure is:
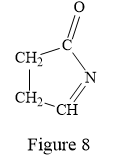
The condensed structure for the given line structure is shown in Figure 8 above.
(e)
Interpretation:
Given line structure is to be drawn using condensed formula.
Concept introduction:
The condensed formula indicates how the atoms should be connected in a given molecule. Each non-hydrogen atom is written explicitly, followed immediately by the number of hydrogen atoms that are bonded to it. Multiple bonds are not shown explicitly in the condensed structure. To arrive at a total charge of zero, each carbon should have a maximum of four bonds while each oxygen should have a maximum of two bonds and two lone pairs. A parenthesis in the condensed formula represents that the repetitive unit is attached to the previous carbon atom. Rings are generally shown in their condensed formulas, but they are commonly shown in their partially condensed form. Parentheses are also used to clarify when two or three groups are attached to the same carbon atom.
Answer to Problem 1.64P
For the given line structure, the condensed structure is:
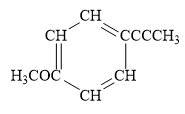
Explanation of Solution
The given line structure is:
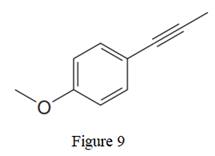
In the above line structure, the disubstituted benzene ring is present. One substituent of the benzene ring is a three carbon chain with an internal triple bond. The other substituent is a methoxy group,
Thus, the condensed structure for the given line structure is:
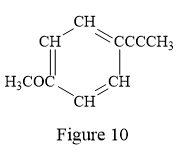
The condensed structure for the given line structure is shown in Figure 10 above.
(f)
Interpretation:
Given line structure is to be drawn using condensed formula.
Concept introduction:
The condensed formula indicates how the atoms should be connected in a given molecule. Each non-hydrogen atom is written explicitly, followed immediately by the number of hydrogen atoms that are bonded to it. To arrive at a total charge of zero, each carbon should have a maximum of four bonds while each oxygen should have a maximum of two bonds and two lone pairs. A parenthesis in the condensed formula represents that the repetitive unit is attached to the previous carbon atom. Rings are generally now shown in their condensed formulas, but they are commonly shown in their partially condensed form. Parentheses are also used to clarify when two or three groups are attached to the same carbon atom. A formal charge is shown explicitly on the atom.
Answer to Problem 1.64P
For the given line structure, the condensed structure is:
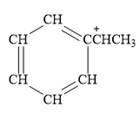
Explanation of Solution
The given line structure is:
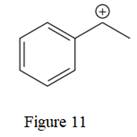
The above line structure is a structure for a cation. A carbocation is a carbon bearing a positive formal charge which is explicitly shown in the condensed formula. A six membered carbon ring with alternate double and single bonds is present and is shown as a partial condensed structure.
Thus, the condensed structure for the given line structure is:
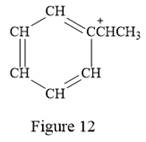
The condensed structure for the given line structure is shown in Figure 12 above.
(g)
Interpretation:
Given line structure is to be drawn using condensed formula.
Concept introduction:
The condensed formula indicates how the atoms should be connected in a given molecule. Each non-hydrogen atom is written explicitly, followed immediately by the number of hydrogen atoms that are bonded to it. To arrive at a total charge of zero, each carbon should have a maximum of four bonds while each oxygen should have a maximum of two bonds and two lone pairs. A parenthesis in the condensed formula represents that the repetitive unit is attached to the previous carbon atom. Rings are generally now shown in their condensed formulas, but they are commonly shown in their partially condensed form. Parentheses are also used to clarify when two or three groups are attached to the same carbon atom. A formal charge is shown explicitly on the atom.
Answer to Problem 1.64P
For the given line structure, the condensed structure is:
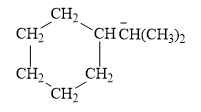
Explanation of Solution
The given line structure is:
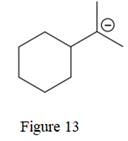
The above line structure is a structure for an anion. A six membered carbon ring with single bonds is present. Each carbon atom is written explicitly followed immediately by the number of hydrogen atoms that are bonded to it. The negative charge on the carbon atom is shown explicitly. The two methyl groups attached to the carbon bearing a negative charge are shown in the parenthesis.
Thus, the condensed structure for the given line structure is:
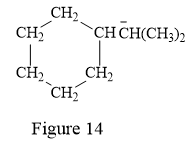
The condensed structure for the given line structure is shown in Figure 14 above.
(h)
Interpretation:
Given line structure is to be drawn using condensed formula.
Concept introduction:
The condensed formula indicates how the atoms should be connected in a given molecule. Each non-hydrogen atom is written explicitly, followed immediately by the number of hydrogen atoms that are bonded to it. To arrive at a total charge of zero, each carbon should have a maximum of four bonds while each oxygen should have a maximum of two bonds and two lone pairs. A parenthesis in the condensed formula represents that the repetitive unit is attached to the previous carbon atom. Rings are generally now shown in their condensed formulas, but they are commonly shown in their partially condensed form. Parentheses are also used to clarify when two or three groups are attached to the same carbon atom. A formal charge is shown explicitly on the atom.
Answer to Problem 1.64P
For the given line structure, the condensed structure is:
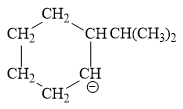
Explanation of Solution
The given line structure is:
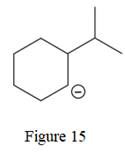
The above line structure is a six membered ring with a negative charge on one of the carbon atoms of the ring. The carbon bearing a negative charge is shown as is. The ring is monosubstituted with an isopropyl group. The two methyl groups in the isopropyl fragments is shown with the help of parenthesis.
Thus, the condensed structure for the given line structure is:
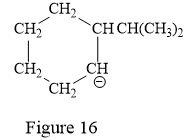
The condensed structure for the given line structure is shown in Figure 16 above.
(i)
Interpretation:
Given line structure is to be drawn using condensed formula.
Concept introduction:
The condensed formula indicates how the atoms should be connected in a given molecule. To arrive at a total charge of zero, each carbon should have a maximum of four bonds while each oxygen should have a maximum of two bonds and two lone pairs. A parenthesis in the condensed formula represents that the repetitive unit is attached to the previous carbon atom. The
Answer to Problem 1.64P
For the given line structure, the condensed structure is:
![]()
Explanation of Solution
The given line structure is:
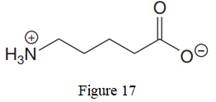
The above line structure is a chain of five carbon atoms. One end of the chain has carboxylate ion, in which the oxygen carries a negative charge. The other end of the chain has a nitrogen atom with three hydrogen atoms directly attached to it and carrying a positive charge. Formal charges on atoms are shown explicitly.
Thus, the condensed structure for the given line structure is:
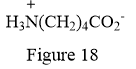
The condensed structure for the given line structure is shown in Figure 18 above.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: PRINCIPLES AND M
- ogin - PaymentN MapQuest 3 Overview - SAP NetW... Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. CI 1. NaBH4 2. H₂O C Clever | Portal Job Op Problem Atoms, Bonds and Rings Draw or tap a new bond toarrow_forward2. Draw the remaining two resonance structures for the carbocation intermediate in the meta nitration of methyl benzoate AND explain why the meta orientation is preferred. Hint: how is the placement of the cation favorable after addition of nitronium relative to the electron withdrawing group? (2 pts) H NO2 CO₂Mearrow_forwardLabel all absorptions over 1500 cm-1. Please be specific and mark IR if needed for explanation. Compound OH sp^3 C-H C=O C-O Triglyceridearrow_forward
- Identify the intermediate that is INITIALLY formed in a saponification reaction (hydrolysis of an ester). III -OH H₂O HO OH HO O || A B C III D IV IVarrow_forwardHelp me answer this practice sheet I found for an answer guidearrow_forwardshow the retrosynthesis of this molecule step by step starting with 1,3-dimethoxy benzene H3CO OH OH OCH 3arrow_forward
- Consider the reaction of a propanoate ester with hydroxide ion shown below. A series of four alcohol leaving groups were tested to determine which would be the best leaving group. Based on the pKa values of the alcohols, predict which alcohol would produce the fastest hydrolysis reaction. HO FOR A Alcohol I, pKa =16.0 B Alcohol II, pKa =10.0 C Alcohol III, pKa = 7.2 + ROH D Alcohol IV, pKa = 6.6arrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. :0: NaOH, H₂O 00:4 Na O heat NaO Select to Add Arrows Select to Add Arrows :0: Na a NaOH, H2O :0: NaOH, H2O heat heat Na ONH Select to Add Arrowsarrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. H CH3NH3+ :0: :0: HO CH3NH2 HH iSelect to Add Arrows i Select to Add Arrows i HH CH3NH3+ CH3NH2 Select to Add Arrows i CH3NH3 CH3NH2 ايكدا HH Select to Add Arrowsarrow_forward
- The reaction is carried out with gases: A → B + C at 300 K. The total pressure is measured as a function of time (table). If the reaction order is 2, calculate the rate or kinetic constant k (in mol-1 L s¹) Ptotal (atm) 492 676 760 808 861 t(s) 0 600 1200 1800 3000arrow_forwardcan someone give a description of this NMR including whether its a triplt singlet doublet where the peak is around at ppm and what functional group it representsarrow_forward1. Determine the relationship between the following molecules as identical, diastereomers, or enantiomers (6 points, 2 points each). OH OH OH A-A OH HOT HO- ACHN and HO- ACHN OH HO HO ° OH and OH OH SH and ...SHarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





