
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure for the given molecule is to be completed.
Concept introduction:
Lewis structures involve only valence electrons. When drawing a Lewis structure, the first step is to calculate the total number of valence electrons. For a complete Lewis structure of a molecule, the atoms must complete their normal valency by bond formation and lone pairs of electrons. Maximum number of covalent bonds formed by any neutral atom with maximum number of lone pairs is
| Atom | Number of bond | Number of lone pairs |
| C | 4 | 0 |
| H | 1 | 0 |
| O | 2 | 2 |
| N | 1 | 1 |
| F | 1 | 3 |
Answer to Problem 1.46P
The complete Lewis structure for the given molecule is
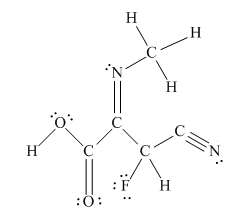
Explanation of Solution
The given structure is
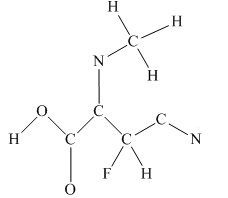
Total valence electron count for the given molecule is
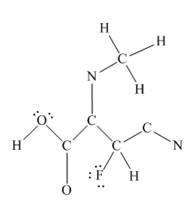
The other oxygen atom has formed only one bond with carbon. This is converted to a double bond and two lone pairs are placed on the oxygen atom so that its octet is complete. A double bond is placed between C and N atom to complete the octet of carbon and a lone pair is placed in nitrogen to complete its octet.
A triple bond is placed between the other C and N to complete the octet of carbon and a lone pair is placed in the nitrogen to complete its octet.

This structure now accounts for all 54 electrons and the octet of each atom, except hydrogen, is complete. The duet for all hydrogens is complete.
The Lewis structure for the given molecule is completed from total valence electron count.
(b)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure for the given molecule is to be completed.
Concept introduction:
Lewis structures involve only valence electrons. When drawing a Lewis structure, the first step is to calculate the total number of valence electrons. For a complete Lewis structure of a molecule, every carbon atom must form four covalent bonds whereas the hydrogen atom forms one bond.
Answer to Problem 1.46P
The complete Lewis structure for the given molecule is
Explanation of Solution
The given structure is
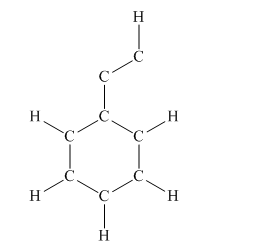
Total valence electron count for the given molecule must be

This structure now accounts for all 38 electrons and the octet of each atom, except hydrogen, is complete. The duet for all hydrogen atoms is complete.
The Lewis structure for the given molecule is completed from total valence electron count.
(c)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure for the given molecule is to be completed.
Concept introduction:
Lewis structures involve only valence electrons. When drawing a Lewis structure, the first step is to calculate the total number of valence electrons. For a complete Lewis structure of a molecule, the atoms must complete their normal valency by bond formation and lone pairs of electrons. Maximum numbers of covalent bonds formed by any neutral atom with maximum number of lone pair are
| Atom | Number of bond | Number of lone pairs |
| C | 4 | 0 |
| H | 1 | 0 |
| O | 2 | 2 |
| N | 1 | 1 |
Answer to Problem 1.46P
The complete Lewis structure for the given molecule is
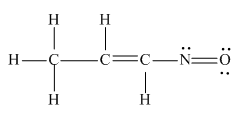
Explanation of Solution
The given structure is
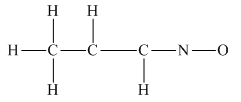
Total valence electron count for the given molecule is
The oxygen atom has formed only one bond with nitrogen. This is converted to a double bond and two lone pairs are placed on the oxygen atom so that its octet is complete. Another lone pair is placed on the nitrogen atom so that its octet is complete.
A double bond is placed between the C atoms attached to one hydrogen each. This completes the octet of both carbon atoms

This structure now accounts for all the 28 electrons, and the octet of each atom, except hydrogen, is complete. The duet for all hydrogen atoms is complete.
The Lewis structure for the given molecule is completed from total valence electron count.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: PRINCIPLES AND M
- 3) Draw a detailed mechanism and predict the product of the reaction shown? 1) EtMgBr 2) H3O+arrow_forwardHow to draw the mechanism for this reaction?arrow_forward> H₂C=C-CH2-CH3 B. H₂O Pt C. + H2 + H₂O H D. 16. Give the IUPAC name for each of the following: B. Cl Cl c. Cl Cl 17. Draw the line-angle formula for each of the following compounds: 1. phenol 2. 1,3-dichlorobenzene 3. 4-ethyltoluene < Previous Submit Assignment Next ▸arrow_forward
- Consider the following nucleophilic substitution reaction. The compound listed above the arrow is the solvent for the reaction. If nothing is listed over the arrow, then the nucleophile is also the solvent for the reaction. Part 1 of 2 Br CH,CN + I¯ What is the correct mechanism for the reaction? Select the single best answer. @SN2 ○ SN 1 Part: 1/2 Part 2 of 2 Draw the products for the reaction. Include both the major organic product and the inorganic product. If more than one stereoisomer is possible, draw only one stereoisomer. Include stereochemistry where relevant. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X હૈarrow_forward20.33 Think-Pair-Share (a) Rank the following dienes and dienophiles in order of increasing reactivity in the Diels-Alder reaction. (i) CO₂Et (ii) COEt || CO₂Et MeO MeO (b) Draw the product that results from the most reactive diene and most reactive dienophile shown in part (a). (c) Draw a depiction of the orbital overlap involved in the pericyclic reaction that oc- curs between the diene and dienophile in part (b). (d) Is the major product formed in part (b) the endo or exo configuration? Explain your reasoning.arrow_forward20.40 The following compound undergoes an intramolecular Diels-Alder reaction to give a tricyclic product. Propose a structural formula for the product. CN heat An intramolecular Diels-Alder adductarrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

