
Concept explainers
Assign formal charges to each
a. 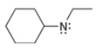 b.
b. 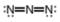 c.
c. 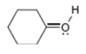 d.
d. 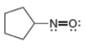
(a)
Interpretation: The formal charge to each
Concept introduction:
The formal charge on an atom is calculated by the formula,
Answer to Problem 1.40P
In the given molecule, the formal charge on nitrogen atom is
Explanation of Solution
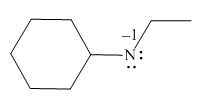
The given molecule is,
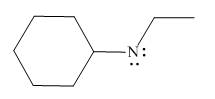
Figure 1
The formal charge on an atom is calculated by the formula,
For the nitrogen atom,
Substitute these values in above equation to calculate the formal charge on nitrogen atom.
Thus, in the given molecule, the formal charge on nitrogen atom is

Figure 2
In the given molecule, the formal charge on nitrogen atom is
(b)
Interpretation: The formal charge to each
Concept introduction: The formal charge on an atom is calculated by the formula,
Answer to Problem 1.40P
The formal charge to each
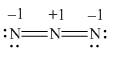
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is,
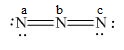
Figure 3
Here, a, b, and c are used to indicate nitrogen atoms.
The formal charge on an atom is calculated by the formula,
For the nitrogen atom,
Substitute these values in the above equation to calculate the formal charge on
In the given molecule, bond pairs and lone pairs in
Thus, the formal charge on
For the nitrogen atom,
Substitute these values in the above equation to calculate the formal charge on
Thus, the formal charge on
Hence, the formal charge to each
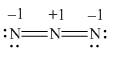
Figure 4
In the given molecule, the formal charge on nitrogen atom of both
(c)
Interpretation: The formal charge to each
Concept introduction: The formal charge on an atom is calculated by the formula,
Answer to Problem 1.40P
In the given molecule, the formal charge on oxygen atom is
Explanation of Solution
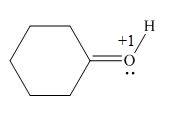
The given species is,
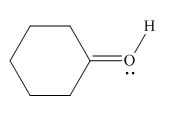
Figure 5
The formal charge on an atom is calculated by the formula,
For the oxygen atom,
Substitute these values in above equation, to calculate the formal charge on oxygen atom.
Thus, in the given molecule, the formal charge on oxygen atom is

Figure 6
In the given molecule, the formal charge on oxygen atom is
(d)
Interpretation: The formal charge to each
Concept introduction: The formal charge on an atom is calculated by the formula,
Answer to Problem 1.40P
In the given molecule, the formal charge on both nitrogen and oxygen atom is zero as shown below.
Explanation of Solution
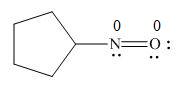
The given species is,
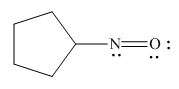
Figure 7
The formal charge on an atom is calculated by the formula,
For the oxygen atom,
Substitute these values in above equation, to calculate the formal charge on oxygen atom.
For the nitrogen atom,
Substitute these values in above equation, to calculate the formal charge on nitrogen atom.
Thus, in the given molecule, the formal charge on both nitrogen and oxygen is zero as shown below.

Figure 8
In the given molecule, the formal charge on both nitrogen and oxygen is zero.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Physical Universe
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
Organic Chemistry
The Cosmic Perspective (8th Edition)
- The number of imaginary replicas of a system of N particlesA) can never become infiniteB) can become infiniteC) cannot be greater than Avogadro's numberD) is always greater than Avogadro's number.arrow_forwardElectronic contribution to the heat capacity at constant volume A) is always zero B) is zero, except for excited levels whose energy is comparable to KT C) equals 3/2 Nk D) equals Nk exp(BE)arrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forward
- Calculate the packing factor of CaTiO3. It has a perovskite structure. Data: ionic radii Co²+ = 0.106 nm, Ti4+ = 0.064 nm, O² = 0.132 nm; lattice constant is a = 2(rTi4+ + ro2-). Ca2+ 02- T14+ Consider the ions as rigid spheres. 1. 0.581 or 58.1% 2. -0.581 or -58.1 % 3. 0.254 or 25.4%arrow_forwardGeneral formula etherarrow_forwardPlease provide the retrosynthetic analysis and forward synthesis of the molecule on the left from the starting material on the right. Please include hand-drawn structures! will upvote! Please correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forward
- Please provide the retrosynthetic analysis and forward synthesis of the molecule on the left from the starting material on the right. Please include hand-drawn structures! will upvote!arrow_forward(please correct answer and don't used hand raiting) Please provide the retrosynthetic analysis and forward synthesis of the molecule on the left from the starting material on the right. Please include hand-drawn structures! will upvote!arrow_forwardCaTiO3 has a perovskite structure. Calculate the packing factor.Data: ionic radii Co+2 = 0.106 nm, Ti+4 = 0.064 nm, O-2 = 0.132 nm; lattice constant is a = 2(rTi4+ + rO-2).(a) 0.581(b) -0.581(c) 0.254(d) -0.254arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





