
Concept explainers
Potomac Automotive Co. manufactures engines that are made only on customers’ orders and to their specifications. During January, the company worked on Jobs 007, 008, 009, and 010. The following figures summarize the cost records for the month:
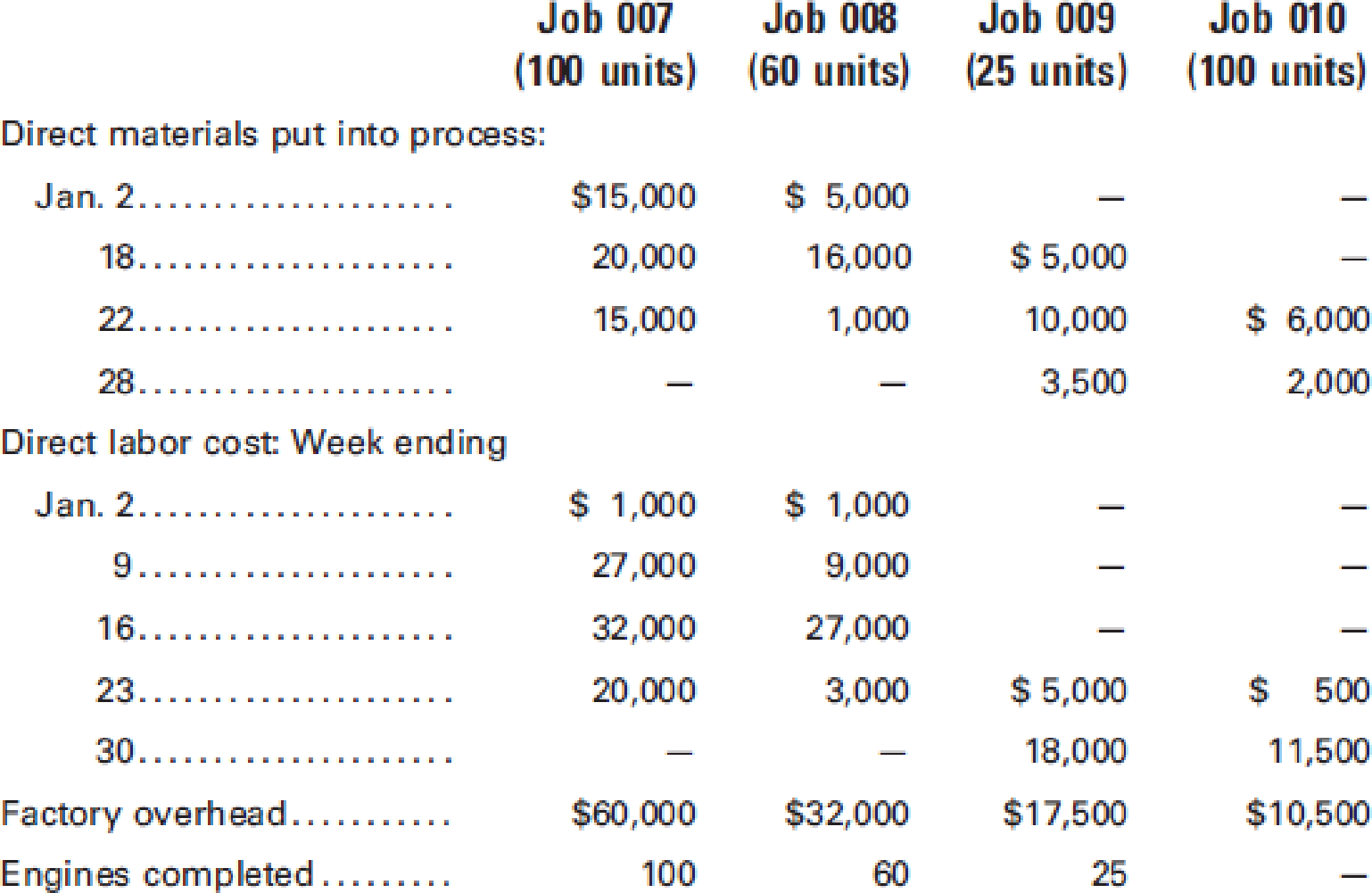
Jobs 007 and 008 have been completed and delivered to the customer at a total selling price of $426,000, on account. Job 009 is finished but has not yet been delivered. Job 010 is still in process. There were no materials or work in process inventories at the beginning of the month. Material purchases were $115,000, and there were no indirect materials used during the month.
Required:
- 1. Prepare a summary showing the total cost of each job completed during the month or in process at the end of the month.
- 2. Prepare the summary
journal entries for the month to record the distribution of materials, labor, andoverhead costs. - 3. Determine the cost of the inventories of completed engines and engines in process at the end of the month.
- 4. Prepare the journal entries to record the completion of the jobs and the sale of the jobs.
- 5. Prepare a statement of cost of goods manufactured.
1.
Determine the total production cost for each job.
Explanation of Solution
Production costs are those costs that are incurred for manufacturing a product or providing the service to the end user. The following are three basic elements of production costs.
Calculate the total production cost for each job.
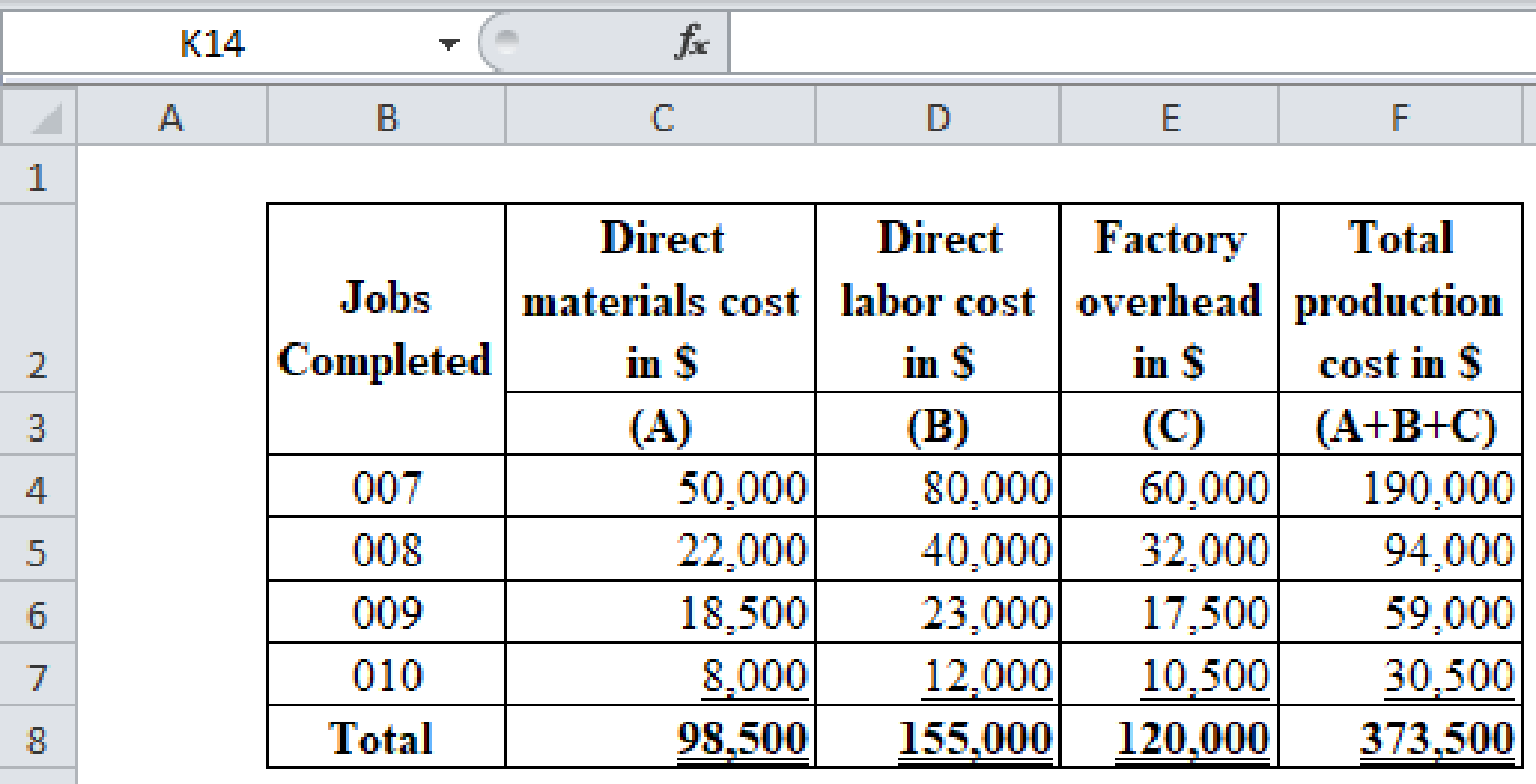
(Figure 1)
Excel workings:
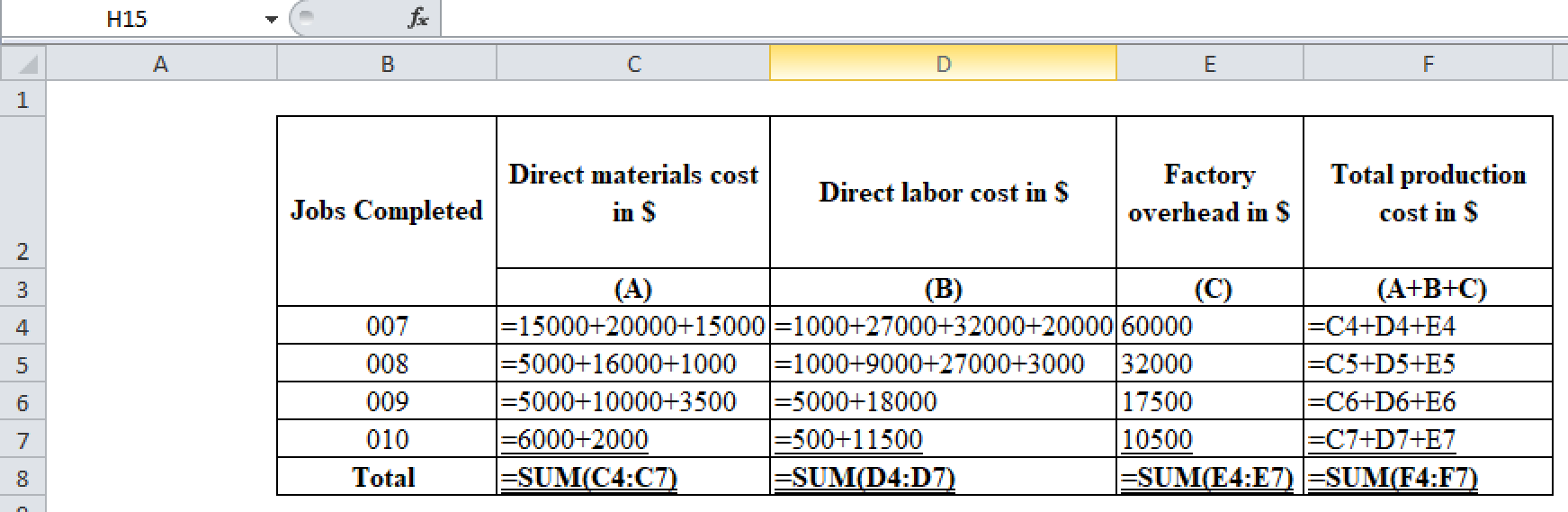
(Figure 2)
2.
Prepare journal entry to record the distribution of materials, labor and overhead cost.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare journal entry to record the distribution of materials, labor and overhead cost.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Work in process inventory | 98,500 | ||
| Material inventory | 98,500 | ||
| (To record the issuance of materials to production) |
(Table 1)
| Date | Accounts title and explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Work in process inventory | 155,000 | ||
| Payroll | 155,000 | ||
| (To record the distribution of payroll) |
(Table 2)
| Date | Accounts title and explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Work in process inventory | 120,000 | ||
| Factory overhead | 120,000 | ||
| (To record the distribution of factory overhead) |
(Table 3)
3.
Identify the cost of the inventories for the engines completed and the engines that are in process during the end of the month.
Explanation of Solution
- Cost of the inventories for the completed and not yet delivered engines is $59,000 (Job 009).
- Cost of inventories that are in process during the end of the month is $30,500 (Job 010).
4.
Prepare journal entry to record the given transactions.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare journal entry to record the completion of jobs.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Finished goods | 343,000 | ||
| Work in process (1) | 343,000 | ||
| (To record jobs that were completed) |
(Table 4)
Prepare journal entry to record the sale of jobs.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Accounts receivable | 426,000 | ||
| Sales | 426,000 | ||
| (To record the sale on account during June) |
(Table 5)
| Date | Accounts title and explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Cost of goods sold (2) | 284,000 | ||
| Finished goods inventory | 284,000 | ||
| (To record cost of goods sold) |
(Table 6)
Working note 1: Calculate the value of jobs completed.
Working note 2: Calculate the value of cost of goods sold.
5.
Compute the Company P’s statement of cost of goods manufactured for the month ended January 31.
Explanation of Solution
Compute the Company P’s statement of cost of goods manufactured for the month ended January 31.
| Company P | ||
| Statement of cost of goods manufactured | ||
| For the month ended January 31 | ||
| Particulars | Amount in $ | Amount in $ |
| Direct materials: | ||
| Inventory, January 1 | 0 | |
| Add: Purchase | 115,000 | |
| Total cost of available materials | 115,000 | |
| Less: Inventory, January 31 (3) | 16,500 | |
| Cost of materials used | 98,500 | |
| Less: Indirect materials used | 0 | |
| Cost of direct materials used in production | 98,500 | |
| Direct labor | 155,000 | |
| Factory Overhead | 120,000 | |
| Total manufacturing cost | 373,500 | |
| Add: work in process inventory, January 1 | 0 | |
| 373,500 | ||
| Less: Work in process inventory, January 31 | 30,500 | |
| Cost of goods sold manufactured | 343,000 | |
(Table 7)
Working note 3: Calculate the value of ending inventory.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Principles of Cost Accounting
- Please don't use AI And give correct answer .arrow_forwardLouisa Pharmaceutical Company is a maker of drugs for high blood pressure and uses a process costing system. The following information pertains to the final department of Goodheart's blockbuster drug called Mintia. Beginning work-in-process (40% completed) 1,025 units Transferred-in 4,900 units Normal spoilage 445 units Abnormal spoilage 245 units Good units transferred out 4,500 units Ending work-in-process (1/3 completed) 735 units Conversion costs in beginning inventory $ 3,250 Current conversion costs $ 7,800 Louisa calculates separate costs of spoilage by computing both normal and abnormal spoiled units. Normal spoilage costs are reallocated to good units and abnormal spoilage costs are charged as a loss. The units of Mintia that are spoiled are the result of defects not discovered before inspection of finished units. Materials are added at the beginning of the process. Using the weighted-average method, answer the following question: What are the…arrow_forwardQuick answerarrow_forward
- Financial accounting questionarrow_forwardOn November 30, Sullivan Enterprises had Accounts Receivable of $145,600. During the month of December, the company received total payments of $175,000 from credit customers. The Accounts Receivable on December 31 was $98,200. What was the number of credit sales during December?arrow_forwardPaterson Manufacturing uses both standards and budgets. For the year, estimated production of Product Z is 620,000 units. The total estimated cost for materials and labor are $1,512,000 and $1,984,000, respectively. Compute the estimates for: (a) a standard cost per unit (b) a budgeted cost for total production (Round standard costs to 2 decimal places, e.g., $1.25.)arrow_forward
 Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College PubPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College PubPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,



