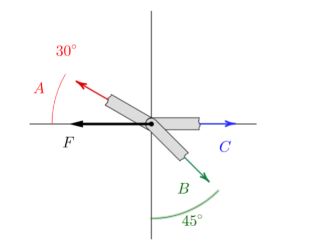
The diagram shows the free body diagram of a joint in a truss which is supporting a load, F. In the FBD the direction (sense) of forces A and B are assumed, so may not be correct. Given: F = 325 kN and C = 200 kN. 1. Draw a neat, labeled free body diagram representing the situation. 2. Write two equilibrium equations, symbolically, based on your free body diagram. 3. Solve your equations to determine the magnitudes of forces A and B necessary for equilibrium. 4. Indicate whether forces A and B are in tension or compression
The diagram shows the free body diagram of a joint in a truss which is supporting a load, F. In the FBD the direction (sense) of forces A and B are assumed, so may not be correct. Given: F = 325 kN and C = 200 kN.
1. Draw a neat, labeled free body diagram representing the situation.
2. Write two equilibrium equations, symbolically, based on your free body diagram.
3. Solve your equations to determine the magnitudes of forces A and B necessary for equilibrium.
4. Indicate whether forces A and B are in tension or compression

Given:
F = 325 kN and C = 200 kN.
1. Draw a neat, labeled free body diagram representing the situation.
2. Write two equilibrium equations, symbolically, based on your free body diagram.
3. Solve your equations to determine the magnitudes of forces A and B necessary for equilibrium.
4. Indicate whether forces A and B are in tension or compression
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images









