Tests the claim that u > µz. Assume the samples are random and independent. 01 = 0.57 ; o2 = 0.53 = 42.69 ; z2 = 42.43 n1 = 41 ; n2 = 42 Standard Error Z-Test Statistic (71 – 72) – (µ – 42) n1 n2 a. Calculate the Standard Error o- = (3 decimal places) b. Calculate the Z-test statistic using the standard error from part a. z = (2 decimal places) c. At a = 0.1, Use the distribution table to find the critical values for the rejection region (3 decimal places)
Q: -11. Test the clatm that the population means are different. Use level of significance 0.01. sample…
A: Solution: Given information: n1= 49 Sample size of population 1n2= 64 Sample size of population…
Q: To test H0: μ=100 versus H1: μ≠100, a simple random sample size of n=18 is obtained from a…
A: Given: Null Hypothesis H0:μ=100 Alternative Hypothesis H1:μ≠100 Sample size n=18
Q: If x is a normally distributed random variable with μ = 18 and o = 2.5, then where will the density…
A: Since you have asked multiple questions, we will solve the first question for you. If you want any…
Q: Height and weight are two measurements used to track a child's development. An organization measures…
A:
Q: you are testing ho: u=0 against ha=u not equal 0 based on an SRS of four observations from a normal…
A: we have given that H0: mu=0 vs Ha:mu not=0 and n=4 ,level of significance (alpha)=0.005
Q: 42. Consider the random variable (X, Y) of Exercise 9. (a) Find the curve of regression of X on Y.…
A: Detailed explanation:Regression Curves and Conditional Expectation:In statistics, regression…
Q: A test is made of Ho: u = 43 versus H;: u> 43. A sample of size n= 60 is drawn, and x= 46. The…
A: Introduction: Denote μ as the true mean of the data. The null and alternative hypotheses are: H0: μ…
Q: What df1 for the interaction between gende
A: From the given output, the df for interaction between gender and age is 2.
Q: Calculate Z-score for a random variable X = 60 is normally distributed with mean = 50 and standard…
A: Mean()=50standard deviation()=8X=60
Q: A random sample is obtained from a population with a mean of µ = 20. After a treatment is…
A: A random sample is obtained from a population with a mean of µ = 20. After treatment is administered…
Q: I wish to determine evaluate whether my sample of 8 apples came from a population that has a mean…
A: Solution: Let X be the mass. The given data for X is 190, 200, 205, 205, 210, 210, 212 and 215.
Q: A population of values has a normal distribution with u = 156.4 and o = 96.5. You intend to draw a…
A: X follows a Normal distribution with mean = 156.4 and S.D = 96.5 x̅ follows a Normal…
Q: None
A: Step 1:Given that Initial TCLP concentrations:6.1, 4.2, 5.8, 6.5 true population mean is 95% The…
Q: Strength of concrete: The compressive strength, in kilopascals, was measured for concrete blocks…
A: The objective of this question is to determine whether there is a significant difference in the mean…
Q: State whether the standardized test statistic t indicates that you should reject the null…
A: Solution: Given information: The critical values are -t0= -2.272 and t0=2.272 The rejection region…
Q: of # o} $1 = 0.75; s2 = 0.71 E = 34.08 ; z2 = 34.32 %3D %3D n1 = 23 ; n2 = 32 %3! a. Calculate the…
A: Note: According to bartleby experts question answers guidelines an expert can solve only first three…
Q: Let x be a random variable representing the dividend yield of some stocks. Assume x has a normal…
A: State the hypotheses.
Q: Given the sample statistics n= 13, F;= 138, L = 577, SFL = -43, SFF= 1735, estimate the expected…
A: It is given that n = 13, ∑F = 138, ∑L = 577 SFL = -43, SFF = 1735
Q: a The dean of a university estimates that the mean number of classroom hours per week for full-time…
A: a)Null and alternate hypothesis: C. H0:μ=11.0Ha:μ≠11.0
Q: Tests the claim that 41 > p2. Assume the samples are normally distributed, random and independent.…
A: Solution Dear students as per guidelines we answer the first three subparts only. Ples pose other in…
Q: A random sample of 61 produced the summary statistics x 0.373 and s = 0.054. Complete parts a and b.…
A:
Q: Use the Shapiro-Wilk test to check the normality assumption for the variable Rct. According to this…
A: The Shapiro-Wilk test is a statistical test used to determine whether a dataset is normally…
Q: Tests the claim that #1 # p2. Assume the samples are normally distributed, random and independent.…
A: Solution
Q: 8.40 (EX) Magnets for pain relief 1/5: A randomized, double-blind experiment studied whether…
A: Given that : n1=29 n2=21
Q: Tests the claim that 41 <2. Assume the samples are random and independent. 01 = 0.65 ; o2 = 0.62 Z1…
A: Note: According to Bartle by experts question answers guidelines an expert can solve only first…
Q: Suppose a company produces lightbulbs with a mean lifetime of 1000 hours and a standard deviation of…
A: The z-score formula is, z=x-μσ In the formula, x be the random variable, μ be the population mean,…
Q: d. Find the probability that more than 68 favor a charter school using the normal approximation and…
A:
Q: Variable Obs Mean Std. dev. Min Max Heigth Weight MaleFemale 8.64 5.074249 1 13.2 170.8 31.67333 130…
A: R hat2 is known as adjusted R-squared.
Q: Use the following data to answer question 8 - 12. A number of studies have claimed evidence that the…
A: From the provided information,

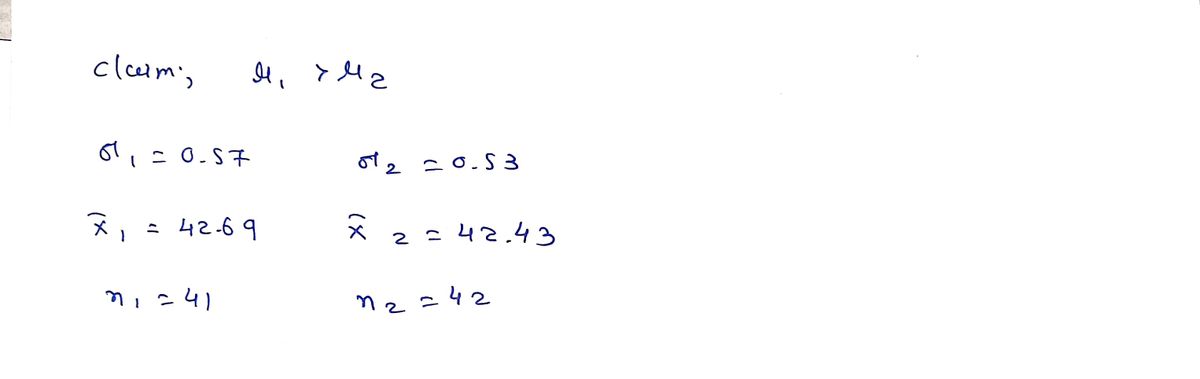
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

- 617. please state all 6 steps of the p method clearly please! Strength of concrete: The compressive strength, in kilopascals, was measured for concrete blocks from five different batches of concrete, both three and six days after pouring. The data are as follows. Can you conclude that the mean strength after three days differs from the mean strength after six days? Let μ1 represent the mean strength after three days and =μd−μ1μ2 . Use the =α0.05 level and the P -value method with the TI-84 Plus calculator. Block 1 2 3 4 5 After 3 days 1371 1379 1344 1383 1386 After 6 days 1328 1337 1344 1321 134526 The table to the right shows the cost per ounce (in dollars) for a random sample of toothpastes exhibiting very good stain removal, good stain removal, and fair stain removal. At α=0.01, can you conclude that the mean costs per ounce are different? Perform a one-way ANOVA test by completing parts a through d. Assume that each sample is drawn from a normal population, that the samples are independent of each other, and that the populations have the same variances. Very good stain removal Good stain removal Fair stain removal 0.37 0.75 0.60 0.49 2.66 1.18 0.33 0.46 0.46 1.64 0.33 0.50 0.58 0.41 1.39 (b) Identify the degrees of freedom for the numerator and for the denominator, determine the critical value, and determine the rejection region. The degrees of freedom for the numerator, d.f.N, is ____ and the degrees of freedom for the denominator, d.f.D, is _____ The critical…
- Tests the claim that 1 # p2. Assume the samples are normally distributed, random and independent. of + o S1 =0.77 ; s2 = 0.82 E1 = 48.92 ; z2 = 48.94 n1 = 24; n2 = 31 a. Calculate the Standard Error s-, = (use 3 decimal places) (use 2 decimal places) b. Calculate the t-test statistic using the standard error from part a. t = c. What are the degrees of freedom? df %3! d. At a = 0.02, Use the distribution table to find the critical values for the rejection region t = ± (use 4 decimal places) e. What is your conclusion? O Fail to reject the null hypothesis and do not support the claim O Reject the alternative hypothesis and support the claim O Accept the null hypothesis and support the claim O Reject the null hypothesis and support the claim O Accept the alternative hypothesis and reject the claim-2 2. 1), find c given P(Z > c) = 0.046, please show you For a standard normal distribution (u 0 and o answer to 2 decimal places.Suppose in a local Kindergarten through 12th grade (K -12) school district, 49% of the population favor a charter school for grades K through 5. A simple random sample of 144 is surveyed. a. Find the mean and the standard deviation of X of B(144, 0.49). Round off to 4 decimal places. O = b. Now approximate X of B(144, 0.49) using the normal approximation with the random variable Y and the table. Round off to 4 decimal places. Y - N( c. Find the probability that at most 81 favor a charter school using the normal approximation and the table. (Round off to z-values up to 2 decimal places.) P(X 75) - P(Y > a (Z > e. Find the probability that exactly 81 favor a charter school using the normal approximation and the table. (Round off to z-values up to 2 decimal places.) P(X = 81) - P(Suppose in a local Kindergarten through 12th grade (K -12) school district, 49% of the population favor a charter school for grades K through 5. A simple random sample of 144 is surveyed. a. Find the mean and the standard deviation of X of B(144, 0.49). Round off to 4 decimal places. O = b. Now approximate X of B(144, 0.49) using the normal approximation with the random variable Y and the table. Round off to 4 decimal places. Y - N( c. Find the probability that at most 81 favor a charter school using the normal approximation and the table. (Round off to z-values up to 2 decimal places.) P(X 75) - P(Y > a (Z > e. Find the probability that exactly 81 favor a charter school using the normal approximation and the table. (Round off to z-values up to 2 decimal places.) P(X = 81) - P(answer pleaseJ Suppose that Shoe Sices Of American women have a bell Shaped elu standard with a mean of 8,37 and a eleviation of 1.49, using the empirical Rule what percentage of american women have Shoe Sizes that are no more than 9.su? do not Roundl your answerplease,detailed solution for you to understandA random sample of size 10 yielded roughly "mound-shaped" data with a sample mean of 63.5 and a sample variance of 60.8. Let (L, OU) be the interval estimate that contains the population mean with 95% probability. Find the width of the interval. That is, find 0 – 0₁. 4.52 5.49 5.58 5.70 9.04 10.99 11.16 11.40 none of the other answers give the correct widthRecommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman