Select four items that are involved in or related to transcriptional control of gene expression (in either pro- or eu-karyotes). -Slide nucleosomes around -control membrane hydrophobicity -methylate DNA -protein denaturation -TFIID and its friends -control mRNA stability -control protein stability -operator/repressor -dynamic instability
The expression of a gene is controlled by a process known as gene regulation. The process of gene regulation occurs in both prokaryote and eukaryotes as the synthesis of various proteins is regulated by this mechanism. The gene regulation in prokaryotes occurs at the transcription level while in eukaryotes it occur at multiple level including epigenetic (DNA level), RNA level (transcriptional and post-transcriptional modification).
The control of gene expression occurs on 2 levels. 1st, transcription is controlled by limiting the mRNA’s amount produced from a particular gene. The 2nd level of control is via post-transcriptional events that involve the regulation of translation of mRNA into the proteins.
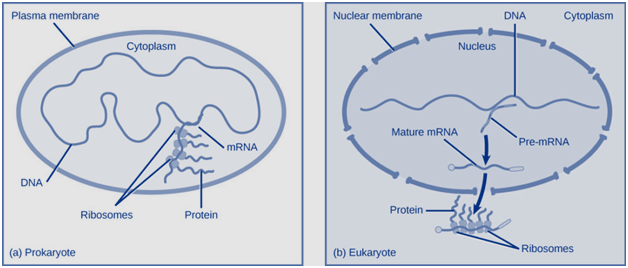
Prokaryotic organisms lacks cell nucleus and are single celled organisms. The DNA in the prokaryotic organism float freely in the cytoplasm of cell as there is no cell nucleus. In synthesis of protein, the process of transcription as well as translation almost occurs simultaneously. The transcription stops when no more protein is needed. As a result, regulation of the DNA transcription is a primary method to control the type of protein and amount of each protein expressed in the prokaryotic cell. All subsequent steps automatically occur. More transcription occurs when more protein is required. Therefore, the control of gene expression in the prokaryotic cells is at transcriptional level mostly.
In contrast, the eukaryotic cell possesses intracellular organelles adding to their complexity. The DNA is present inside the nucleus of the cell and the transcription of DNA into the RNA occurs here. After the synthesis of RNA, it is transported out of the nucleus to the cytoplasm of the cell. Then, in the cytoplasm ribosome translate RNA into proteins. So, transcription occurs inside the nucleus whereas the translation occurs in the cytoplasm. Therefore, the gene regulation may occur at any stage of the process. Regulation can occur at the epigenetic level when the DNA is uncoiled as well loosened from the nucleosome and bind transcription factors. Gene regulation may occur at the transcriptional level when the transcription of the RNA occurs. It may occur at the post transcriptional level when the RNA is transported out to the cytoplasm. It may occur at the translational level when the translation of RNA into protein occurs as well as it may occur at the post translational level after the protein is synthesized.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images









