Qloss = 90kW 250 kPa Combustion 80 kPa 650°C gases 420°C 70 m/s m = 1.2 kg/s m = 1.2 kg/s
Theory and Design for Mechanical Measurements
Measurement is a term that refers to analyzing a manufactured component regarding the degree of accuracy for dimensions, tolerances, geometric profile, roundness, flatness, smoothness, etc. Measurement always involves comparing the manufactured component or the prototype with a standard specimen whose dimensions and other parameters are assumed to be perfect and do not undergo changes with respect to time.Precisely in mechanical engineering the branch that deals with the application of scientific principles for measurements is known as metrology. The domain of metrology in general deals with various measurements like mechanical, chemical, thermodynamic, physical, and biological measurements. In mechanical engineering, the measurements are limited to mechanical specific such as length, mass, surface profile, flatness, roundness, viscosity, heat transfer, etc.
Basic principles of engineering metrology
Metrology is described as the science of measurement, precision, and accuracy. In other words, it is a method of measurement based on units and predefined standards.
This is a repeated question.
I have asked this question but it was rejected. I am submitting the problems to check my understanding. I completed the problems already and I am not being graded on them.
If you are able to, please state your assumptions and table.


Given data,

Assumptions: -
(1) The flow is assumed to be steady and incompressible
(2) The gas is assumed to be an ideal gas.
Writing the steady flow energy equation for the nozzle,
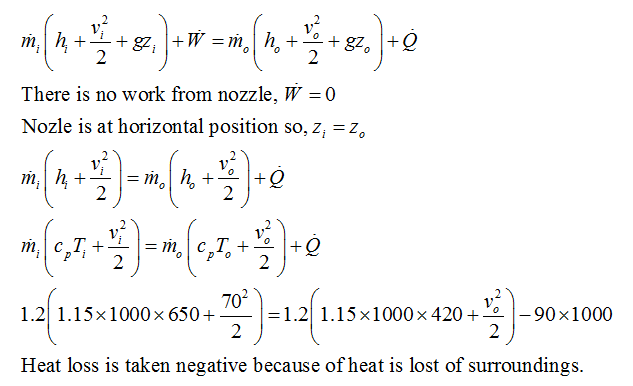

Velocity at the exit of the nozzle is 827 m/sec.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 7 images









