In this lab, you will practice defining and using interface, abstract class, abstract methods , superclass and subclass. You will write an inheritance hierarchy of three-dimensional shapes. Make a top-level shape interface that has methods for getting information such as the volume and surface area of a three-dimensional shape. Then make classes and subclasses that implement various shapes such as spheres, cylinders. You will also place common behavior in superclasses whenever possible, and use abstract classes as appropriate. Add methods to the subclasses to represent the unique behavior of each three-dimensional shape, such as a method to get a sphere’s radius. You need to figure out the formulas to calculate the area, surface area and volume for different shapes.1. Use NetBeans IDE to do the following: a. Start NetBeans.b. Please create a new project in a folder in your H: drive or your own flash drive and name your new project as:COSC241_c. Under the above new created project, please create a package named Lab2d. In the Lab2 package create an interface named Shape3D.java with the following code:// An interface for three-dimensional shapes.public interface Shape3D { public double getVolume(); public double getSurfaceArea();}e. In the Lab2 package create a class named Sphere.java, the class Sphere should implement the interface Shape3d. Define the class Sphere with following requirements:// Represents a perfect sphere.public class Sphere implements Shape3D {//fill in instance fields required by a shape sphere ... //Constructor ... // Define a new methods return the radius COSC241Lab2Page 2 of 4 public double getRadius() { ...// fill in corresponding statement to return the raduis }public double getSurfaceArea() { .... // Fill in statements return the surface area } public double getVolume() { .... //// Fill in statements return the volume }}f. In the Lab2 package create an abstract class named CircularShape.java which implements interface Shape3D. The abstract class CircularShape will work as a superclass. // An abstract superclass for shapes with a circular cross-section.public abstract class CircularShape implements Shape3D { //fill in instance fields required ... //Constructor ... public double getDiameter() { ...// fill in corresponding statement } public double getRadius() { ...// fill in corresponding statement } public double getCrossSectionArea() { ...// fill in statements to return the area of cross section } public double getCrossSectionPerimeter() { ...// fill in statements to return the perimeter of cross section }}g. In the Lab2 package create an abstract class named CircularShapeWithHeight.java which extends CircularShape. The abstract COSC241Lab2Page 3 of 4class CircularShapeWithHeight will be defined with new field data and a new methods as following:// An abstract superclass for shapes with a circular cross-section// that extends over some height.public abstract class CircularShapeWithHeight extends CircularShape { // add new instance of height ... // Constructor ..... public double getHeight() { ....// add statements return the height of the shape }}h. In the Lab2 package create a class named Cylinder.java which extends CircularShapeWithHeight. The class Cylinder will be defined as following:// Represents a cylinder shape.public class Cylinder extends CircularShapeWithHeight {// instance fields ......//Constructor ....... public double getSurfaceArea() { ......// Add statements here to return the surface of the cylinder } public double getVolume() { ........// add statements here to return the volume of the cylinder }}i. In Lab2 package you will create a class called testShapes.java. In the testShapes, created a static void main method where you will test the two different 3-dimensional shapes. You should use Scanner to let user input values from keyboard to define the shapes.The output of running your testShape.java should be like following:Please enter the radius for a sphere:The radius you entered is 5.The surface area of your sphere is 314.1592653589793 and its volumn is 523.5987755982989 Please enter the radius and height for a cylinder:The radius is 5 and the height is 6 . COSC241Lab2Page 4 of 4The surface area of your Cylinder is 345.5751918948772 and its volumn is 471.23889803846896j. Save your files, test the above program, and debug if needed.
In this lab, you will practice defining and using interface, abstract class, abstract methods , superclass and subclass. You will write an inheritance hierarchy of three-dimensional shapes. Make a top-level shape interface that has methods for getting information such as the volume and surface area of a three-dimensional shape. Then make classes and subclasses that implement various shapes such as spheres, cylinders. You will also place common behavior in superclasses whenever possible, and use abstract classes as appropriate. Add methods to the subclasses to represent the unique behavior of each three-dimensional shape, such as a method to get a sphere’s radius. You need to figure out the formulas to calculate the area, surface area and volume for different shapes.1. Use NetBeans IDE to do the following: a. Start NetBeans.b. Please create a new project in a folder in your H: drive or your own flash drive and name your new project as:COSC241_c. Under the above new created project, please create a package named Lab2d. In the Lab2 package create an interface named Shape3D.java with the following code:// An interface for three-dimensional shapes.public interface Shape3D { public double getVolume(); public double getSurfaceArea();}e. In the Lab2 package create a class named Sphere.java, the class Sphere should implement the interface Shape3d. Define the class Sphere with following requirements:// Represents a perfect sphere.public class Sphere implements Shape3D {//fill in instance fields required by a shape sphere ... //Constructor ... // Define a new methods return the radius COSC241Lab2Page 2 of 4 public double getRadius() { ...// fill in corresponding statement to return the raduis }public double getSurfaceArea() { .... // Fill in statements return the surface area } public double getVolume() { .... //// Fill in statements return the volume }}f. In the Lab2 package create an abstract class named CircularShape.java which implements interface Shape3D. The abstract class CircularShape will work as a superclass. // An abstract superclass for shapes with a circular cross-section.public abstract class CircularShape implements Shape3D { //fill in instance fields required ... //Constructor ... public double getDiameter() { ...// fill in corresponding statement } public double getRadius() { ...// fill in corresponding statement } public double getCrossSectionArea() { ...// fill in statements to return the area of cross section } public double getCrossSectionPerimeter() { ...// fill in statements to return the perimeter of cross section }}g. In the Lab2 package create an abstract class named CircularShapeWithHeight.java which extends CircularShape. The abstract COSC241Lab2Page 3 of 4class CircularShapeWithHeight will be defined with new field data and a new methods as following:// An abstract superclass for shapes with a circular cross-section// that extends over some height.public abstract class CircularShapeWithHeight extends CircularShape { // add new instance of height ... // Constructor ..... public double getHeight() { ....// add statements return the height of the shape }}h. In the Lab2 package create a class named Cylinder.java which extends CircularShapeWithHeight. The class Cylinder will be defined as following:// Represents a cylinder shape.public class Cylinder extends CircularShapeWithHeight {// instance fields ......//Constructor ....... public double getSurfaceArea() { ......// Add statements here to return the surface of the cylinder } public double getVolume() { ........// add statements here to return the volume of the cylinder }}i. In Lab2 package you will create a class called testShapes.java. In the testShapes, created a static void main method where you will test the two different 3-dimensional shapes. You should use Scanner to let user input values from keyboard to define the shapes.The output of running your testShape.java should be like following:Please enter the radius for a sphere:The radius you entered is 5.The surface area of your sphere is 314.1592653589793 and its volumn is 523.5987755982989 Please enter the radius and height for a cylinder:The radius is 5 and the height is 6 . COSC241Lab2Page 4 of 4The surface area of your Cylinder is 345.5751918948772 and its volumn is 471.23889803846896j. Save your files, test the above program, and debug if needed.
Database System Concepts
7th Edition
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Chapter1: Introduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1PE
Related questions
Question
100%
In this lab, you will practice defining and using interface, abstract class, abstract methods , superclass and subclass. You will write an inheritance hierarchy of three-dimensional shapes. Make a top-level shape interface that has methods for getting information such as the volume and surface area of a three-dimensional shape. Then make classes and subclasses that implement various shapes such as spheres, cylinders. You will also place common behavior in superclasses whenever possible, and use abstract classes as appropriate. Add methods to the subclasses to represent the unique behavior of each three-dimensional shape, such as a method to get a sphere’s radius. You need to figure out the formulas to calculate the area, surface area and volume for different shapes.1. Use NetBeans IDE to do the following: a. Start NetBeans.b. Please create a new project in a folder in your H: drive or your own flash drive and name your new project as:COSC241<your section number>_<your username>c. Under the above new created project, please create a package named Lab2d. In the Lab2 package create an interface named Shape3D.java with the following code:// An interface for three-dimensional shapes.public interface Shape3D { public double getVolume(); public double getSurfaceArea();}e. In the Lab2 package create a class named Sphere.java, the class Sphere should implement the interface Shape3d. Define the class Sphere with following requirements:// Represents a perfect sphere.public class Sphere implements Shape3D {//fill in instance fields required by a shape sphere ... //Constructor ... // Define a new methods return the radius
COSC241Lab2Page 2 of 4 public double getRadius() { ...// fill in corresponding statement to return the raduis }public double getSurfaceArea() { .... // Fill in statements return the surface area } public double getVolume() { .... //// Fill in statements return the volume }}f. In the Lab2 package create an abstract class named CircularShape.java which implements interface Shape3D. The abstract class CircularShape will work as a superclass. // An abstract superclass for shapes with a circular cross-section.public abstract class CircularShape implements Shape3D { //fill in instance fields required ... //Constructor ... public double getDiameter() { ...// fill in corresponding statement } public double getRadius() { ...// fill in corresponding statement } public double getCrossSectionArea() { ...// fill in statements to return the area of cross section } public double getCrossSectionPerimeter() { ...// fill in statements to return the perimeter of cross section }}g. In the Lab2 package create an abstract class named CircularShapeWithHeight.java which extends CircularShape. The abstract
COSC241Lab2Page 3 of 4class CircularShapeWithHeight will be defined with new field data and a new methods as following:// An abstract superclass for shapes with a circular cross-section// that extends over some height.public abstract class CircularShapeWithHeight extends CircularShape { // add new instance of height ... // Constructor ..... public double getHeight() { ....// add statements return the height of the shape }}h. In the Lab2 package create a class named Cylinder.java which extends CircularShapeWithHeight. The class Cylinder will be defined as following:// Represents a cylinder shape.public class Cylinder extends CircularShapeWithHeight {// instance fields ......//Constructor ....... public double getSurfaceArea() { ......// Add statements here to return the surface of the cylinder } public double getVolume() { ........// add statements here to return the volume of the cylinder }}i. In Lab2 package you will create a class called testShapes.java. In the testShapes, created a static void main method where you will test the two different 3-dimensional shapes. You should use Scanner to let user input values from keyboard to define the shapes.The output of running your testShape.java should be like following:Please enter the radius for a sphere:The radius you entered is 5.The surface area of your sphere is 314.1592653589793 and its volumn is 523.5987755982989 Please enter the radius and height for a cylinder:The radius is 5 and the height is 6 .
COSC241Lab2Page 4 of 4The surface area of your Cylinder is 345.5751918948772 and its volumn is 471.23889803846896j. Save your files, test the above program, and debug if needed.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Note: Please Check the formulas of Sphere and Cylinder once.
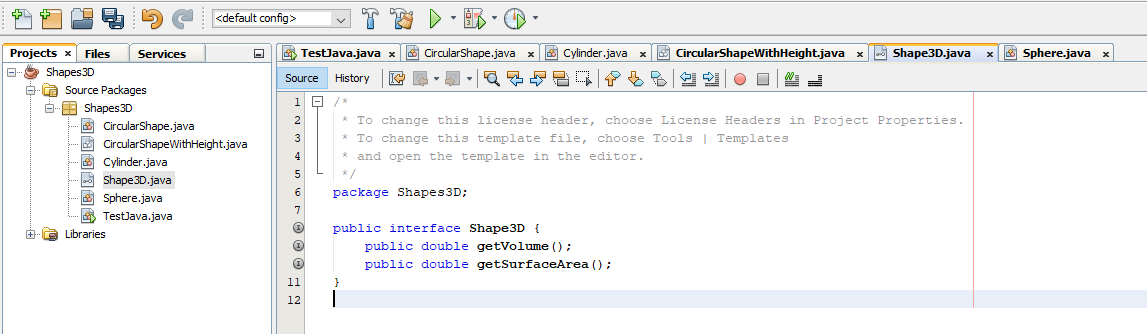
Shape3D Interface:
package Shapes3D;
public interface Shape3D {
public double getVolume();
public double getSurfaceArea();
}
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 6 steps with 7 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:
9780078022159
Author:
Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:
9780134444321
Author:
Tony Gaddis
Publisher:
PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:
9780132737968
Author:
Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:
PEARSON

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:
9780078022159
Author:
Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:
9780134444321
Author:
Tony Gaddis
Publisher:
PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:
9780132737968
Author:
Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:
PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:
9780133976892
Author:
Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:
PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag…
Computer Science
ISBN:
9781337627900
Author:
Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:
9780073373843
Author:
Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education