a uniform temperature change in both bars CD and EF. Determine the temperature change (AT) at which points A and E first come into contact. Report your answer rounded to the nearest degree. 100 in initial gap = 0.11 in I T E A AEF 100 in = 2.0 in² EEF = 12,000 ksi EF = 13.5 x 10-6 1/°F LEF = 50 in B 14 k 100 in C ACD ECD = 1.5 in² Y = 29,000 ksi acD = 6.5 x 10-6 1/°F LCD = 150 in Z
a uniform temperature change in both bars CD and EF. Determine the temperature change (AT) at which points A and E first come into contact. Report your answer rounded to the nearest degree. 100 in initial gap = 0.11 in I T E A AEF 100 in = 2.0 in² EEF = 12,000 ksi EF = 13.5 x 10-6 1/°F LEF = 50 in B 14 k 100 in C ACD ECD = 1.5 in² Y = 29,000 ksi acD = 6.5 x 10-6 1/°F LCD = 150 in Z
Engineering Fundamentals: An Introduction to Engineering (MindTap Course List)
5th Edition
ISBN:9781305084766
Author:Saeed Moaveni
Publisher:Saeed Moaveni
Chapter12: Electric Current And Related Variables In Engineering
Section12.2: Electrical Circuits And Components
Problem 6BYG
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:### Problem Statement
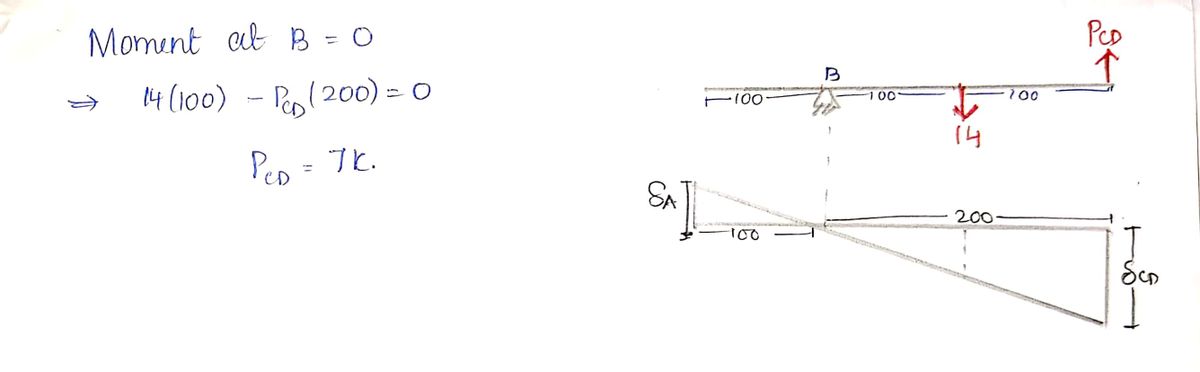
Bar ABC is rigid and rotates freely about point B. The loads consist of a point load and a uniform temperature change in both bars CD and EF. Determine the temperature change (ΔT) at which points A and E first come into contact. Report your answer rounded to the nearest degree.
### Diagram Explanation
The diagram shows a setup where bar ABC is horizontal and supported at point B. It is subject to a 14 kips (14,000 pounds) load at point C. Two vertical bars, CD and EF, connect at points C and E respectively.
**Bar CD:**
- Sectional Area (\(A_{CD}\)): 1.5 in²
- Young's Modulus (\(E_{CD}\)): 29,000 ksi
- Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (\(\alpha_{CD}\)): \(6.5 \times 10^{-6}\) 1/°F
- Length (\(L_{CD}\)): 150 in
**Bar EF:**
- Sectional Area (\(A_{EF}\)): 2.0 in²
- Young's Modulus (\(E_{EF}\)): 12,000 ksi
- Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (\(\alpha_{EF}\)): \(13.5 \times 10^{-6}\) 1/°F
- Length (\(L_{EF}\)): 50 in
### Initial Conditions
- The initial gap between points A and E is 0.11 inches.
- Bar ABC measures 300 inches in total, with 100 inches spacing between each point (A to B, B to C, and C to D).
### Axes and Orientation
- The vertical axis is labeled as Y.
- The horizontal axis into the paper is labeled as Z.
The problem involves calculating the temperature change required for thermal expansion in bars CD and EF such that points A and E touch.
Expert Solution
Step 1: Deflection diagram
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Engineering Fundamentals: An Introduction to Engi…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781305084766
Author:
Saeed Moaveni
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Residential Construction Academy: House Wiring (M…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781285852225
Author:
Gregory W Fletcher
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Steel Design (Activate Learning with these NEW ti…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337094740
Author:
Segui, William T.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Fundamentals: An Introduction to Engi…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781305084766
Author:
Saeed Moaveni
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Residential Construction Academy: House Wiring (M…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781285852225
Author:
Gregory W Fletcher
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Steel Design (Activate Learning with these NEW ti…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337094740
Author:
Segui, William T.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Materials Science And Engineering Properties
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781111988609
Author:
Charles Gilmore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Architectural Drafting and Design (MindTap Course…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781285165738
Author:
Alan Jefferis, David A. Madsen, David P. Madsen
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Residential Construction Academy: House Wiring (M…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337402415
Author:
Gregory W Fletcher
Publisher:
Cengage Learning