10) Explain how the Km and [VO] of a reaction between a fixed amount of catalase and a gradually increasing amount of H₂O₂ would be affected by an allosteric inhibitor. Why would the Km and [VO be affected in this way?
10) Explain how the Km and [VO] of a reaction between a fixed amount of catalase and a gradually increasing amount of H₂O₂ would be affected by an allosteric inhibitor. Why would the Km and [VO be affected in this way?
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Chapter1: Biochemistry: An Evolving Science
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
![**Question 10:**
Explain how the Km and [V0] of a reaction between a fixed amount of catalase and a gradually increasing amount of H2O2 would be affected by an allosteric inhibitor. Why would the Km and [V0] be affected in this way?
---
**Explanation:**
To answer this question, it is important to understand the concepts of Km, [V0], and allosteric inhibition:
- **Km (Michaelis constant):** This parameter indicates the substrate concentration at which the reaction velocity is half of the maximum velocity (Vmax). It gives an idea about the affinity of the enzyme for the substrate; a lower Km indicates higher affinity.
- **[V0] (Initial Reaction Velocity):** This is the initial rate at which the reaction occurs when the substrate concentration is very low compared to the enzyme concentration.
- **Allosteric Inhibition:** Allosteric inhibitors bind to an enzyme at a site other than the active site, causing a conformational change that reduces enzyme activity.
**Effect of Allosteric Inhibitors:**
1. **Km Changes:** Typically, allosteric inhibitors may alter the conformation of the enzyme, potentially affecting the affinity of the enzyme for the substrate. This can lead to an increase in Km, indicating that a higher substrate concentration is needed to reach half of Vmax.
2. **[V0] Changes:** The initial velocity ([V0]) can be reduced because the conformational change caused by the inhibitor decreases the overall ability of the enzyme to catalyze the reaction effectively, even at the beginning when substrate concentration is low.
Thus, the presence of an allosteric inhibitor would likely increase the Km and decrease [V0], due to the inhibitor-induced conformational changes affecting substrate binding and catalytic efficiency.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F78a96f4b-c4a7-4e44-95dd-3606c481f172%2F17a7eb7b-28c2-4890-aaca-603425aa0ead%2Fnqingvc_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:**Question 10:**
Explain how the Km and [V0] of a reaction between a fixed amount of catalase and a gradually increasing amount of H2O2 would be affected by an allosteric inhibitor. Why would the Km and [V0] be affected in this way?
---
**Explanation:**
To answer this question, it is important to understand the concepts of Km, [V0], and allosteric inhibition:
- **Km (Michaelis constant):** This parameter indicates the substrate concentration at which the reaction velocity is half of the maximum velocity (Vmax). It gives an idea about the affinity of the enzyme for the substrate; a lower Km indicates higher affinity.
- **[V0] (Initial Reaction Velocity):** This is the initial rate at which the reaction occurs when the substrate concentration is very low compared to the enzyme concentration.
- **Allosteric Inhibition:** Allosteric inhibitors bind to an enzyme at a site other than the active site, causing a conformational change that reduces enzyme activity.
**Effect of Allosteric Inhibitors:**
1. **Km Changes:** Typically, allosteric inhibitors may alter the conformation of the enzyme, potentially affecting the affinity of the enzyme for the substrate. This can lead to an increase in Km, indicating that a higher substrate concentration is needed to reach half of Vmax.
2. **[V0] Changes:** The initial velocity ([V0]) can be reduced because the conformational change caused by the inhibitor decreases the overall ability of the enzyme to catalyze the reaction effectively, even at the beginning when substrate concentration is low.
Thus, the presence of an allosteric inhibitor would likely increase the Km and decrease [V0], due to the inhibitor-induced conformational changes affecting substrate binding and catalytic efficiency.
Expert Solution
Step 1: Allosteric Inhibition kinetics
An allosteric inhibitor doesn't competes with the substrate for binding at active site. It binds to the allosteric site of the ES complex forming ESI which doesn't yield the product.
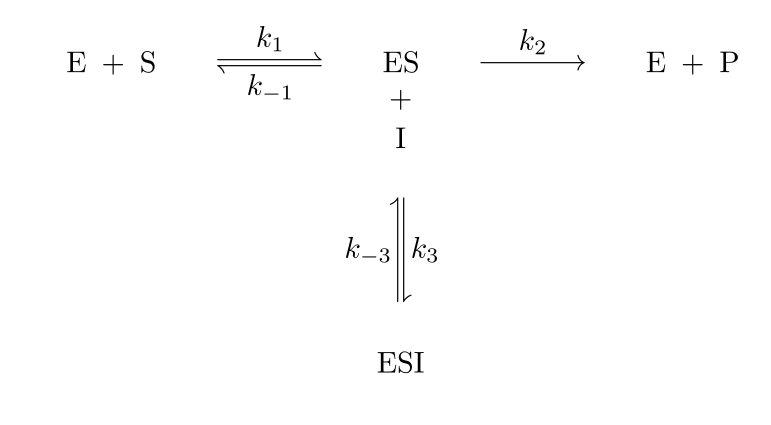
Let k2=kcat k3/k-3=KI
Km= (k-1+k2)/km
v0=kcat[ET]
vmax=kcat[ES]
[ET]=[E]+[ES]+[ESI]
[ES][I]=KI [ESI]
[E][S]/[ES]=Km
([ET]-[ES]-[ESI])[S]/[ES]=Km
([ET][S]/[ES])-([ES][S]/[ES])-([ESI])[S]/[ES])=Km
(vmax[S]/v0)-[S]-[I][S]/KI =Km
v0= vmax[S]/Km+[S](1+[I]/KI ) Eqn 1
On comparing the above equation of allosteric inhibition with Michaelis-Menten kinetics equation with no inhibition, we can conclude:
Vmax is reduced
Km remains the same
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781319114671
Author:
Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781464126116
Author:
David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul…
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781118918401
Author:
Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:
WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781319114671
Author:
Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781464126116
Author:
David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul…
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781118918401
Author:
Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:
WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305961135
Author:
Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological …
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9780134015187
Author:
John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:
PEARSON