What is a single-phase induction motor?
The single-phase induction motor or engine consists of a single rotating phase in the stator and a rotating cage in the rotor. When phase one supply is connected to the stator winding, a magnetic field is generated. In the pulsating field, the rotor does not rotate due to inertia. So, a single-phase import motor does not start and requires some initial methods.
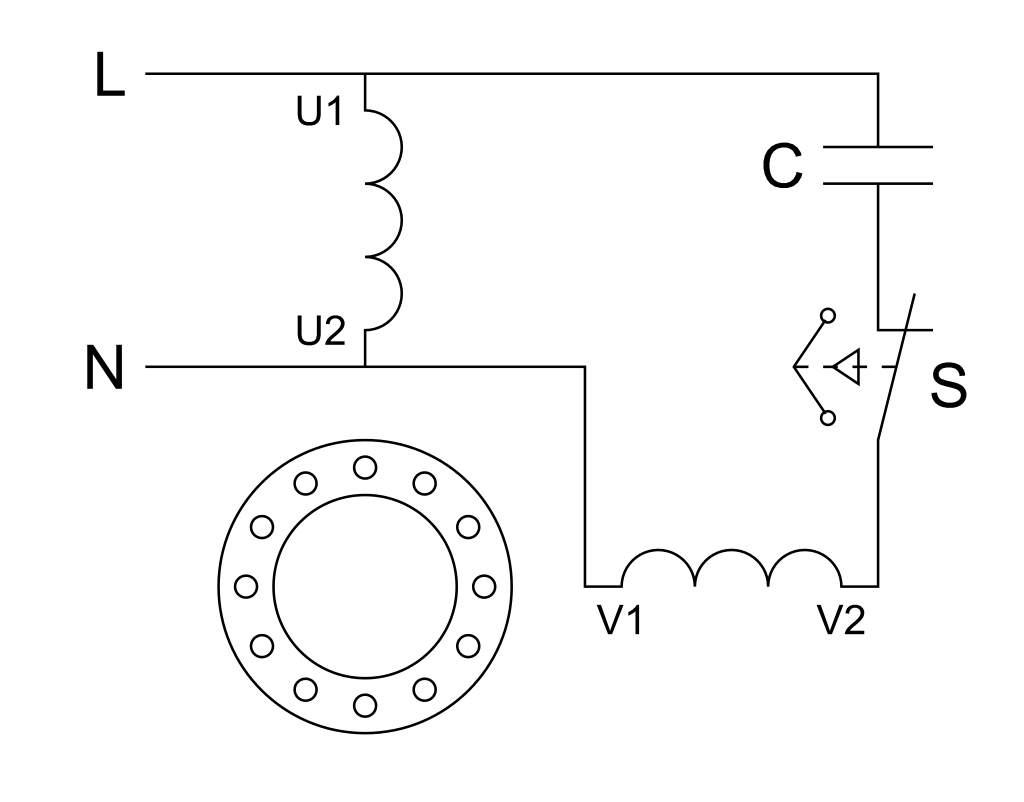
Construction of single-phase induction motor
A single-phase induction motor is similar to a third-phase squirrel cage induction motor except that there is a single-phase turning (instead of a single-phase rotation in the 3-phase motors) mounted on the stator and a rotating cage rotor inserted inside the stator as it rotates freely with the help of bearings mounted on the motor shaft.
The single-phase induction motor has two important components:
- Stator
- Rotor
Stator
The stator has the only difference, which is in the stator winding. Stator winding is a single-phase motor winding instead of a three-phase turn. The stator core is similar to the core of a three-phase induction motor.
In a single-phase induction motor, there are two twisting systems used in the stator, other than the shaded-pole induction motor. Of the two windows, one fold is the main rotation and the second is the auxiliary rotation.
The stator core is laminated to reduce the current loss of eddy. A single-phase supply is provided for stator winding (main winding).
Rotor
The rotor of a single-phase motor is similar to a squirrel cage induction motor's rotor. Instead of rotor winding, rotor bars are used and short-circuited end rings. Therefore, make a complete path to the rotor cycle. The rotor bars are fastened to the ends to increase the car's mechanical strength.
Rotor slots are twisted at some angle to avoid magnetic contact. And it is used to make the engine run smoothly and quietly.
Working of single-phase induction motor
A single-phase AC supply is provided by stator winding (main winding). The alternating current flowing through the stator winding produces magnetic flux. This fluid is known as flux.
Now, we assume that the rotor rotates and is placed in a magnetic field that is generated by the stator winding. According to Faraday's law, the starting current flowing in the rotor rotation is the approximate path. This current is rotor current.
Due to the rotor current, flux is produced near the rotor winding. This flow is known as rotor flux. There are two main types; the main flux produced by the stator and secondly, the rotor flux generated by the rotor. Interaction between the main flux and the rotor flux, the torque is generated in the rotor and begins to rotate. The stator field alternates naturally. The stator field speed is the same as the sync speed. The synchronization speed of the motor depends on the pole value and supply frequency.
In this case, the inserted effect is equal to the large field created by the stator. Now, both fields rotate differently and are naturally different. Therefore, both fields are cut by the rotor circuit and the EMF is attached to the rotor conductor. As a result of this EMF, the current begins to flow in the rotor circuit and introduces the rotor flux.
Due to the contact between the stator flux and the rotor flux motor it continues to rotate, the theory is Double Revolving Theory. Now, from the above definition, we can conclude that single-phase motors do not start.
For this car to start automatically, we need a stator flux that rotates in the environment instead of changing the environment.
Types of single-phase induction motor
Single-phase induction motors are of the following types:
Split-phase induction motor
In this type of motor, additional winging is damaged in the same stator spine. Therefore, there are two windings in the stator. One twist is known as the main rotation or running rotation and the second rotation is known as the starting rotation or auxiliary rotation. The centrifugal switch is connected to a series of auxiliary windows.
The auxiliary winding is a strong winding. The auxiliary winding has a few curves with a small diameter. The purpose of the auxiliary winding is to develop a difference in phase between the two variables produced by the rotor winding.
The amount of stator flux is due to the current effect of these two curves. As shown in the phasor diagram, the current result is represented as (I). It will create a phase difference between the variable and the output producing a rotating magnetic field. And the engine starts to spin.
The auxiliary winding is used only to start the engine. This threat does not apply to operating conditions. When the engine reaches 75 to 80% of the sync speed, the centrifugal button opens; and it only works on the main turns.
The phase difference caused by this method is relatively small. Therefore, the initial torque of this motor is incorrect. Therefore, this car is used in low startup systems such as fans, blowers, grinders, pumps, etc.
Capacitor start induction motor
This type of engine is an improved version of the split-phase induction motor. The disadvantage of introducing a split-phase is the production of low torque. Because in this motor, the phase difference made is very small. This impairment compensates for this motor with the help of a capacitor connected to a series of auxiliary windows.
The capacitor used in this motor is a dry kind of capacitor. It is designed for use with alternating current. But this capacitor can not be used for regular works. In this method too, a centrifugal switch cuts the capacitor and auxiliary windows when the engine runs at 75-80% of the sync speed.
The current through the app will guide the supply voltage to another angle. This angle is higher than the angle raised in the segment of the input divider. Therefore, the initial torque of this motor is very high compared to the split-phase induction motor. The initial torque of this motor is 300% higher than the full torque of the load.
Due to the high initial torque, this motor is used in systems where high torque is required, such as Lath machine, compressor, drilling rigs, etc.
Permanent capacitor induction motor
A low-cost capacitor is always connected to the auxiliary winding. Here, the capacitor has a low capacitance. The capacitor increases the initial torque but is low compared to the capacitor start induction motor. The power and efficiency feature of this motor is very high and has a high initial torque of 80% of full loading torque.
This type of motor is used in operating systems such as fan exhaust, blower, heater, etc.
Usage of single-phase induction motor
Single-phase motors or engines do not start and work better than three-phase induction motors or engines. They are available at 0.5 Horsepower to 15 Horsepower and are still widely used in clocks, refrigerators, freezers and heaters, fans, table fans, ceiling fans, ventilation fans, air coolers, and water coolers, tools, washing machines, dryers, type authors, photostats printers, water pumps and submersible, computers, and mining equipment.
Context and Applications
This topic is important for professional exams in both undergraduate and postgraduate courses like
- Bachelors in Technology in Civil Engineering
- Masters in Technology in Civil Engineering
Practice problems
1. What will happen if the capacitor of a single-phase induction motor is short-circuited?
a) The motor will not start
b) The motor will start
c) The motor will start counter-rotating
d) Magnetic field will decrease
Answer- Option a
Explanation- The motor will not start if the capacitor of a single-phase induction motor is short-circuited.
2. Which of the following is present in the rotor winding?
a) Synchronous speed
b) High resistance and low inductance
c) Low resistance and high inductance
d) Induction machines
Answer - Option c
Explanation - The rotor winding has heavy wires of many turnings, low resistance, and high inductance.
3. Which of the following have their starting winding connected to the centrifugal switch?
a) Shaded-pole induction motor
b) Split-phase induction motor
c) Capacitor-run induction motor
d) Synchronous speed motor
Answer- Option b
Explanation- In split-phase induction motor, the starting winding is connected to the centrifugal switch in a series manner.
4. How much torque is developed by the single-phase induction motor at starting?
a) Zero
b) One
c) Less than rated torque
d) More than rated torque
Answer- Option a
Explanation- Zero torque is developed by the single-phase induction motor at starting as rotor current developed is equal and in the opposite direction.
5. What will happen if capacitor that starts the induction motor is replaced by resistance?
a) Capacitor start will take place
b) The induction machines will consume less power
c) The motor will start counter-rotating
d) The motor may get burn
Answer- Option d
Explanation- The motor mat gets burned if the capacitor that starts the induction motor is replaced by resistance. The start period of the motor in such a case is more than 5 seconds.
Want more help with your electrical engineering homework?
*Response times may vary by subject and question complexity. Median response time is 34 minutes for paid subscribers and may be longer for promotional offers.
Search. Solve. Succeed!
Study smarter access to millions of step-by step textbook solutions, our Q&A library, and AI powered Math Solver. Plus, you get 30 questions to ask an expert each month.
Single Phase Induction Motor Homework Questions from Fellow Students
Browse our recently answered Single Phase Induction Motor homework questions.
Search. Solve. Succeed!
Study smarter access to millions of step-by step textbook solutions, our Q&A library, and AI powered Math Solver. Plus, you get 30 questions to ask an expert each month.