What is meant by finishing operation?
Finishing operations are the processes that are applied to the workpiece at the end of a manufacturing process, and after completing all other relevant operations that bring the product to its required dimensions. Finishing operations involve polishing, reducing the surface roughness, eliminating wrinkling, and grinding to enhance the surface texture and provide a better surface finish to the workpiece surface.
Depending on the workpiece and geometry, various kinds of surface finishing operations are applied. In this article, the reader will understand the different processes and techniques of surface finishing operations applied in the manufacturing industries.
Polishing
This process produces a smooth and shiny surface in the metal parts. The surface irregularities are reduced to fine regular distribution. Polishing involves treating the surface either with a chemical or rubbing with abrasive grains. The consequence of rubbing results in the depression of peaks and valleys present in the material surface, thereby producing a smoother surface. The polishing process uses a polishing wheel that has abrasive compounds stuck to the surface, using glue or a strong adhesive. This finishing process requires running the abrasive wheel at a high speed, upon contacting the workpiece with the abrasive wheel, it results in a material removal process. There are various grades and specifications of the abrasive compounds that can be chosen, depending on the application. There are abrasive wheels with coarser abrasive compounds and finer abrasive compounds
Surface coating
There are different surface coating techniques that enhance the surface properties of components.
Electroplating
This surface finishing process provides a thin metallic coating on the workpiece surface. In the electroplating process, the workpiece is dipped inside a solution having dissolved metal, and a positive current is passed through the metallic solution. The workpiece is maintained at a negative side. Metallic ions from the solution move and deposit to the workpiece surface. Electroplating induces a good surface finish along with corrosion-resistant properties.
Electroless plating
This process is similar to electroplating, but in place of electric current, the method utilizes a chemical reagent to dissociate the ions. This is also called the electrochemical process. The reagent is contained inside the metallic solution.
Hot dipping
This surface finishing process is known as the hot galvanizing process, which involves coating the surface with liquid metals. This involves the workpiece being dipped in hot liquid aluminum, tin, zinc, and tin. These metals stick to the surface of the workpiece, resulting in a better surface texture and finish.
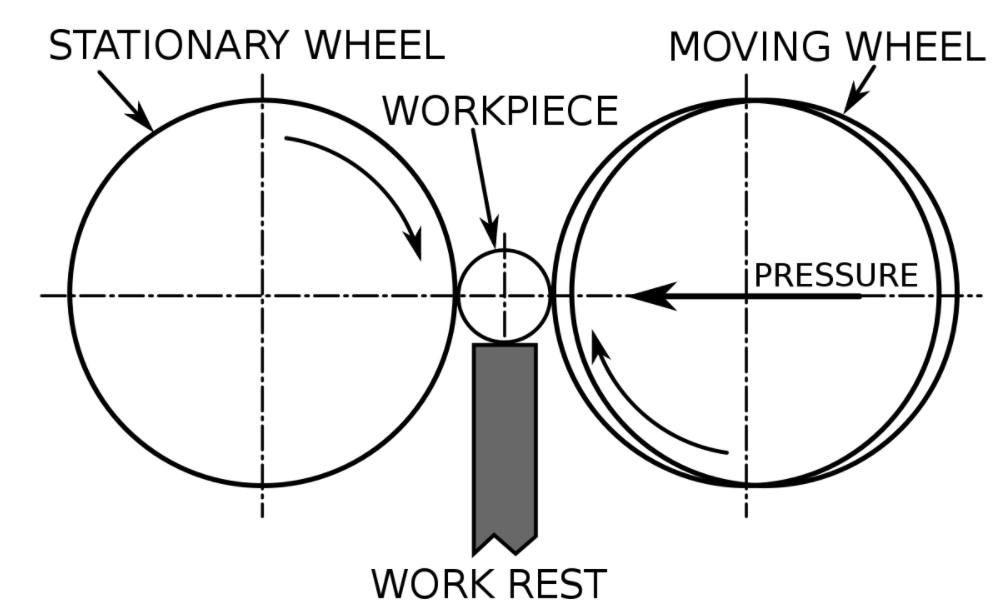
Grinding
It is a process that makes use of abrasive media in the form of a wheel known as a grinding wheel. Grinding is a material removal process. The abrasive media of the grinding wheel behaves as a multi-point cutting tool where each and every grain on the wheel behaves as a cutting tool.
Sandblasting
It is also known as abrasive blasting. In this process, a suitable gas in a cylinder remains pressurized with a mixture of abrasive slurry. This pressurized gas is made to propel through a nozzle targeting the workpiece. The surface irregularities are removed, and the surface deburrs from abrasion.
Superfinishing operations
These processes are applied to achieve a high degree of surface finish and accurate tolerances. In this process, the tool used has fine particles suspended or bonded through suitable adhesives.
Honing
Honing is a surface rubbing process, where a honing tool with fine abrasive grains is scrubbed over the workpiece. Generally, the scrubbing process is carried out in a figure of eight patterns.
Buffing
Buffing uses a buffing tool with fine grains of slurry known as roughs. This process is primarily used to prove a shiny surface finish.
Lapping
In this superfinishing process, two surfaces to be surface finished are kept one above another with fine abrasive slurries in between them. The motion is provided by hand or by using a machine.
Context and Applications
The topic is primarily taught in various engineering degree courses. This topic can be found in the subject of manufacturing methods and production technology of mechanical engineering courses. Besides, the topic is applied in different manufacturing industries that deal with surface finishing operations such as in automobile industries.
- Bachelors of Technology in Civil Engineering
- Bachelors of Technology in Mechanical Engineering
- Masters of Technology in Civil Engineering
- Masters of Technology in Mechanical Engineering
Practice Problems
1. Which of the following finishing process uses abrasive grains?
- Grinding
- Nitriding
- Hot Dipping
- Electroplating
Correct option- a
Explanation: The grinding wheel has abrasive grains on its surface bonded to the surface by suitable adhesives. These grains act as multipoint cutting tools.
2. Which of the following is a superfinishing operation?
- Honing
- Sandblasting
- Electroless plating
- Nitriding
Correct option: a
Explanation: Honing is a superfinishing operation that makes use of fine abrasive slurry bonded on a honing tool. Movement of the tool over the workpiece results in improvement of surface texture.
3. Which of the following finishing processes uses a pressurized gas?
- Buffing
- Honing
- Polishing
- Sandblasting
Correct option: d
Explanation: In the sandblasting process, suitable pressurized gas along with abrasive medium is kept inside a cylinder. The cylinder is provided with a nozzle, which is directed toward the workpiece; the abrasive impinges on the surface of the workpiece and removes materials through abrasion.
4. Which of the following process requires a nitrogen atmosphere?
- Hot Dipping
- Nitriding
- Electrochemical process
- None of these
Correct option: b
Explanation: Nitriding is a process in which a material after manufacturing is subjected to a nitrogen atmosphere. This results in enhancement of the surface hardness of the material.
5. Which of the following process uses a chemical reagent for the movement of ions in a metallic solution?
- Electroplating
- Galvanization
- Electroless plating
- All of these
Correct option: c
Explanation: Electroless plating uses a chemical reagent in the metallic solution that induces the movement of ions in the solution.
Want more help with your civil engineering homework?
*Response times may vary by subject and question complexity. Median response time is 34 minutes for paid subscribers and may be longer for promotional offers.
Search. Solve. Succeed!
Study smarter access to millions of step-by step textbook solutions, our Q&A library, and AI powered Math Solver. Plus, you get 30 questions to ask an expert each month.
Finishing Operations Homework Questions from Fellow Students
Browse our recently answered Finishing Operations homework questions.
Search. Solve. Succeed!
Study smarter access to millions of step-by step textbook solutions, our Q&A library, and AI powered Math Solver. Plus, you get 30 questions to ask an expert each month.