What is Chemical Reaction Engineering?
Chemical reaction engineering is the discipline which deals with the study and optimization of chemical reactions in order to build a better chemical reactor.
Scope of Chemical Reaction Engineering
A typical chemical reaction involves generally three steps. The first one is the physical treatment of raw materials, second one is the chemical treatment step and last one is the physical treatment step of products which leads to the final product. In the industrial level of production, chemical reactors are used to conduct such chemical reactions.
The industrial level of manufacturing requires maximum yield, less harmful and more useful by-products, cheaper raw materials, quality products, and ultimately economic profit. In order to achieve all this, one needs to build the best chemical reactor that will accomplish all these goals in industrial manufacturing; Chemical reaction engineering plays its significant role here. This branch of chemical engineering will allow one to design a chemical reactor with all industrial benefits.
Chemical reaction engineering involves the selection of optimum reaction conditions for a reactor to produce a given chemical more efficiently. This includes choosing the temperature, pressure, suitable catalyst and so on. In order to design a reactor, two things have to be known. First one is the reaction rate expression and the second one is the reaction conditions which includes temperature, pressure, suitable catalyst, composition of the reactants and so on.
History of Chemical Reaction Engineering
The two main courses under chemical engineering are chemical reaction engineering and separation. Among these two, chemical reaction engineering can be considered as the heart of chemical engineering. It has been established to be applied in the field of petrochemical industry. However, nowadays it finds its application mostly in the fields of the chemical production industries.
The term chemical reaction engineering was coined by Dutch engineer Johannes Cornelis Vlugter. The idea was presented in the first European Symposium on Chemical reaction engineering, which was held in Amsterdam in1957. It was the first of its kind in Europe. Before that in the 1950s, a group of research students at the Shell Amsterdam research center and the University of Delft has started chemical reaction engineering as a separate discipline.
How Chemical Reaction Engineering Works?
he chemical reaction engineering tries to find out solutions for the following questions:
- What changes are expected to occur during a chemical reaction?
- How fast will the reaction occur? (regarding the rate of the chemical reaction)
- What are the optimum reaction conditions to get desired products? (including temperature, pressure, chemical composition and so on)
- What is the perfect reactor design? (including size, type, energy factors and configuration)
- Need of catalyst and how to develop and design an appropriate catalyst which is suitable for the industrial production?
Also, the scale of capacity of the process which is selected for the production should be considered.
In chemical reaction engineering solutions to all the above problems must be found out and should rectify all the possible pitfalls.
Pillars and Building Blocks of Chemical Reaction Engineering
In chemical reaction engineering, one has to find solutions for a wide variety of problems from different context. In order to solve all these, there exist some basis ideas which will lead to an elaborate level of application discussion. These simple and basic ideas are referred as pillars of chemical reaction engineering. They are called so because these are the foundations on which different level of applications and solutions rest. There are six major pillars for chemical reaction engineering. They are as follows:
- Mole balances
- Rate laws
- Stoichiometry
- Energy balances
- Diffusion
- Contacting
They reflect not only chemical reaction analysis aspects but also diffusion and contacting physical phenomena that affect the chemical reactor's efficiency.
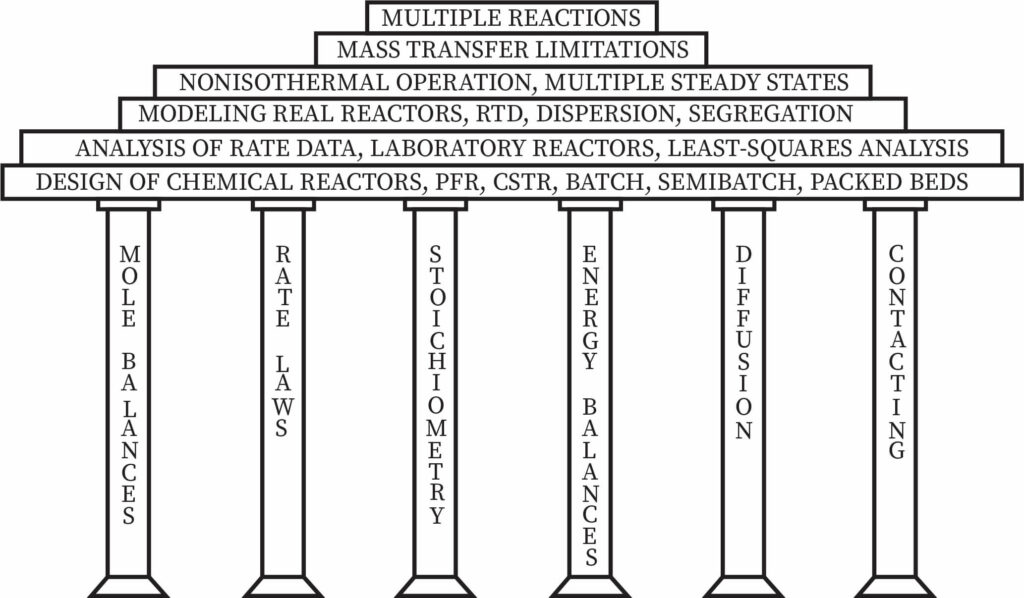
In order to solve the chemical reaction engineering problems related to isothermal reaction processes, a primary algorithm is required which is referred as building blocks of chemical reaction engineering.
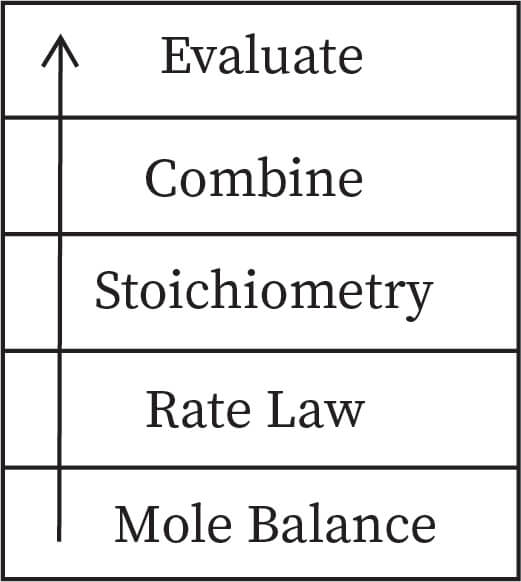
These components in the building blocks should be followed in the same order when solving a chemical reaction engineering problem. When dealing with non-isothermal reactions, the ‘combine’ component of the building blocks should be replaced by energy balance. This is because of the fact that non-isothermal reactions seem to require a solution which is produced by a computer. As a result, ‘combine’ block would not be needed since this computer would do it for us. The chemical reaction engineering algorithm is built on these foundations and building blocks.
How to Approach a Chemical Reaction in Chemical Reaction Engineering?
Let’s take an example of production of ammonia gas commercially.
N₂ + 3H₂ → 2NH3
Dinitrogen and dihydrogen are reacted to get ammonia in the presence of an iron catalyst. Analysing this reaction, it can be understood that one unit of dinitrogen with three units of dihydrogen will yield 2 units of ammonia. The presence of iron catalyst during the reaction has a great significance since it speeds up the reaction rate.
In chemical reaction engineering, on the way of approaching the reaction, one may think that why couldn’t introduce a new, more efficient catalyst and increase the reaction rate? However, simply changing the catalyst will not do any help. Temperature and pressure also have very important roles in this reaction since there is a chance for a backward reaction.
The reaction is an exothermic reaction . Thus, increasing the reaction temperature will shift the reaction to the left side. To overcome this problem a compromising temperature is selected which is in between 700 to 750 K.
When the pressure of the system is increased, the reaction will shift to the right side, which means more yield, since increase in pressure will shift a reaction to the side with less number of molecules. (In this reaction, on the left-hand side, four molecules are there and on the right-hand side, only two molecules are there). The suitable pressure is fixed between 150 to 300 atm.
Thus, to get a commercially profitable rate of ammonia, the reactor conditions were set at 150-300 atm pressure and 700 K to 750 K temperature.
Importance
Chemical reaction engineering can be applied in the field of industrial chemistry, petrochemical production areas, and also in many other commercial production fields. Understanding chemical reaction engineering will allow one to get a better yield by altering and controlling the reactor settings.
Context and Application
This topic is significant in the professional exams for both undergraduate and graduate courses, especially for Bachelors and Masters in Chemistry and Chemical Engineering courses.
Practice Problem
Select the correct order of building blocks in chemical reaction engineering of non isothermal reactions from the below.
a. Mole balance, energy balance, combine, rate laws, evaluate
b. Mole balance, rate laws, stoichiometry, energy balance
c. Mole balance, rate laws, stoichiometry, combine, evaluate
d. Mole balance, rate laws, energy balance, combine, evaluate
Answer: (b) Mole balance, rate laws, stoichiometry, energy balance.
Want more help with your chemical engineering homework?
*Response times may vary by subject and question complexity. Median response time is 34 minutes for paid subscribers and may be longer for promotional offers.
Search. Solve. Succeed!
Study smarter access to millions of step-by step textbook solutions, our Q&A library, and AI powered Math Solver. Plus, you get 30 questions to ask an expert each month.
Chemical Reaction Engineering Homework Questions from Fellow Students
Browse our recently answered Chemical Reaction Engineering homework questions.
Search. Solve. Succeed!
Study smarter access to millions of step-by step textbook solutions, our Q&A library, and AI powered Math Solver. Plus, you get 30 questions to ask an expert each month.