Concept explainers
Size and Life
Physicists look for simple models and general principles that underlie and explain diverse physical phenomena. In the first 13 chapters of this textbook, you’ve seen that just a handful of general principles and laws can be used to solve a wide range of problems. Can this approach have any relevance to a subject like biology? It may seem surprising, but there are general 'laws of biology“’ that apply, with quantitative accuracy, to organisms as diverse as elephants and mice.
Let’s look at an example. An elephant uses more metabolic power than a mouse. This is not surprising, as an elephant is much bigger. But recasting the data shows an interesting trend. When we looked at the energy required to raise the temperature of different substances, we considered specific heat. The “specific” meant that we considered the heat required for 1 kilogram. For animals, rather than metabolic rate, we can look at the specific metabolic rate, the metabolic power used per kilogram of tissue. If we factor out the mass difference between a mouse and an elephant, are their specific metabolic powers the same?
In fact, the specific metabolic rate varies quite a bit among mammals, as the graph of specific metabolic rate versus mass shows. But there is an interesting trend: All of the data points lie on a single smooth curve. In other words, there really is a biological law we can use to predict a mammal’s metabolic rate knowing only its mass M. In particular, the specific metabolic rate is proportional to M –0.25. Because a 4000 kg elephant is 160,000 times more massive than a 25 g mouse, the mouse’s specific metabolic power is (160,000)0.25 = 20 times that of the elephant. A law that shows how a property scales with the size of a system is called a scaling law.
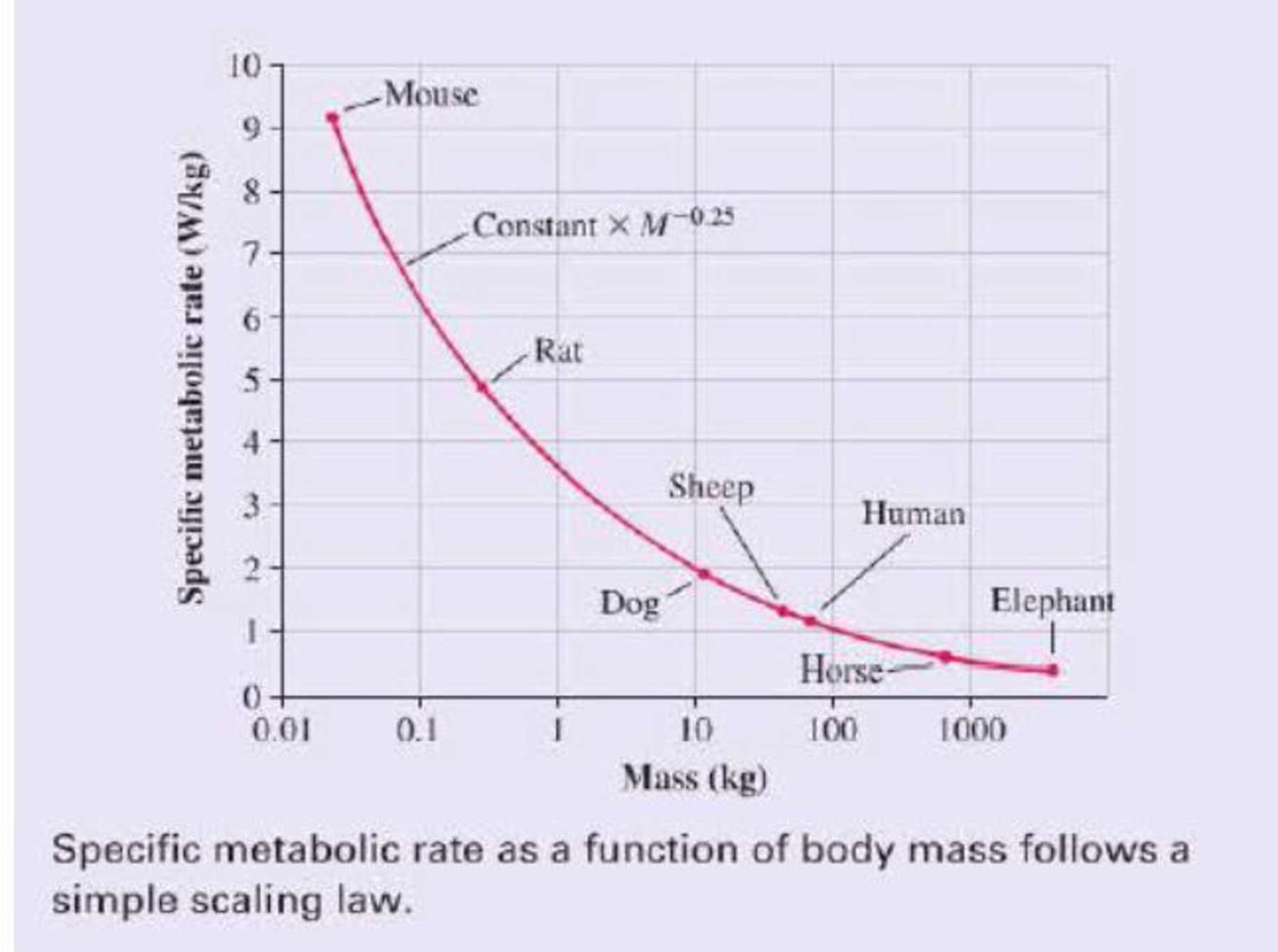
A similar scaling law holds for birds, reptiles, and even bacteria. Why should a single simple relationship hold true for organisms that range in size from a single cell to a 100 ton blue whale? Interestingly, no one knows for sure. It is a matter of current research to find out just what this and other scaling laws tell us about the nature of life.
Perhaps the metabolic-power scaling law is a result of
If heat dissipation were the only factor limiting metabolism, we can show that the specific metabolic rate should scale as M–0.33quite different from the M–0.25 scaling observed. Clearly, another factor is at work. Exactly what underlies the M–0.25 scaling is still a matter of debate, but some recent analysis suggests the scaling is due to limitations not of heat transfer but of fluid flow. Cells in mice, elephants, and all mammals receive nutrients and oxygen for metabolism from the bloodstream. Because the minimum size of a capillary is about the same for all mammals, the structure of the circulatory system must vary from animal to animal. The human aorta has a diameter of about 1 inch; in a mouse, the diameter is approximately l/20th of this. Thus a mouse has fewer levels of branching to smaller and smaller blood vessels as we move from the aorta to the capillaries. The smaller blood vessels in mice mean that viscosity is more of a factor throughout the circulatory system. The circulatory system of a mouse is quite different from that of ail elephant.
A model of specific metabolic rate based on blood-flow limitations predicts a M–0.25 law, exactly as observed. The model also makes other testable predictions. For example, the model predicts that the smallest possible mammal should have a body mass of about 1 gram—exactly the size of the smallest shrew. Even smaller animals have different types of circulatory' systems; in the smallest animals, nutrient transport is by diffusion alone. But the model can be extended to predict that the specific metabolic rate for these animals will follow a scaling law similar to that for mammals, exactly as observed. It is too soon to know if this model will ultimately prove to be correct, but it’s indisputable that there are large-scale regularities in biology that follow mathematical relationships based on the laws of physics.
The following questions are related to the passage "Size and Life" on the previous page.
A typical timber wolf has a mass of 40 kg, a typical jackrabbit a mass of 2.5 kg. Given the scaling law presented in the passage, we’d expect the specific metabolic rate of the jackrabbit to be higher by a factor of
- A. 2
- B. 4
- C. 8
- D. 16
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter P Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
- Based on your graph, explain how centripetal force is affected when the hanging mass changes. Does your graph verify the relationship in the equation r = x^i + y^j = r cos ωt I + r sin ωt^j?arrow_forwardDid your experiment results in Data Table 3 verify, to within a reasonable experimental error, the condition of equilibrium of Equation 6: Στanti-clockwise = Στclockwise? Support your response with experimental data. My data shows that they are not equal to each other. So what does this mean? Thanks!arrow_forwardPlease help, everytime I try to input the data only one point shows on the graph. Graph of centripetal force, Fc, versus V E2 from Activity 1. Include a line of best fit and record the equation of the line.arrow_forward
- Explain how your experiment met the condition for equilibrium in Equation 4: ΣFvertical = ΣFy = 0.arrow_forwardCan i get answer and solution for this question and can you teach me What we use to get the answer.arrow_forwardCan i get answer and solution and can you teach me how to get it.arrow_forward
- Consider a image that is located 30 cm in front of a lens. It forms an upright image 7.5 cm from the lens. Theillumination is so bright that that a faint inverted image, due to reflection off the front of the lens, is observedat 6.0 cm on the incident side of the lens. The lens is then turned around. Then it is observed that the faint,inverted image is now 10 cm on the incident side of the lens.What is the index of refraction of the lens?arrow_forward2. In class, we discussed several different flow scenarios for which we can make enough assumptions to simplify the Navier-Stokes equations enough to solve them and obtain an exact solution. Consulting the cylindrical form of the Navier-Stokes equations copied below, please answer the following questions. др a 1 a + +0x- + +O₂ = Pgr + μl 18²v, 2 ave ²v₁] az2 + at or r de r Əz dr ar Vodvz др [18 + + +Or + +Vz = Pgz +fl at ar r 20 ôz ôz dr ave дов V,Ve ave +Or + + = pge at dr r 80 Əz + az2 a.) In class, we discussed how the Navier-Stokes equations are an embodiment of Newton's 2nd law, F = ma (where bolded terms are vectors). Name the 3 forces that we are considering in our analysis of fluid flow for this class. др a 10 1 ve 2 av 2200] + +μ or 42 30 b.) If we make the assumption that flow is "fully developed" in the z direction, which term(s) would go to zero? Write the term below, describe what the term means in simple language (i.e. do not simply state "it is the derivative of a with…arrow_forward1. Consult the form of the x-direction Navier-Stokes equation below that we discussed in class. (For this problem, only the x direction equation is shown for simplicity). Note that the equation provided is for a Cartesian coordinate system. In the spaces below, indicate which of the following assumptions would allow you to eliminate a term from the equation. If one of the assumptions provided would not allow you to eliminate a particular term, write "none" in the space provided. du ди at ( + + + 매일) du ди = - Pgx dy др dx ²u Fu u + fl + ax2 ay² az2 - дх - Əz 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Assumption Flow is in the horizontal direction (e.g. patient lying on hospital bed) Flow is unidirectional in the x-direction Steady flow We consider the flow to be between two flat, infinitely wide plates There is no pressure gradient Flow is axisymmetric Term(s) in equationarrow_forward
- Don't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forwardwhy did the expert subtract the force exerted by the hand and the elbow by the force due to the weight of the hand and forearm and force exerted by the tricep. Does the order matter and how do you determine what to put first. Question 4 AP, CHAPTER 13 FROM BASIC BIOMECHANICS 8TH EDITIONarrow_forwardThe drawing illustrates the dispersion of light by a prism. The prism is made from a certain type of glass, and has a cross section shaped like an equilateral triangle. The indices of refraction for the red and violet light in this type of glass are 1.649 and 1.694, respectively. The angle of incidence for both the red and violet light is 60.0°. Find the angles of refraction at which the (a) red and (b) violet rays emerge into the air from the prism. Glass prism Incident light Normal (a) Normal Incident light Red (660 nm) (b) Violet (410 nm)arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College





