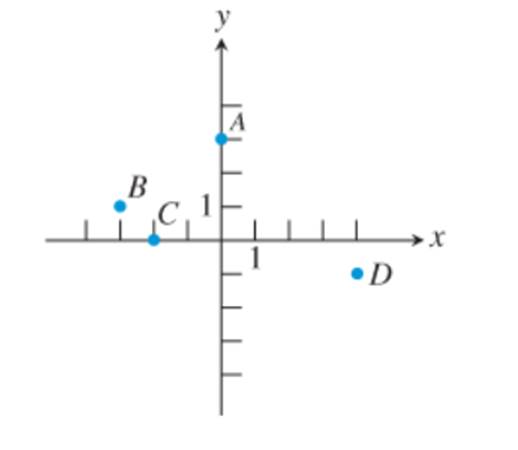
Estimate the coordinates of the points given in graph.
Given information:
The given graph is:
Formula used:
- In a graph both the axes are marked with bars with equal length.
- The y coordinate of point on x -axis is 0.
- The x coordinate of point on y -axis is 0.
- The right side of x axis from the center is of positive points, and left is of negative.
- The above side of y axis from the center is of positive points, and downward side is of negative.
Calculation:
To estimate the coordinates of points, A, B, C and D note that both the axes( x and y ) in graph are divided equally with bars.
Since the first bar in x axis is marked 1, i.e. second should be 2, third is 3, and so on, similarly for y axis first is marked 1, i.e. second is 2, third is 3, and so on.
Since, point A is on y -axis, i.e. the x coordinate of point A is 0 and it is on third bar above the center along y-axis(i.e. positive), i.e. it’s y coordinate is 3. Thus, the coordinate of point A is (0,3).
Similarly, for point B note that:
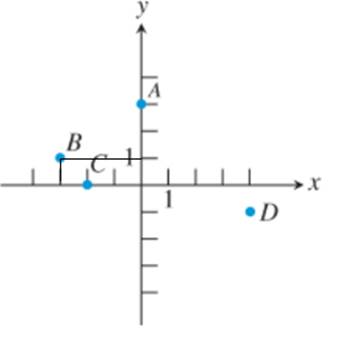
This point is along 3 bar to the left hand side from center on x- axis, i.e. negative coordinate and 1 bars to the upper side from the center on y- axis, and since each bar is of 1 unit i.e. it’s coordinate is
Now C is on x -axis thus it’s y coordinate of point on y -axis is 0, and it is 2 bars left hand side from the center on x- axis, i.e. x -coordinate is negative.
Thus, coordinate of C is:
Similarly, for point D note that
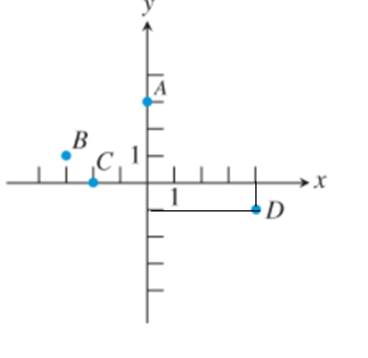
Note that it is corresponding to the 4 bars to the right hand side of the x -axis from the center i.e. positive and 1 bars down from the center on y- axis, i.e. negative and since each bar is of 1 unit i.e. it’s coordinate is:
Thus, coordinates of given points are:
Chapter P Solutions
EBK PRECALCULUS:GRAPHICAL,...-NASTA ED.
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





