
Concept explainers
Interpretation: Whether the answers in CTQ are in agreement with Memorization Task NW1.2 given below or not should be given.
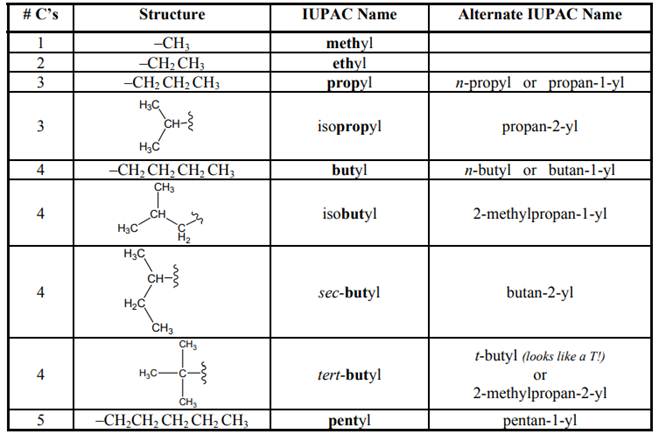
Concept introduction: Systematic way to name different organic compounds is
Rules for nomenclature of
1 The longest continuous carbon chain is identified first and named in accordance with number of carbon atoms present in it. For example, hydrocarbon with one carbon atom has prefix “meth”, that with two carbon atoms has prefix “eth”, that with three carbon atoms has prefix “prop” and so on. Suffix used for alkanes is “ane.”
2. Substituents attached to parent carbon chain are to be identified. These are named by removal of single hydrogen atom from carbon chain end and named by replacement of suffix “ane” by “yl.” For example if
3. Carbons of parent chain are named in such way that substituents acquire the lowest numbers.
4. If same substituent is present more than one time in molecule, it is represented by prefix “di”, “tri” and so on. It depends on number of times substituent occurs in molecule.
5. If two or more substituents are present in molecule, these are named in alphabetical order.
6. If carbon chains of same length exist in same molecule, chain with the largest number of side chains, followed by lowest number to substituents, chain with the greatest number of carbon atoms in smaller chain and chain with the least branched side chains are preferred over other ones.
7. Prefix “cyclo” is used if cyclic alkane is present in molecule.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter NW1 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
- Synthesize 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- If possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forwardSynthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forward
- We mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained if (E)-2-butenal and 3-oxo-butanenitrile are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardQuestion 3 (4 points), Draw a full arrow-pushing mechanism for the following reaction Please draw all structures clearly. Note that this intramolecular cyclization is analogous to the mechanism for halohydrin formation. COH Br + HBr Brarrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if 2,2-dimethylpropanal and acetaldehyde are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
