
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure for the given molecule is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
When assigning priorities to substituents, the atom having the greater
Answer to Problem C.32P
The structure of
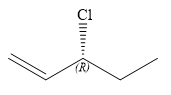
Explanation of Solution
The given name is:
In this compound, the root is pentene. The compound contains a double bond between C1 and C2 carbon atoms. The longest continuous carbon chain contains five carbon atoms. A chlorine is attached to C3 carbon atom of the root. The structure of the molecule without considering its stereochemistry is:
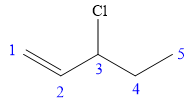
There is one chiral carbon at C3 in the above molecule. The required configuration at the chiral carbon atom is R.
At C3 carbon atom, the four substituents are:
Applying the first tiebreaker,
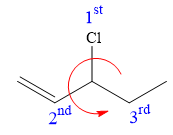
Thus, in order to have R configuration at C3 carbon atom, the first-priority substituent must be attached by a dash bond. Therefore, the correct structure for

The structure for the given name is drawn as shown above.
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure for the given molecule is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
When assigning priorities to substituents, the atom having the greater atomic number has higher priority. In case of comparison between isotopes, the one having the greater atomic mass gets higher priority. When the fourth priority substituent is pointing away (it is attached by a dash bond) and the first, second, and third priority substituents are arranged clockwise, the configuration is R. When the fourth priority substituent is pointing away (it is attached by a dash bond) and the first, second, and third priority substituents are arranged counterclockwise, the configuration is S. If the fourth priority substituent is attached by a wedge bond, then the clockwise or counterclockwise arrangement of the first, second, and third priority substituents is determined and that arrangement is reversed before assigning R or S. If the fourth priority substituent is in the plane of the page, then it is switched with the substituent that points away. Then the clockwise or counterclockwise arrangement of the first, second and third priority substituents is determined and that arrangement is reversed before assigning R or S. When writing the IUPAC name, the R or S designation is written in parenthesis for each asymmetric carbon atom and hyphens are used to separate those designations from the rest of the IUPAC name.
Answer to Problem C.32P
The structure of
Explanation of Solution
The given name is
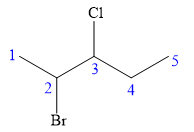
There are two chiral carbon atoms at C2 and C3 in the above molecule. The required configuration at both the chiral carbon atoms is S.
At C2 carbon atom, the four substituents are:
Applying the first tiebreaker,
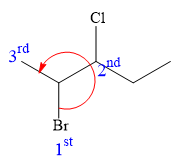
Thus, in order to maintain this arrangement of substituents at the C2 carbon atom, the fourth-priority substituent must be attached by a dash bond
At C3 carbon atom, the four substituents are:
Applying the first tiebreaker,
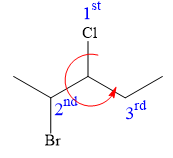
Thus, in order to maintain this arrangement of substituents at the C3 carbon atom, the fourth-priority substituent must be attached by a dash bond
Therefore, the correct structure for

The structure for the given name is drawn as shown above.
(c)
Interpretation:
The structure for the given molecule is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
When assigning priorities to substituents, the atom having the greater atomic number has higher priority. In case of comparison between isotopes, the one having the greater atomic mass gets higher priority.
When the fourth priority substituent is pointing away (it is attached by a dash bond) and the first, second, and third priority substituents are arranged clockwise, the configuration is R.
When the fourth priority substituent is pointing away (it is attached by a dash bond) and the first, second, and third priority substituents are arranged counterclockwise, the configuration is S.
If the fourth priority substituent is attached by a wedge bond, then the clockwise or counterclockwise arrangement of the first, second, and third priority substituents is determined and that arrangement is reversed before assigning R or S.
If the fourth priority substituent is in the plane of the page, then it is switched with the substituent that points away. Then the clockwise or counterclockwise arrangement of the first, second and third priority substituents is determined and that arrangement is reversed before assigning R or S. When writing the IUPAC name, the R or S designation is written in parenthesis for each asymmetric carbon atom and hyphens are used to separate those designations from the rest of the IUPAC name.
Answer to Problem C.32P
The structure of
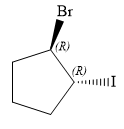
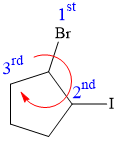
Explanation of Solution
The given name is:
In this compound, the root is cyclopentane. One bromine atom and one iodine atom is attached to C1 and C2 carbon atom of the root.
The structure of the molecule, without considering its stereochemistry, is:
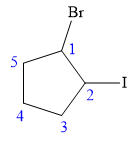
There are two chiral carbon atoms at C1 and C2 in the above molecule. The required configuration at both the chiral carbon atoms is R.
At C1 carbon atom, the four substituents are:
Applying the first tiebreaker,
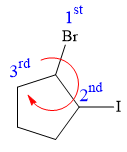
Thus, in order to maintain this arrangement of substituents at C2 carbon atom, the fourth-priority substituent must be attached by a dash bond
At C3 carbon atom, the four substituents are:
Applying the first tiebreaker,

Thus, in order to maintain this arrangement of substituents at the C3 carbon atom, the fourth-priority substituent must be attached by a dash bond
Therefore, the correct structure for
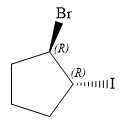
The structure for the given name is drawn as shown above.
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure for the given molecule is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
When assigning priorities to substituents, the atom having the greater atomic number has higher priority. In case of comparison between isotopes, the one having the greater atomic mass gets higher priority. When the fourth priority substituent is pointing away (it is attached by a dash bond) and the first, second, and third priority substituents are arranged clockwise, the configuration is R. When the fourth priority substituent is pointing away (it is attached by a dash bond) and the first, second, and third priority substituents are arranged counterclockwise, the configuration is S. If the fourth priority substituent is attached by a wedge bond, then the clockwise or counterclockwise arrangement of the first, second, and third priority substituents is determined and that arrangement is reversed before assigning R or S. If the fourth priority substituent is in the plane of the page, then it is switched with the substituent that points away. Then the clockwise or counterclockwise arrangement of the first, second, and third priority substituents is determined and that arrangement is reversed before assigning R or S. When writing the IUPAC name, the R or S designation is written in parenthesis for each asymmetric carbon atom and hyphens are used to separate those designations from the rest of the IUPAC name.
Answer to Problem C.32P
The structure of
Explanation of Solution
The given name is:
In this compound, the root is cyclohexene. The cyclohexane ring contains one double bond between C1 and C2 carbon atoms. One chlorine atom is attached at the C3 carbon atom of the root. The structure of the molecule without considering its stereochemistry is:
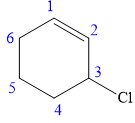
There is one chiral carbon at C3 in the above molecule. The required configuration at the chiral carbon atom is S.
At C3 carbon atom, the four substituents are:
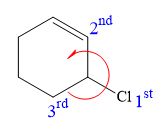
Thus, in order to maintain this arrangement of substituents at the C2 carbon atom, the first priority substituent should be attached by a dash bond. Therefore, the correct structure for
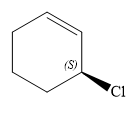
The structure for the given name is drawn as shown above.
(e)
Interpretation:
The structure for the given molecule is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
When assigning priorities to substituents, the atom having the greater atomic number has higher priority. In case of comparison between isotopes, the one having the greater atomic mass gets higher priority. When the fourth priority substituent is pointing away (it is attached by a dash bond) and the first, second, and third priority substituents are arranged clockwise, the configuration is R. When the fourth priority substituent is pointing away (it is attached by a dash bond) and the first, second, and third priority substituents are arranged counterclockwise, the configuration is S. If the fourth priority substituent is attached by a wedge bond, then the clockwise or counterclockwise arrangement of the first, second, and third priority substituents is determined and that arrangement is reversed before assigning R or S. If the fourth priority substituent is in the plane of the page, then it is switched with the substituent that points away. Then the clockwise or counterclockwise arrangement of the first, second, and third priority substituents is determined and that arrangement is reversed before assigning R or S. When writing the IUPAC name, the R or S designation is written in parenthesis for each asymmetric carbon atom and hyphens are used to separate those designations from the rest of the IUPAC name.
Answer to Problem C.32P
The structure of
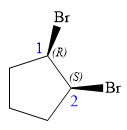
Explanation of Solution
The given name is:
In this compound, the root is cyclopentane. Two bromine atoms are attached at C1 and C2 carbon atoms of the root. The structure of the molecule without considering its stereochemistry is:
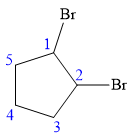
There are two chiral carbon atoms at C1 and C2 carbon atoms. The required configuration at C1 is R and that at C2 is S.
At C1 carbon atom, the four substituents are:
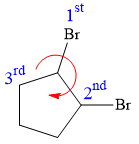
Thus, in order to have R configuration, and maintain this arrangement of substituents at the C1 carbon atom, the first-priority substituent must be attached by a wedge bond.
At C2 carbon atom, the four substituents are:
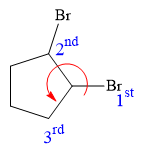
Thus, in order to have R configuration, and maintain this arrangement of substituents at the C1 carbon atom, the first-priority substituent must be attached by a dash bond.
Therefore, the correct structure for

The structure for the given name is drawn as shown above.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter C Solutions
EBK GET READY FOR ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- 6. Choose the compound that will produce the spectrum below and assign the signals as carbonyl, aryl, or alkyl. 100 ō (ppm) 50 0 7. 200 150 Assign all of the protons on the spectrum below. 8. A B 4 E C 3 ō (ppm) 2 1 0 Choose the compound that will produce the spectrum below and assign the signals to the corresponding protons. OH 6 OH 3 2 1 0 4 ō (ppm)arrow_forwardIn the Thermo Fisher application note about wine analysis (Lesson 3), the following chromatogram was collected of nine components of wine. If peak 3 has a retention time of 3.15 minutes and a peak width of 0.070 minutes, and peak 4 has a retention time of 3.24 minutes and a peak width of 0.075 minutes, what is the resolution factor between the two peaks? [Hint: it will help to review Lesson 2 for this question.] MAU 300 200 T 34 5 100- 1 2 CO 6 7 8 9 0 2.4 2.6 2.8 3.0 3.2 3.4 3.6 3.8 4.0 4.2 4.4 4.6 4.8 5.0 5.2 Minutes 3.22 0.62 1.04 O 1.24arrow_forwardThe diagram shows two metals, A and B, which melt at 1000°C and 1400°C. State the weight percentage of the primary constituent (grains of C) that would be obtained by solidifying a 20% alloy of B. 1000°C a+L L+C 900°С 12 α a+C 45 1200 C L+y 140096 C+Y a+ß 800°C 700°C C+B 96 92 a+B 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 A % peso B Barrow_forward
- 8. Choose the compound that will produce the spectrum below and assign the signals to the corresponding protons. 2 4 3 ō (ppm) OH 4 6 6 СОН 2 1 0arrow_forward7. Assign all of the protons on the spectrum below. A B 2 C E 2 1 3 6 4 3 2 1 0arrow_forwarde. If (3R,4R)-3,4-dichloro-2,5-dimethylhexane and (3R,4S)-3,4-dichloro-2,5-dimethylhexane are in a solution at the same concentration, would this solution be expected to rotate plane polarized light (that is, be optically active)? Please provide your reasoning for your answer. [If you read this problem carefully, you will not need to draw out the structures to arrive at your answer...]arrow_forward
- 1. How many neighbors does the proton that produces the multiplet below have? 2. 3. اللـ Draw a partial structure from the multiplet below. (The integration of the multiplet is 6) M Using the additivity constants found in appendix G of your lab manual, calculate the approximate chemical shifts of the protons indicated below. (Show your work!!!) B A Br SHarrow_forward1) Suppose 0.1 kg ice at 0°C (273K) is in 0.5kg water at 20°C (293K). What is the change in entropy of the ice as it melts at 0°? To produce the original "water gas" mixture, carbon (in a combustible form known as coke) is reacted with steam: 131.4 kJ + H20(g) + C(s) → CO(g) + H2(g) From this information and the equations in the previous problem, calculate the enthalpy for the combustion or carbon to form carbon dioxide. kindly show me how to solve this long problem. Thanksarrow_forward4. An 'H-NMR of a compound is acquired. The integration for signal A is 5692 and the integration for signal B is 25614. What is the simplest whole number ratio of protons for signals A and B? (Show your work!!!) 5. Assign the carbons in the NMR below as either carbonyl, aromatic, or alkyl. 200 150 100 50 ō (ppm) 1arrow_forward
- Speaking of composite materials, indicate the correct option:(A). Composite materials can only be: metal-polymer or polymer-polymer.(B). Composite materials can be made up of particles, but not fibers or sheets.(C). When the reinforcing particles are uniformly distributed in a composite material, there may be a greater tendency for it to have isotropic properties.(D). None of the above is correct.arrow_forwardIf we are talking about viscoelastic modulus or viscoelastic relaxation modulus in polymers, indicate the correct option.(A). It reports the variation of elastic behavior as a function of time.(B). It is only useful for defining its glass transition temperature.(C). It only allows us to define the polymer degradation temperature.(D). Neither option is correct.arrow_forwardWhen natural light falls perpendicularly on a material A, it has a reflectivity of 0.813%. Indicate the value of the refractive index.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





