
Concept explainers
Mental Tasks and Drugs. In the text Statistical Theory and Methodology in Science and Engineering (New York: Wiley. I960). K. A. Brownlee provides data on an experiment involving a person's ability to perform a mental task before and after taking one of four drugs. Fifty-six subjects performed a task that involved mental addition. The subjects were then randomly divided into four groups. Each group drank a beverage containing one of four drugs, labeled A, B, C, and D. After a period of time for the drugs to take effect, each subject repeated the mental addition test. We want to relate the after test score (after) to the before test score (before) and the drug that was taken. The data from the experiment are presented in the following table.
In this study, the drug labeled B was a placebo, that is, it contained no drug and should have no effect on a person’s ability to perform a mental task. Define three indicator variables as follows:
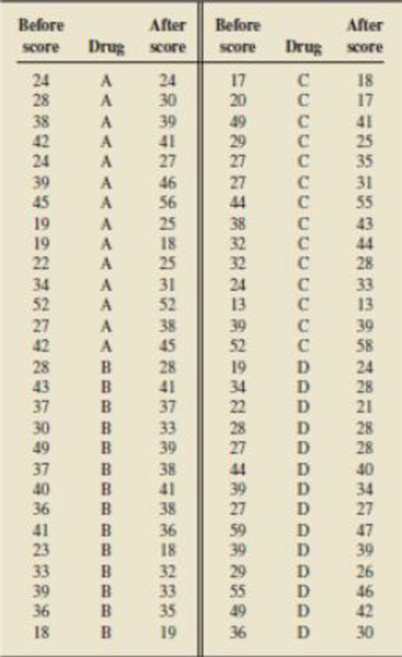
- a. Output B.57 on page B-93 provides a plot of after versus before, using a different plot symbol for each drug. Bases on this plot, does it appear that drug is a useful predictor variable? Explain your answer.
- b. We obtained the
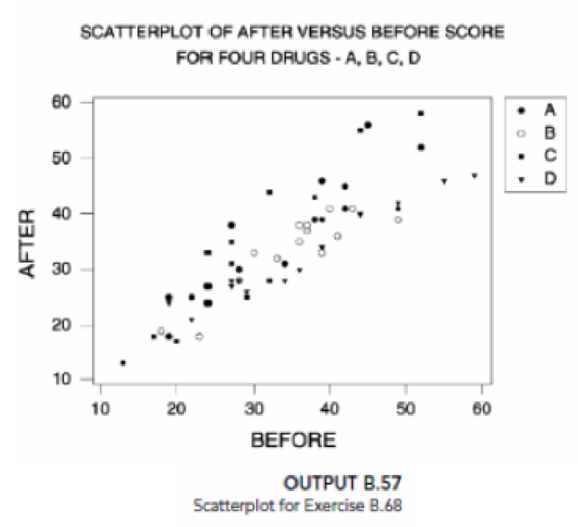
regression analysis of after on before and the three indicator variables druga, drugc, and drugd, as shown in Output B.55 on page B-93. Conduct the t-tests for the individual utility of the four predictor variables at the 5% level of significance. Interpret your results. - c. Explain what the t-test for the utility of the indicator variable druga means in terms of comparing the effect of drug A to the effect of the placebo on the after mental task scores.
- d. Which drugs have on effect on the after mental task score that is different from the placebo?
- e. Based on Output B.58, obtain 1he regression equations relating after to before for each of the four drugs.
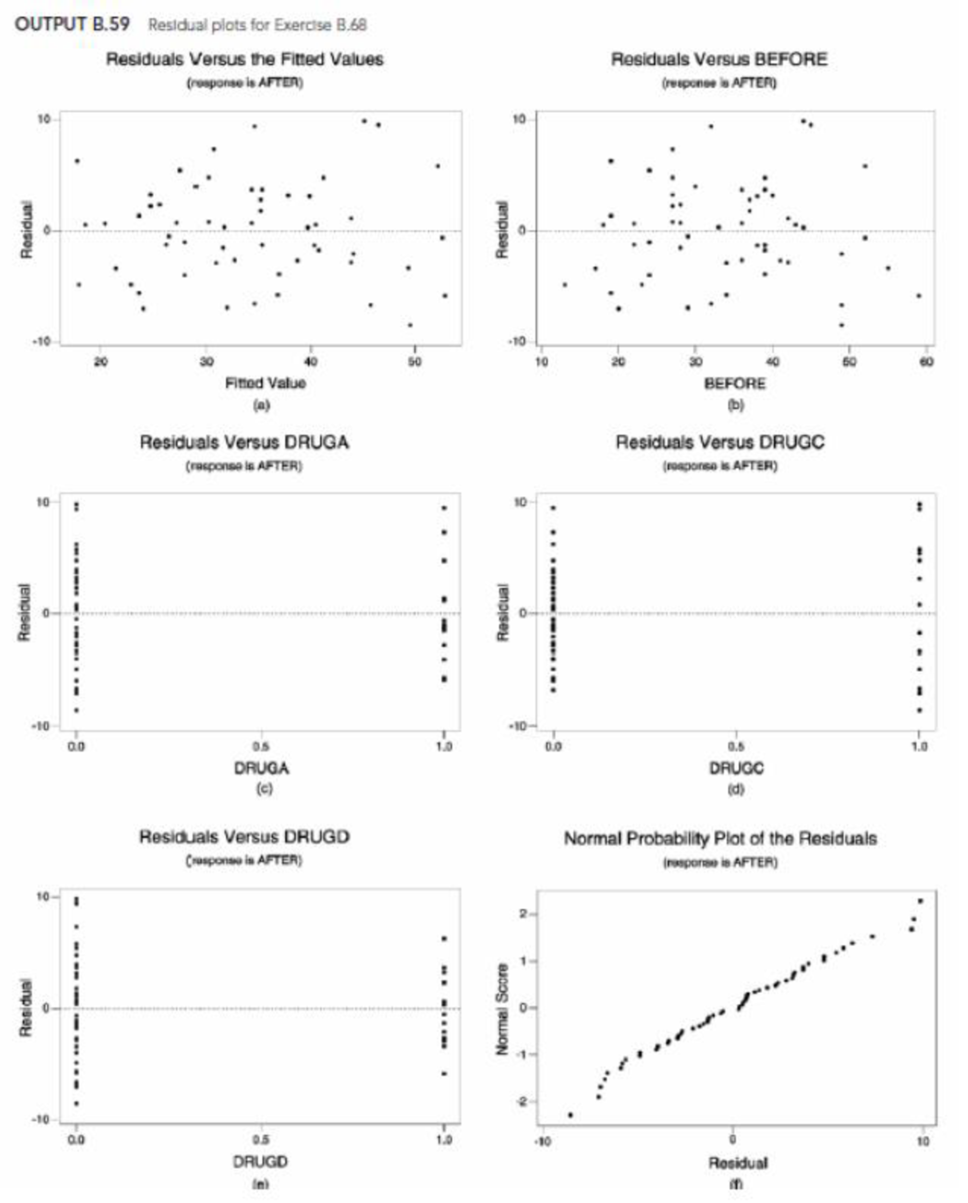
- f. Outputs B.59(a)–(f) provide, respectively, plots of residuals versus fitted values, residuals versus before, and residuals versus each indicator variable, and a normal probability plot of the residuals. Perform a residual analysis to assess the appropriateness of the regression equation, constancy of the conditional standard deviations, and normality of the conditional distributions. Check for outliers and influential observations.
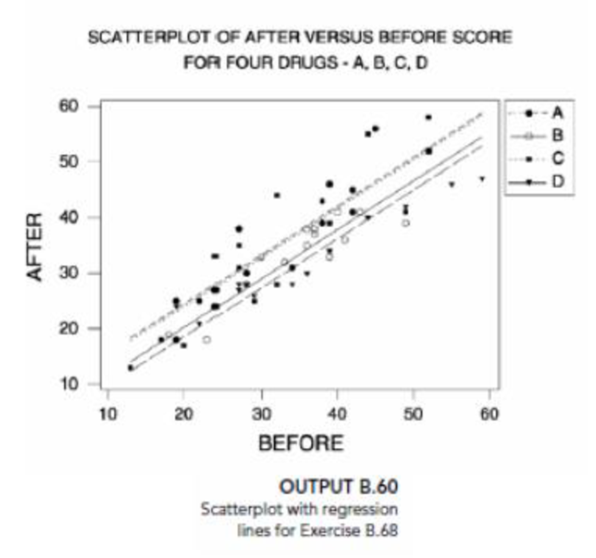
- g. Output B.60 on page B-95 provides a
scatterplot of after versus before with the regression lines for the four drugs. Based on this output and your residual analysis in part (f), do you feel that this model fits the data well? Explain your answer. - h. To check for possible interactions between the before score and. the drug, we obtained the regression analysis of after on before, druga, drugc, drugd, druga·before, drugc·before and drugd·before. The output is in Output B.61 on page B-96. Is there an interaction between drug and before, that is, are any of the cross-product terms useful predictor variables in the regression equation that contains the other terms in the model? Use α = 0.05.
Regression Analysis: AFTER versus BEFORE, DRUDA, DRUGC, DRUGD
Analysis of Variance
OUTPUT B.58 Regression output for Exercise B.68
Regression Analysis: AFTER versus BEFORE, DRUDA, DRUGC, DRUGD, DRUGA*BEF, DRUGC*BEF, …
Analysis of Variance
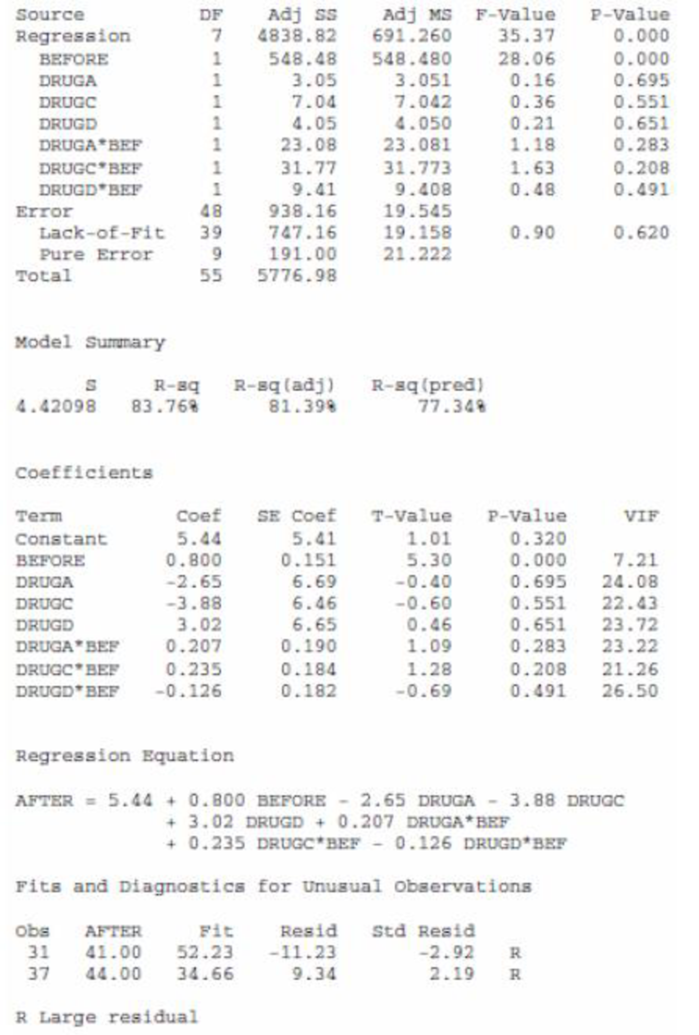
OUTPUT B.61 Regression output For Exercise B.68
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter B Solutions
Introductory Statistics (10th Edition)
- Suppose a random sample of 459 married couples found that 307 had two or more personality preferences in common. In another random sample of 471 married couples, it was found that only 31 had no preferences in common. Let p1 be the population proportion of all married couples who have two or more personality preferences in common. Let p2 be the population proportion of all married couples who have no personality preferences in common. Find a95% confidence interval for . Round your answer to three decimal places.arrow_forwardA history teacher interviewed a random sample of 80 students about their preferences in learning activities outside of school and whether they are considering watching a historical movie at the cinema. 69 answered that they would like to go to the cinema. Let p represent the proportion of students who want to watch a historical movie. Determine the maximal margin of error. Use α = 0.05. Round your answer to three decimal places. arrow_forwardA random sample of medical files is used to estimate the proportion p of all people who have blood type B. If you have no preliminary estimate for p, how many medical files should you include in a random sample in order to be 99% sure that the point estimate will be within a distance of 0.07 from p? Round your answer to the next higher whole number.arrow_forward
- A clinical study is designed to assess the average length of hospital stay of patients who underwent surgery. A preliminary study of a random sample of 70 surgery patients’ records showed that the standard deviation of the lengths of stay of all surgery patients is 7.5 days. How large should a sample to estimate the desired mean to within 1 day at 95% confidence? Round your answer to the whole number.arrow_forwardA clinical study is designed to assess the average length of hospital stay of patients who underwent surgery. A preliminary study of a random sample of 70 surgery patients’ records showed that the standard deviation of the lengths of stay of all surgery patients is 7.5 days. How large should a sample to estimate the desired mean to within 1 day at 95% confidence? Round your answer to the whole number.arrow_forwardIn the experiment a sample of subjects is drawn of people who have an elbow surgery. Each of the people included in the sample was interviewed about their health status and measurements were taken before and after surgery. Are the measurements before and after the operation independent or dependent samples?arrow_forward
- iid 1. The CLT provides an approximate sampling distribution for the arithmetic average Ỹ of a random sample Y₁, . . ., Yn f(y). The parameters of the approximate sampling distribution depend on the mean and variance of the underlying random variables (i.e., the population mean and variance). The approximation can be written to emphasize this, using the expec- tation and variance of one of the random variables in the sample instead of the parameters μ, 02: YNEY, · (1 (EY,, varyi n For the following population distributions f, write the approximate distribution of the sample mean. (a) Exponential with rate ẞ: f(y) = ß exp{−ßy} 1 (b) Chi-square with degrees of freedom: f(y) = ( 4 ) 2 y = exp { — ½/ } г( (c) Poisson with rate λ: P(Y = y) = exp(-\} > y! y²arrow_forward2. Let Y₁,……., Y be a random sample with common mean μ and common variance σ². Use the CLT to write an expression approximating the CDF P(Ỹ ≤ x) in terms of µ, σ² and n, and the standard normal CDF Fz(·).arrow_forwardmatharrow_forward
- Compute the median of the following data. 32, 41, 36, 42, 29, 30, 40, 22, 25, 37arrow_forwardTask Description: Read the following case study and answer the questions that follow. Ella is a 9-year-old third-grade student in an inclusive classroom. She has been diagnosed with Emotional and Behavioural Disorder (EBD). She has been struggling academically and socially due to challenges related to self-regulation, impulsivity, and emotional outbursts. Ella's behaviour includes frequent tantrums, defiance toward authority figures, and difficulty forming positive relationships with peers. Despite her challenges, Ella shows an interest in art and creative activities and demonstrates strong verbal skills when calm. Describe 2 strategies that could be implemented that could help Ella regulate her emotions in class (4 marks) Explain 2 strategies that could improve Ella’s social skills (4 marks) Identify 2 accommodations that could be implemented to support Ella academic progress and provide a rationale for your recommendation.(6 marks) Provide a detailed explanation of 2 ways…arrow_forwardQuestion 2: When John started his first job, his first end-of-year salary was $82,500. In the following years, he received salary raises as shown in the following table. Fill the Table: Fill the following table showing his end-of-year salary for each year. I have already provided the end-of-year salaries for the first three years. Calculate the end-of-year salaries for the remaining years using Excel. (If you Excel answer for the top 3 cells is not the same as the one in the following table, your formula / approach is incorrect) (2 points) Geometric Mean of Salary Raises: Calculate the geometric mean of the salary raises using the percentage figures provided in the second column named “% Raise”. (The geometric mean for this calculation should be nearly identical to the arithmetic mean. If your answer deviates significantly from the mean, it's likely incorrect. 2 points) Starting salary % Raise Raise Salary after raise 75000 10% 7500 82500 82500 4% 3300…arrow_forward
 Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning



