
Fundamentals of Statistics (5th Edition)
5th Edition
ISBN: 9780134508306
Author: Michael Sullivan III
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter B.2, Problem 16AYU
Investment Risk Investors not only desire a high return on their money, but they would also like the rate of return to be stable from year to year. An investment manager invests with the goal of reducing volatility (year-to-year fluctuations in the rate of return). The following data represent the rate of return (in percent) for his mutual fund for the past 12 years.
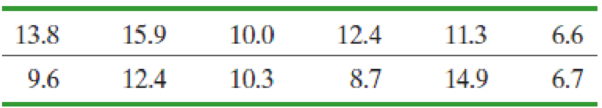
- (a) Verify that the data are
normally distributed by constructing a normalprobability plot. - (b) Determine the sample standard deviation.
- (c) Construct a 95% confidence interval for the population standard deviation of the rate of return.
- (d) The investment manager wants to have a population standard deviation for the rate of return below 6%. Does the confidence interval validate this desire?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Suppose we wish to test the hypothesis that women with a sister’s history of breast cancer are at higher risk of developing breast cancer themselves. Suppose we assume that the prevalence rate of breast cancer is 3% among 60- to 64-year-old U.S. women, whereas it is 5% among women with a sister history. We propose to interview 400 women 40 to 64 years of age with a sister history of the disease. What is the power of such a study assuming that the level of significance is 10%?
I only need help writing the null and alternative hypotheses.
4.96 The breaking strengths for 1-foot-square samples of a particular synthetic fabric are approximately normally distributed with a mean of 2,250 pounds per square inch (psi) and a standard deviation of 10.2 psi. Find the probability of selecting a 1-foot-square sample of material at random that on testing would have a breaking strength in excess of 2,265 psi.4.97 Refer to Exercise 4.96. Suppose that a new synthetic fabric has been developed that may have a different mean breaking strength. A random sample of 15 1-foot sections is obtained, and each section is tested for breaking strength. If we assume that the population standard deviation for the new fabric is identical to that for the old fabric, describe the sampling distribution forybased on random samples of 15 1-foot sections of new fabric
Une Entreprise œuvrant dans le domaine du multividéo donne l'opportunité à ses
programmeurs-analystes d'évaluer la performance des cadres supérieurs.
Voici les résultats obtenues (sur une échelle de 10 à 50) où 50 représentent une
excellente performance. 10 programmeurs furent sélectionnés au hazard pour
évaluer deux cadres. Un rapport Excel est également fourni.
Programmeurs
Cadre A Cadre B
1
34
36
2
32
34
3
18
19
33
38
19
21
21
23
7
35
34
8
20
20
9
34
34
10
36
34
Test d'égalité des espérances: observations pairées
Chapter B.2 Solutions
Fundamentals of Statistics (5th Edition)
Ch. B.2 - True or False: The chi-square distribution is...Ch. B.2 - Prob. 2AYUCh. B.2 - Prob. 3AYUCh. B.2 - Prob. 4AYUCh. B.2 - Prob. 5AYUCh. B.2 - Prob. 6AYUCh. B.2 - In Problems 58, find the critical values 1/22 and...Ch. B.2 - Prob. 8AYUCh. B.2 - Prob. 9AYUCh. B.2 - A simple random sample of size n is drawn from a...
Ch. B.2 - NW 11. pH of Rain The following data represent the...Ch. B.2 - Travel Taxes Travelers pay taxes for flying, car...Ch. B.2 - Crash Test Results The following data represent...Ch. B.2 - Crawling Babies The following data represent the...Ch. B.2 - Peanuts A jar of peanuts is supposed to have 16...Ch. B.2 - Investment Risk Investors not only desire a high...Ch. B.2 - Critical Values Sir R. A. Fisher, a famous...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A television news channel samples 25 gas stations from its local area and uses the results to estimate the average gas price for the state. What’s wrong with its margin of error?arrow_forwardYou’re fed up with keeping Fido locked inside, so you conduct a mail survey to find out people’s opinions on the new dog barking ordinance in a certain city. Of the 10,000 people who receive surveys, 1,000 respond, and only 80 are in favor of it. You calculate the margin of error to be 1.2 percent. Explain why this reported margin of error is misleading.arrow_forwardYou find out that the dietary scale you use each day is off by a factor of 2 ounces (over — at least that’s what you say!). The margin of error for your scale was plus or minus 0.5 ounces before you found this out. What’s the margin of error now?arrow_forward
- Suppose that Sue and Bill each make a confidence interval out of the same data set, but Sue wants a confidence level of 80 percent compared to Bill’s 90 percent. How do their margins of error compare?arrow_forwardSuppose that you conduct a study twice, and the second time you use four times as many people as you did the first time. How does the change affect your margin of error? (Assume the other components remain constant.)arrow_forwardOut of a sample of 200 babysitters, 70 percent are girls, and 30 percent are guys. What’s the margin of error for the percentage of female babysitters? Assume 95 percent confidence.What’s the margin of error for the percentage of male babysitters? Assume 95 percent confidence.arrow_forward
- You sample 100 fish in Pond A at the fish hatchery and find that they average 5.5 inches with a standard deviation of 1 inch. Your sample of 100 fish from Pond B has the same mean, but the standard deviation is 2 inches. How do the margins of error compare? (Assume the confidence levels are the same.)arrow_forwardA survey of 1,000 dental patients produces 450 people who floss their teeth adequately. What’s the margin of error for this result? Assume 90 percent confidence.arrow_forwardThe annual aggregate claim amount of an insurer follows a compound Poisson distribution with parameter 1,000. Individual claim amounts follow a Gamma distribution with shape parameter a = 750 and rate parameter λ = 0.25. 1. Generate 20,000 simulated aggregate claim values for the insurer, using a random number generator seed of 955.Display the first five simulated claim values in your answer script using the R function head(). 2. Plot the empirical density function of the simulated aggregate claim values from Question 1, setting the x-axis range from 2,600,000 to 3,300,000 and the y-axis range from 0 to 0.0000045. 3. Suggest a suitable distribution, including its parameters, that approximates the simulated aggregate claim values from Question 1. 4. Generate 20,000 values from your suggested distribution in Question 3 using a random number generator seed of 955. Use the R function head() to display the first five generated values in your answer script. 5. Plot the empirical density…arrow_forward
- Find binomial probability if: x = 8, n = 10, p = 0.7 x= 3, n=5, p = 0.3 x = 4, n=7, p = 0.6 Quality Control: A factory produces light bulbs with a 2% defect rate. If a random sample of 20 bulbs is tested, what is the probability that exactly 2 bulbs are defective? (hint: p=2% or 0.02; x =2, n=20; use the same logic for the following problems) Marketing Campaign: A marketing company sends out 1,000 promotional emails. The probability of any email being opened is 0.15. What is the probability that exactly 150 emails will be opened? (hint: total emails or n=1000, x =150) Customer Satisfaction: A survey shows that 70% of customers are satisfied with a new product. Out of 10 randomly selected customers, what is the probability that at least 8 are satisfied? (hint: One of the keyword in this question is “at least 8”, it is not “exactly 8”, the correct formula for this should be = 1- (binom.dist(7, 10, 0.7, TRUE)). The part in the princess will give you the probability of seven and less than…arrow_forwardplease answer these questionsarrow_forwardSelon une économiste d’une société financière, les dépenses moyennes pour « meubles et appareils de maison » ont été moins importantes pour les ménages de la région de Montréal, que celles de la région de Québec. Un échantillon aléatoire de 14 ménages pour la région de Montréal et de 16 ménages pour la région Québec est tiré et donne les données suivantes, en ce qui a trait aux dépenses pour ce secteur d’activité économique. On suppose que les données de chaque population sont distribuées selon une loi normale. Nous sommes intéressé à connaitre si les variances des populations sont égales.a) Faites le test d’hypothèse sur deux variances approprié au seuil de signification de 1 %. Inclure les informations suivantes : i. Hypothèse / Identification des populationsii. Valeur(s) critique(s) de Fiii. Règle de décisioniv. Valeur du rapport Fv. Décision et conclusion b) A partir des résultats obtenus en a), est-ce que l’hypothèse d’égalité des variances pour cette…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:9781337278461
Author:Ron Larson
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...
Algebra
ISBN:9781337111348
Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Mod-01 Lec-01 Discrete probability distributions (Part 1); Author: nptelhrd;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6x1pL9Yov1k;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Discrete Probability Distributions; Author: Learn Something;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=m9U4UelWLFs;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Probability Distribution Functions (PMF, PDF, CDF); Author: zedstatistics;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YXLVjCKVP7U;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Discrete Distributions: Binomial, Poisson and Hypergeometric | Statistics for Data Science; Author: Dr. Bharatendra Rai;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lHhyy4JMigg;License: Standard Youtube License